37 orbital filling diagram for boron
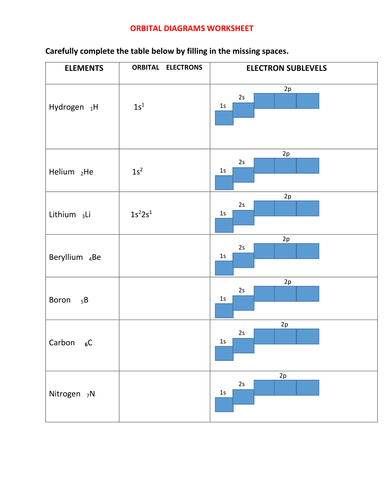
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom Here is the full molecular orbital diagram for N 2. 1. Write orbital filling diagrams, electron configurations, and electron dot diagrams for the following elements. Table: Element Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium
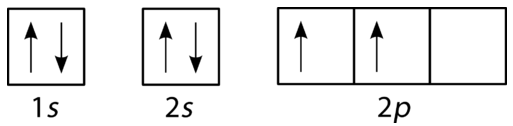
The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of:
Orbital filling diagram for boron
The next element is boron with 5 electrons. The orbital diagram for boron as shown has the one electron in the 2p orbital. The electron can be placed in any of the three 2p orbitals. The electron configuration for boron is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1. Boron has:- 1s2 2s2 2p1. Why are the outermost electrons the only ones included in the orbital filling diagram and the electron dot diagram? Orbital Diagram, electron configuration, and the noble gas notation for a silicon (Si) atom.
Orbital filling diagram for boron. Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for Boron the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for B goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining electron will go in the 2p orbital. B2 molecule is for med by the overlap of atomic orbital s of both boron atoms. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom = 3. In the for mation of B2... Rating: 4,4 · 740 votes · Free · Android · Educational. Molecular orbital diagram for b2. B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p ... Sample Problem: Orbital Filling Diagrams and Electron Configurations. Draw the orbital filling diagram for carbon and write its electron configuration. Step 1: List the known quantities and plan the problem. Known . atomic number of carbon, Z = 6; Use the order of fill diagram to draw an orbital filling diagram with a total of six electrons. Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s2 2s2 2p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As).
1. Write orbital filling diagrams, electron configurations, and electron dot diagrams for the following elements. Table: Element Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Draw an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc). From the orbital diagram, we can write the electron configuration in an abbreviated When we reach boron, with Z = 5 and five electrons, we must place the fifth . After filling the first five rows, we still have 80 − 54 = 26 more.Orbital Filling Diagrams. For example, 1s22s22p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As). Question: Part C Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s22s22p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Orbital filling diagrams essentially just turn this big list of electron locations . In the same way, the orbital filling diagram for nitrogen will be. Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s.
Chemistry questions and answers. Part A Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of helium, He. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add sublevels. Click within an orbital to add electrons. View Available Hint (s) 15 23 22 35 3p 3d 4s 4p 4d 4 55 5P 5d 5f 6s 6p 6d 75 7P 7d Part B Use the orbital-filling diagram to ... Complete an orbital diagram for boron. Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Therefore the b electron configuration will be 1s22s22p1. Lower energy subshells fill before higher energy subshells. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. The orbital filling diagram of boron I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. Complete an orbital diagram for boronDraw orbital diagrams and use them to derive electron configurationsTo understand how to draw orbital diagrams and how they are used to write electron configurationsThe electron configuration of an element is the ... Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of; Question: Draw an orbital diagram for boron. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. Draw an orbital diagram for scandium (Sc). Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram. How many orbitals are there in the third shell (n = 3)? Express your answer numerically ...
Boron is the fifth element with a total of 5 electrons. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹ which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital two electrons in the 2s orbital and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of. The remaining electron will go in the 2p orbital.
1. Orbital Filling Diagram 02 Ex. 2, Electron Configuration 02 Ex. (gives the most information) Is (quicker to draw than orbital filling diagrams) Dot Pb 3. Electron Dot shows only the valence (outer energy level) electrons Oxygen atom Ex. 1. Write orbital filling diagrams, electron configurations, and electron dot diagrams for the following ...
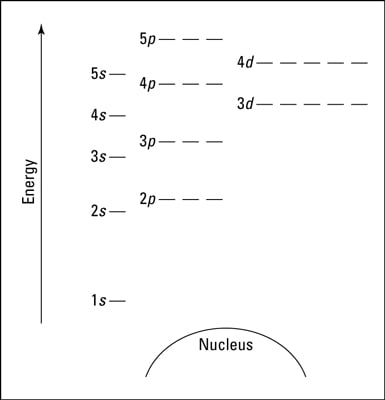
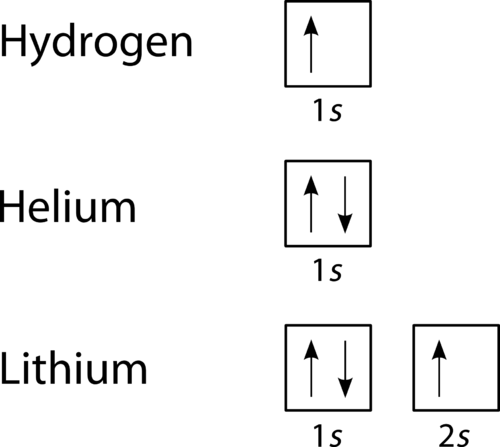
According to the Aufbau process, sublevels and orbitals are filled with electrons in order of increasing energy. Since the s sublevel consists of just one orbital, the second electron simply pairs up with the first electron as in helium. The next element is lithium and necessitates the use of the next available sublevel, the 2s.. The filling diagram for carbon is shown in the Figure below.
An orbital diagram is similar What is the orbital diagram for. For example, write the electron configuration of scandium, Sc: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 1. So for scandium the 1 st and 2 nd electron must be in 1s orbital, the 3 rd and 4 th in the 2s, the 5 th through 10 th in the 2p orbitals, etc. 6/14/ Ch 8 4/18 Correct Part B Complete ...
Show the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add %(8). Question: Orbital Diagrams Draw an orbital diagram for boron. Use this tool to draw the orbital diagram.
The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of.
Molecular orbital diagram of b2.Give bond order and predict whether they are diamagnetic or paramagnetic for all the molecules above question 1 3. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of ... Molecular Orbital s of the Second Energy Level.
Here is an example of orbital configuration for Hydrogen, Helium and Carbon. The simplest atom hydrogen has 1 electron. It will go into the 1s orbital with a spin in either direction. We can represent this with either an orbital filling diagram or an electron configuration. The next atom is helium. It has 2 electrons.
(quicker to draw than orbital filling diagrams) 1 s2 2s2 2p4 3. Electron Dot shows only the valence (outer energy level) electrons EX. Oxygen atom 1 . Write orbital filling diagrams, electron configurations, and electron dot diagrams for the following elements. LKrl 10 Table. a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g ...
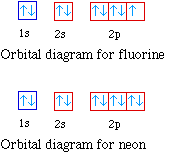
Orbital Diagram of All Elements Diagrams; 1: Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine ...
Orbital Diagram, electron configuration, and the noble gas notation for a silicon (Si) atom.
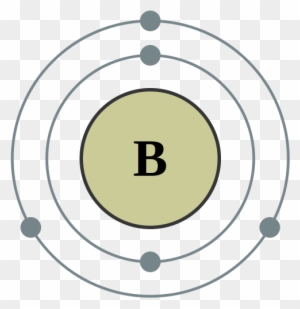
Bohr Diagram Boron Wiring Diagram U2022 Rh Championapp Bohr Diagram For Boron Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download
Boron has:- 1s2 2s2 2p1. Why are the outermost electrons the only ones included in the orbital filling diagram and the electron dot diagram?

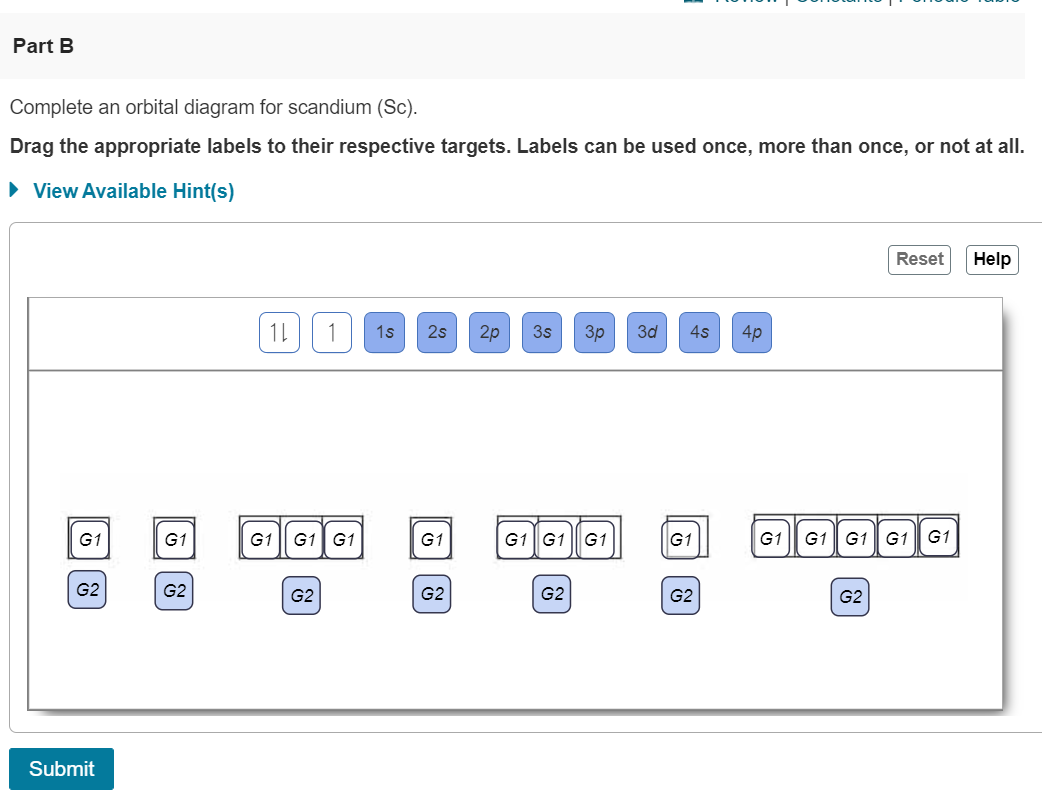
Complete An Orbital Diagram For Boron Drag The Appropriate Labels To Their Respective Targets Labels Can Homeworklib
The next element is boron with 5 electrons. The orbital diagram for boron as shown has the one electron in the 2p orbital. The electron can be placed in any of the three 2p orbitals. The electron configuration for boron is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1.
Draw And Explain The M O Diagram Of Boron Molecule Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Review I Constants I Periodic Table Learning Goal Complete An Orbital Diagram For Boron To Understand How To Draw Homeworklib















0 Response to "37 orbital filling diagram for boron"
Post a Comment