39 what is a motion diagram physics
Rectilinear Motion - The path of the motion is a straight line. Curvilinear Motion - The path of the motion is curved. A few examples of linear motion are the motion of the train, football, the motion of a car on the road, etc. Rotatory Motion. Rotatory motion is the motion that occurs when a body rotates on its own axis. Rotational Motion is defined as the motion of an object around a circular path, in a fixed orbit. Ceiling fan rotation, rotation of the minute hand and the hour hand in the clock, and the opening and closing of the door are some of the examples of rotational motion about a fixed point.
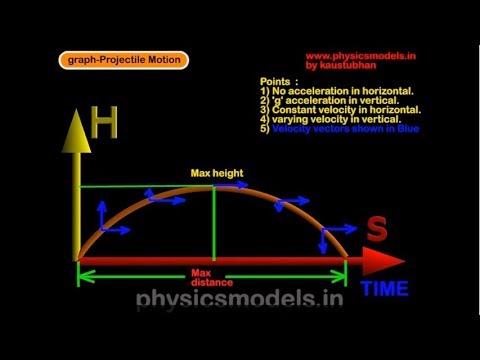
a = −9.8 m/s2. The second method uses the graph and an equation of motion. Since we're given a displacement-time graph, use the displacement-time relationship, a.k.a. the second equation of motion. After 7 seconds, the skydiver has fallen from rest a distance of 240 meters. ∆ s = v0t + ½ at2. a = 2∆ s / t2.

What is a motion diagram physics
A motion diagram represents the velocity position and acceleration of an object at several different times. These spots reveal the objects state of motion. Rank the acceleration from largest to smallest. The motion diagram includes appropriately spaced dots that represent the objects constant speed motion speeding up motion or slowing down motion. A motion diagram is a pictorial description of the motion of an object. It displays the object's location at various equally spaced times on the same diagram; ... The motion diagram for something slowing down would look like _____. dots that get closer together If a car has a negative displacement, what does that indicate?
What is a motion diagram physics. Aug 13, 2020 — An extremely useful tool for bridging the gap between a normal, conversational description of a situation and a physicists' description is the ...Determining the position from... · Determining the velocity from a... Introduction to motion diagrams This work by Andrew Duffy is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This simulation can be found in the ... Picturing Motion: Dot Diagrams • If you related the position of the runner to the background in each frame taken in 1 second intervals, you would conclude that the student is in motion. • This series of images, taken at regular intervals, creates a motion diagram for the change in the student's state of motion.
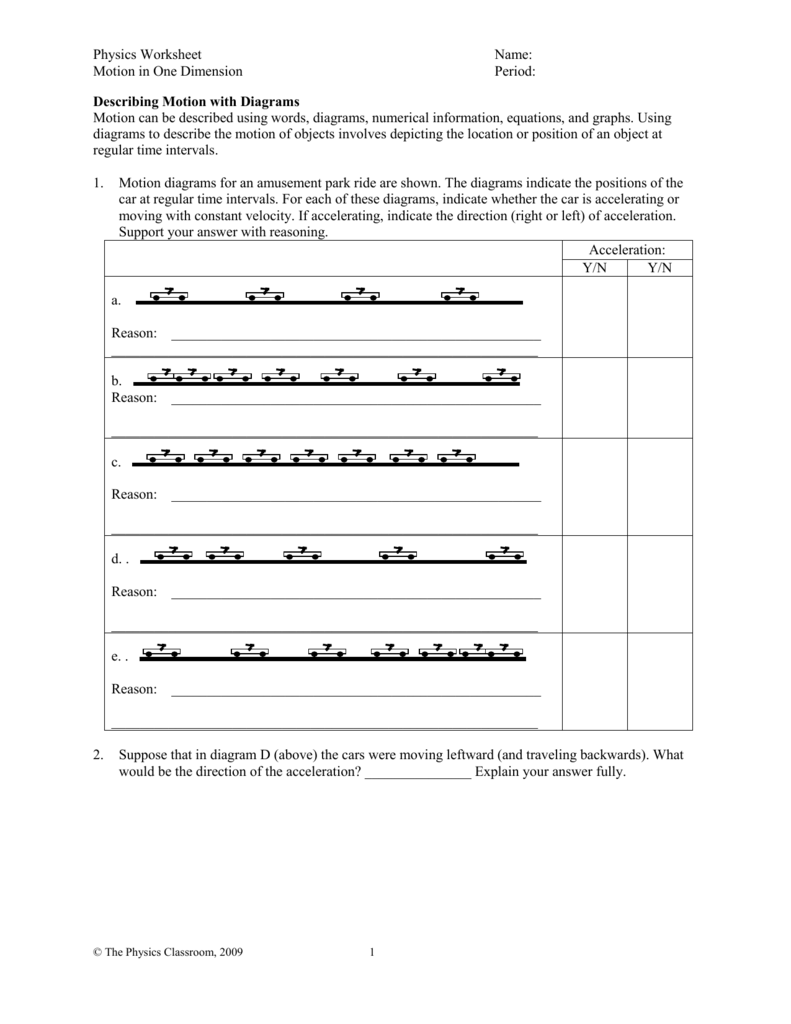
Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about how forces affect the motion of objects. Develop and use a model of a Free Body Diagram to represent the forces acting on an object (both equilibrium and non-equilibrium). Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to explain the relationships among force, mass, and motion. A motion diagram shows the position of a moving object at the beginning and end of a time interval. During that time interval, the speed of the object could have remained the same, increased, or decreased. All that can be determined from the motion diagram is the average velocity. This is a motion diagram of an object moving along the x-direction with constant acceleration. The dots 1, 2, 3, … show the position of the object at equal time intervals ∆t. Which of the following vx-tgraphs best matches the motion shown in the motion diagram? A motion diagram represents the motion of an object by displaying its location at various equally spaced times on the same diagram. Motion diagrams are a pictorial description of an object's motion. They show an object's position and velocity initially, and present several spots in the center of the diagram.
Physics in Motion. Welcome to Physics in Motion - a new digital series for high school physics from Georgia Public Broadcasting! The series is comprised of seven units of study divided into segments. Under each segment, you will find support materials designed to provide practice and reinforce concepts. A teacher toolkit is available and can ... Motion is the process of changing position by moving, or changing place, and has many possible factors involved. Discover Newton's Laws of Motion and the impact of force, speed, velocity ... zero slope implies motion with constant acceleration Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. Transforming a velocity-time graph to an acceleration-time graph means calculating the slope of a line tangent to the curve at any point. And to be clear, this five newtons, this is equal to the weight, the magnitude of the weight of the object. So that was pretty straightforward, the free body diagram for just the block. And it's really important to see that, because notice, in the free body diagram, all you see is the block. But now let's draw the free body diagram for the shelf.
Example Question #4 : Motion Diagrams. The bases on a baseball field are apart. A player hits a home run and runs around all four bases. What is his total displacement? Displacement is a vector. Therefore, magnitude and direction matters and because direction matters the total displacement is 0 feet.
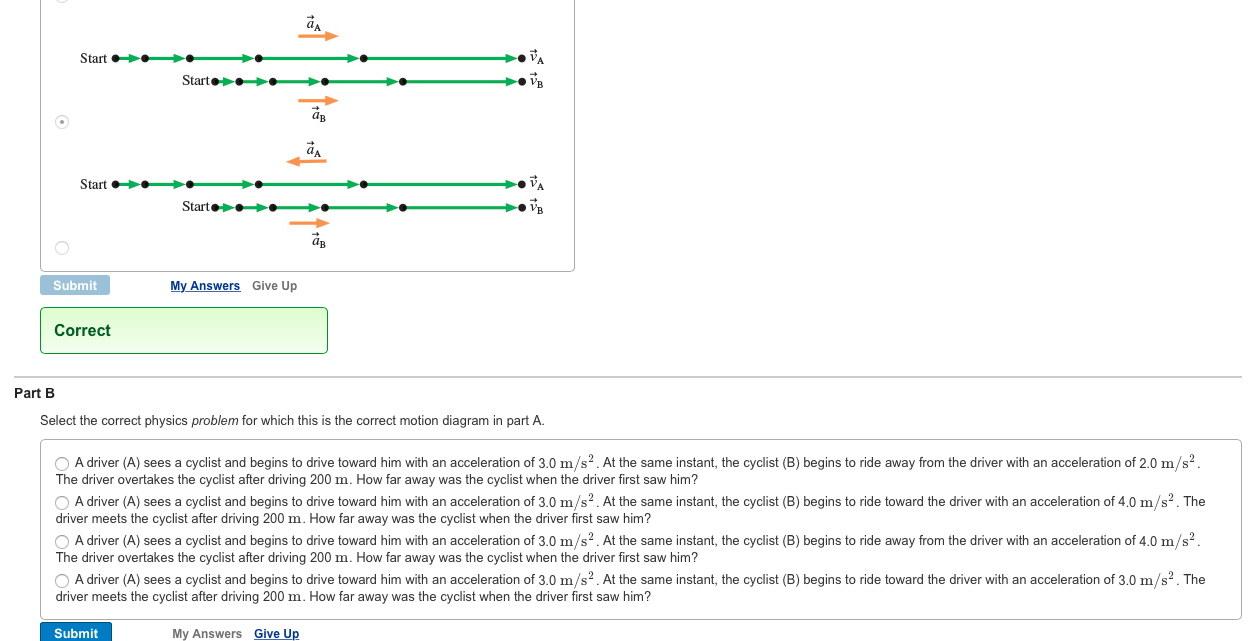
This motion diagram shows two types of constant acceleration. Figure A shows the object speeding up, which is indicated by the distance between the dots getting bigger every second, and figure B ...
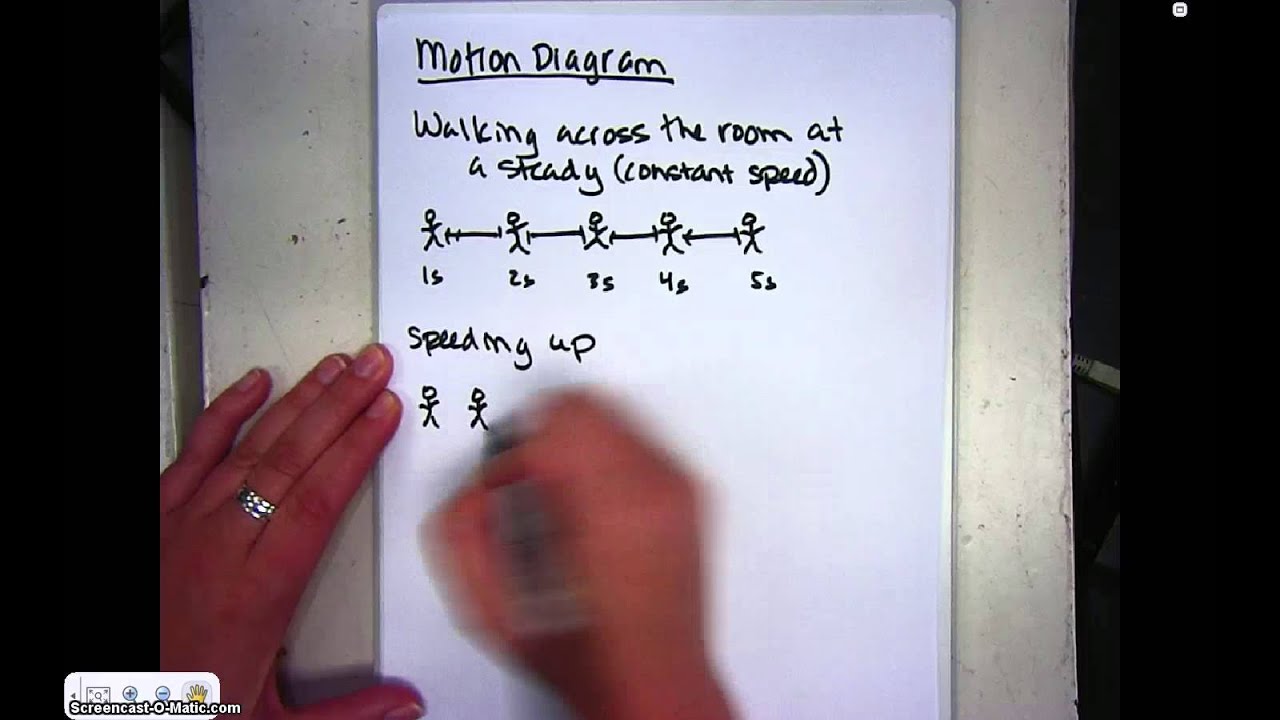
This video introduces the concept of Motion diagrams (also sometimes called dot diagrams) to represent motion in 1D in physics.
A motion diagram represents the motion of an object by displaying its location at various equally spaced times on the same diagram.Motion diagrams are a pictorial description of an object's motion. They show an object's position and velocity initially, and present several spots in the center of the diagram. These spots reveal whether or not the object has accelerated or decelerated.
Physics Motion Worksheet Part I 1. An object goes from one point in space to another. After it arrives at its destination (a) its displacement is the same as its distance traveled. (b) its displacement is always greater than its distance traveled. (c) its displacement is always smaller than its distance traveled.
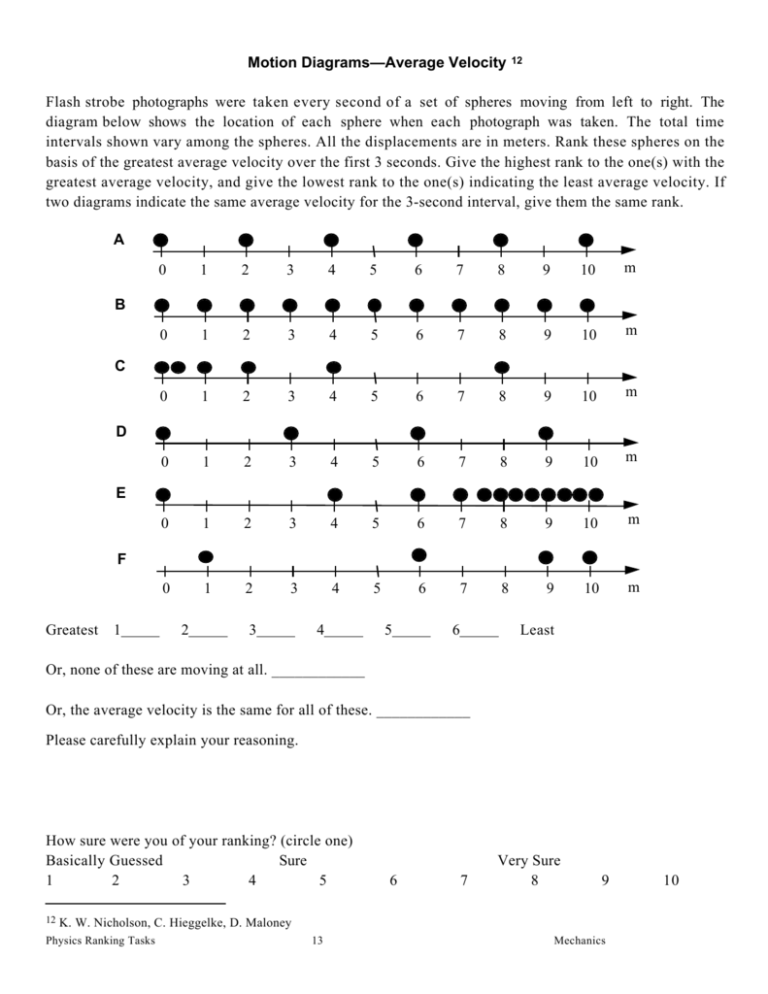
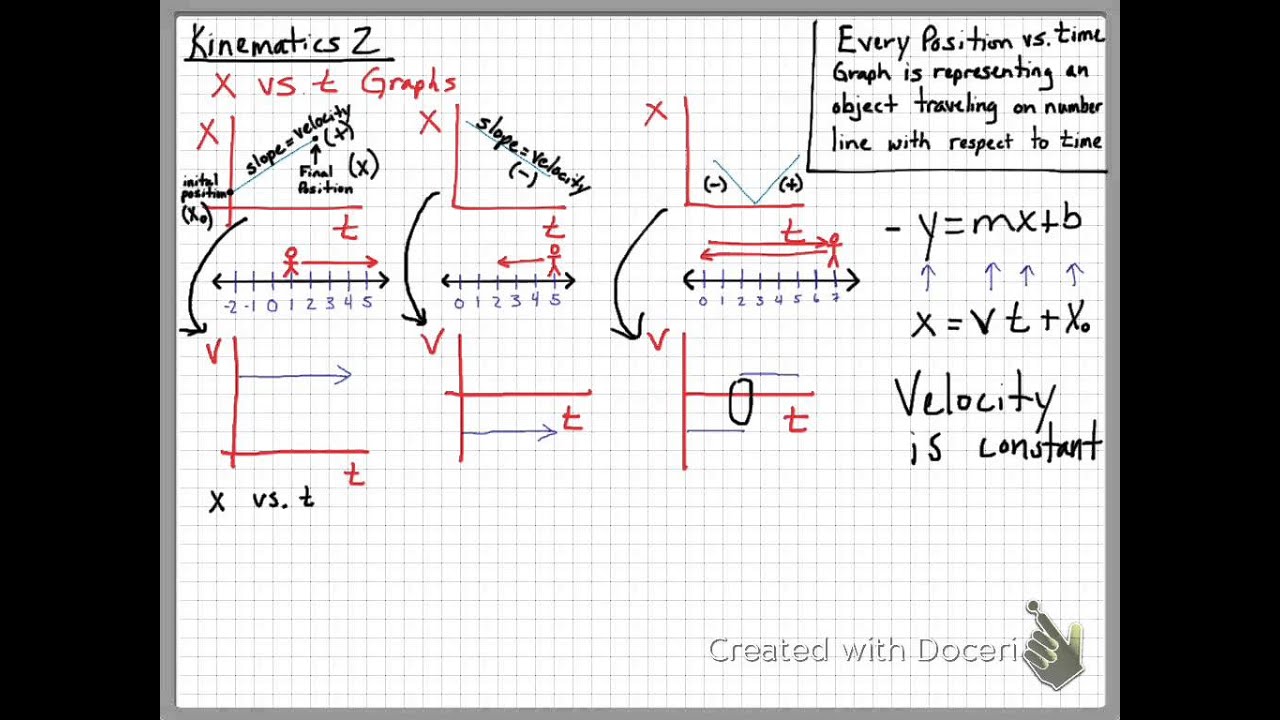
The motion diagrams for three common types of linear motion are described below. Constant Velocity: The first motion diagram, shown in Fig. 1, is for an object moving at a constant speed toward the right. The motion diagram might represent the changing position of a car moving at constant speed along a straight highway.
Which of these diagrams may possibly correspond to the situation at point C on the motion diagram? 1,2,3,4,5. Which of these diagrams correspond to a situation where the moving object (not necessarily the one shown in the motion diagram) is changing its velocity? A car is moving along a straight road at a constant speed.
Dot Diagrams. While the use of ticker tape analyses in Physics labs has mostly been replaced by the use of computer-interfaced motion detectors, the use of ticker tapes or motion diagrams still persists in our Physics curriculum due to the visual nature of representing an object's motion.Such diagrams are referred to as dot diagrams, motion diagrams, oil drop diagrams, and (still) ticker tape ...
This physics textbook is designed to support my personal teaching activities at Duke University, in particular teaching its Physics 141/142, 151/152, or 161/162 series (Introduc-tory Physics for life science majors, engineers, or potential physics majors, respectively).
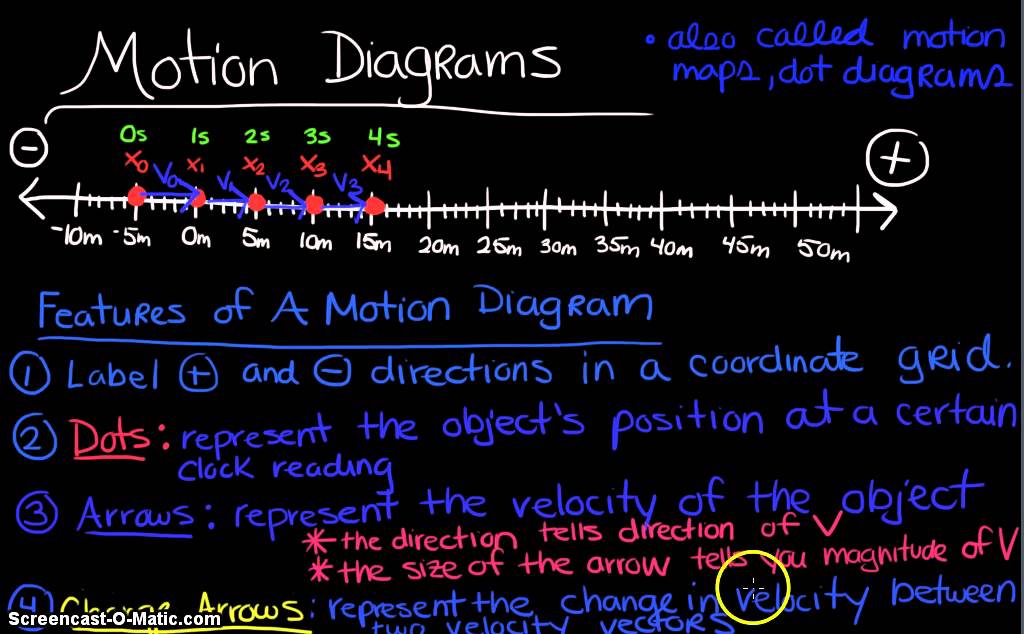
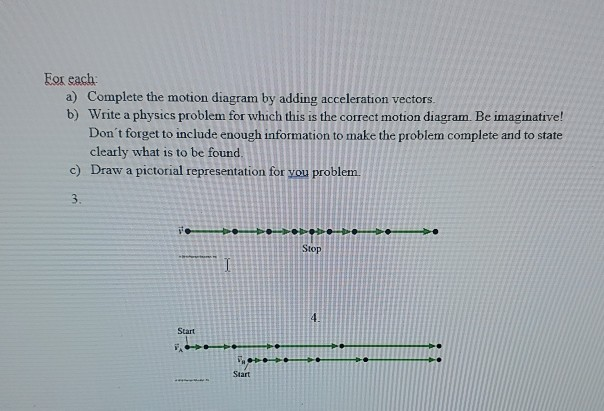
A motion diagram represents the velocity, position, and acceleration of an object at several different times. The times are typically separated by equal time intervals. At each position, the object's velocity and acceleration are represented with arrows.
The Motion Diagrams Concept Builder is a tool that provides a learner with extensive practice relating the verbal description of an object's motion to the motion diagram that describes the same motion. The motion diagram includes appropriately spaced dots that represent the object's constant speed motion, speeding up motion, or slowing down motion.
A motion diagram for this situation is given in The figure shows a motion diagram of a stone thrown upward with velocity v. The stone is thrown at zero y-coordinate and zero time moment. The stone reaches a turning point when time t is equal to 2 seconds.
• A motion diagram is a series of snapshots of the motion of the object, taken at regular time intervals. • A motion diagram shows only the POSITION of the object on the position axis. • A motion diagram depicts the motion of the object over a chosen time period • A motion diagram should specify the direction of +x (positive position)

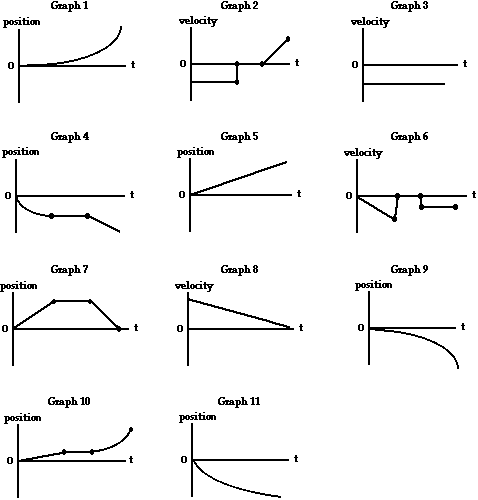
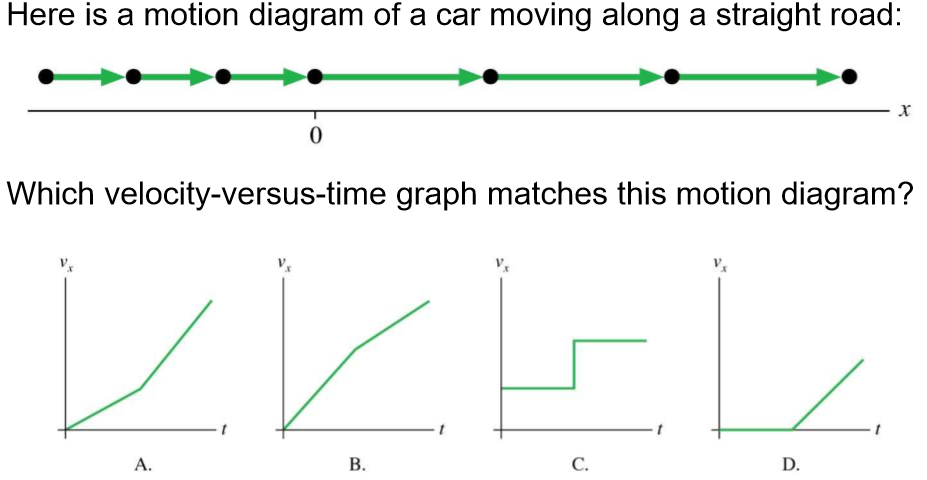
Physics Reference Which Graph Represents The Motion Of A Car That Is Travelling Along A Straight Road With A Speed That Increases Uniformly With Time
The motion diagram for something slowing down would look like _____. dots that get closer together If a car has a negative displacement, what does that indicate?
A motion diagram is a pictorial description of the motion of an object. It displays the object's location at various equally spaced times on the same diagram; ...
A motion diagram represents the velocity position and acceleration of an object at several different times. These spots reveal the objects state of motion. Rank the acceleration from largest to smallest. The motion diagram includes appropriately spaced dots that represent the objects constant speed motion speeding up motion or slowing down motion.

That S How I Roll Frictional Force In Smooth Rolling Motion Vector Diagram For Fundamentals Of Physics Rolling Torque And Angular Momentum The Kinetic Energy Newton S Laws Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock

Physics Chapter 3 Describing Motion 3 1 Picturing Motion Motion Diagram Operational Definition Particle Model 3 2 Where And When Coordinate Systems Scalar Vector Ppt Download

The Figure Shows The Motion Diagram Of A Drag Racer The Camera Took One Frame Every 2 S Make A Position Versus Time Graph For Drag Racer Study Com

A Particle Model Is A Simplified Version Of The Motion Diagram Where The Moving Object Is Replaced By Single Points This Is Shown Under Velocity Banan Physics












0 Response to "39 what is a motion diagram physics"
Post a Comment