41 h20 molecular orbital diagram
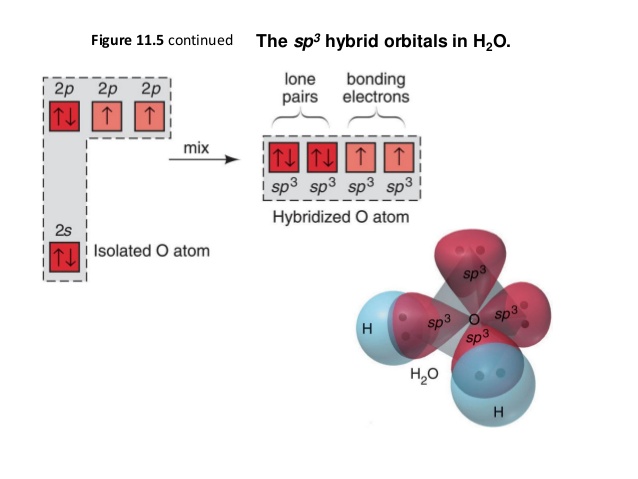
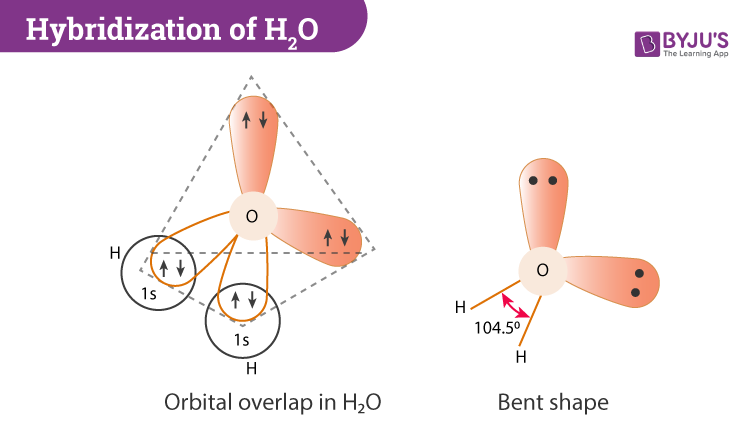
Consider the molecular orbital diagram for H20 and respond to the following questions: (a) (1) What is the total number of the formally bonding and antibonding orbitals in H2O? Answer: (b) (1) List all oxygen orbitals involved in bonding in H20. Answer: (c) (2) Name the oxygen orbitals that would not have been involved in bonding, if the ... Three 2p orbitals of Oxygen and one 2s orbital are hybridized as there are two pairs of bonding electrons and two lone pairs. And as four orbitals of Oxygen are hybridized, the hybridization of H 2 O is sp3. H2O Molecular Geometry. The molecular geometry of any molecule depends on its Lewis structure, the arrangement of atoms and its electrons.
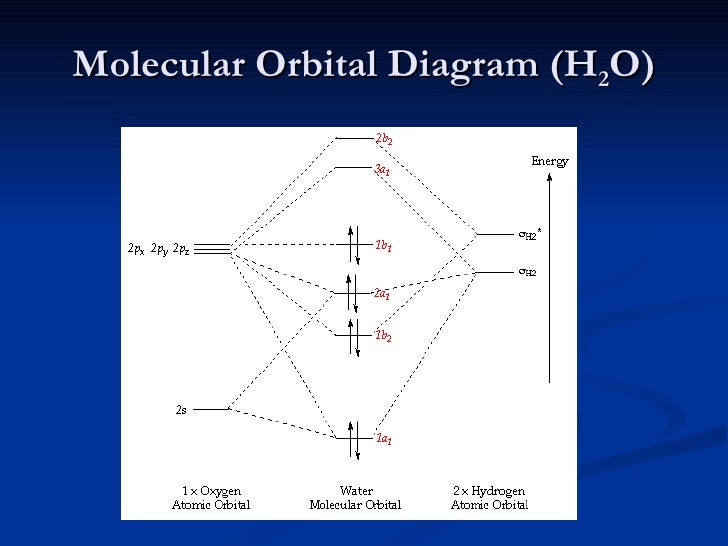
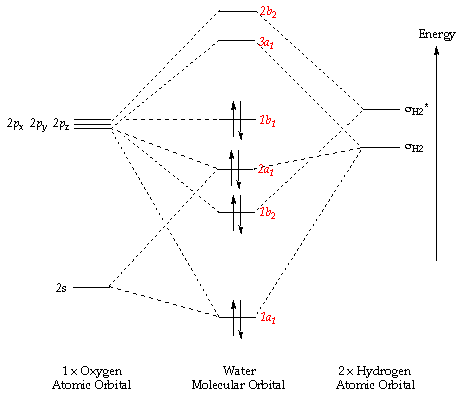
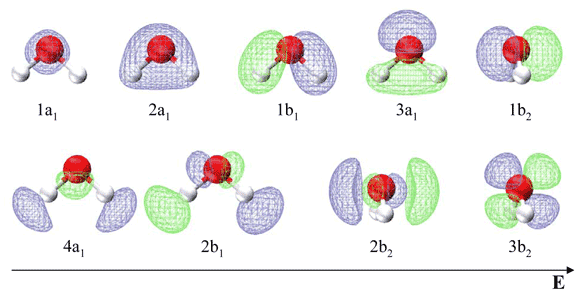
Molecular Orbitals for Water (H 2 O) The five occupied and the lowest three unoccupied molecular orbitals of the isolated molecule (1a 1) 2(2a 1) 2(1b 2) 2(3a 1) 2(1b 1) 2 were calculated using the Restricted Hartree-Fock wave function (RHF) using the 6-31G** basis set (experimental data is given in [1289]). They are set out with the lowest

H20 molecular orbital diagram
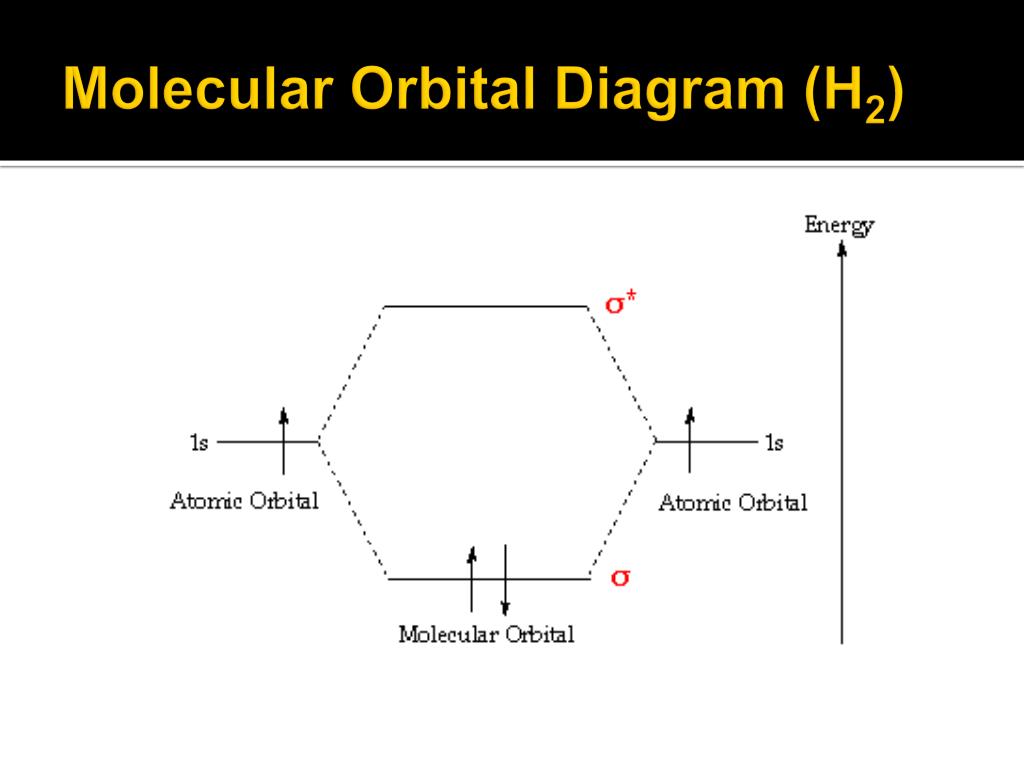
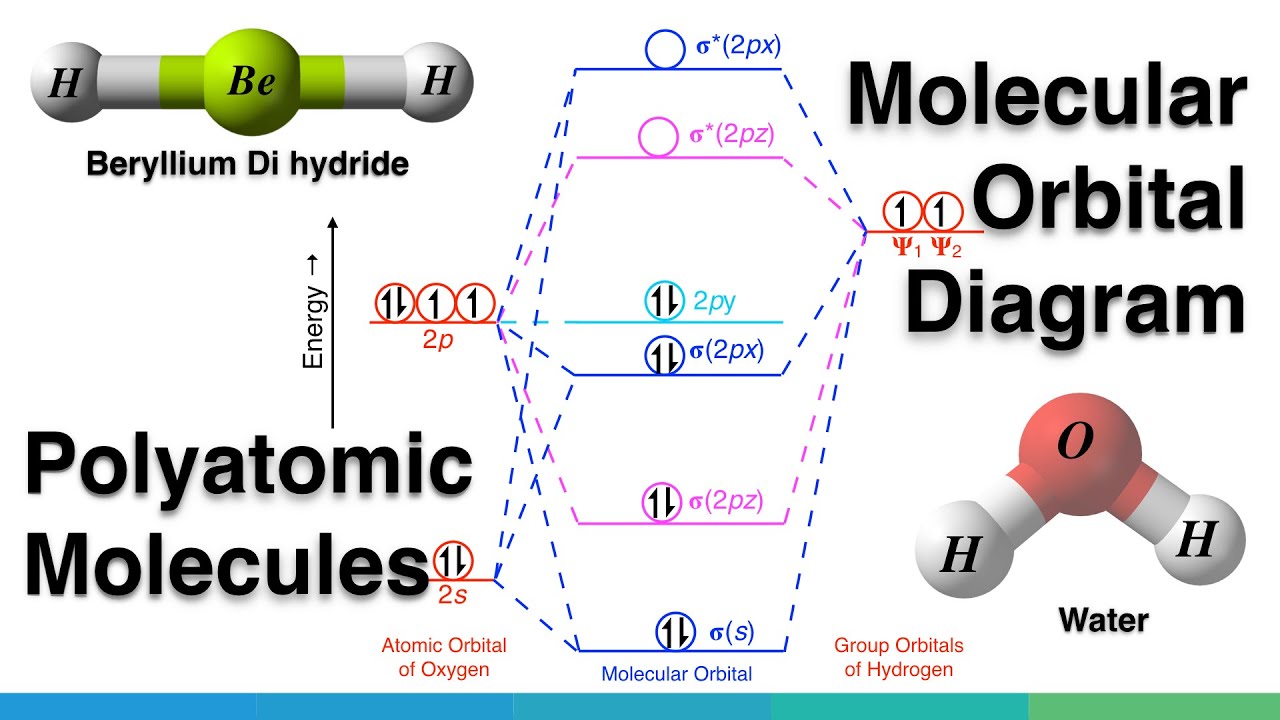
In general, this mixing of n atomic orbitals always generates n molecular orbitals. The hydrogen molecule provides a simple example of MO formation. In the following diagram, two 1s atomic orbitals combine to give a sigma (σ) bonding (low energy) molecular orbital and a second higher energy MO referred to as an antibonding orbital. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... the respective electrons of each are displayed in their orbitals (not shown on the diagram but for oxygen you have 6 valence electrons, this constitutes 2x2s electrons, 4x2p electrons) for H 2 it is 2x 1s now effective molecular orbital formation is done by mixing and overlap of similar atomic orbitals.
H20 molecular orbital diagram. parallel overlap of the two unhybridized p atomic orbitals from each carbon. 15. Ethane, C2H6, has 2(4) + 6(1) = 14 valence electrons. The Lewis structure is: The carbon atoms are sp3 hybridized. The six C‒H sigma bonds are formed from overlap of the sp3 hybrid orbitals on C with the 1s atomic orbitals from the hydrogen atoms. The carbon- Transcribed image text: Part A Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals TE 2p 2p 22 Tap 25 BCN NA? 82 MacBoo Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals 3 2p 2P D SS 0, Ne 02 None of the best ... Learn more about MO diagrams using these hands-on 101 Diagramss that we have collected for you! In the following diagrams, the examples of molecular orbital diagram are illustrated clear pictures. Follow these diagrams to study more about the topic and we'll start by giving you the first H20 MO diagram below. Molecular Orbitals • Themolecularorbital(MO) approachseeks to construct orbitalsfor the bondedsystem. • Approximate wave function solutions are constructed as a Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals(LCAO). • For diatomicmolecules,AB, these LCAO MOshavethe generalform 1 = a A + b B 2 = a A -b B
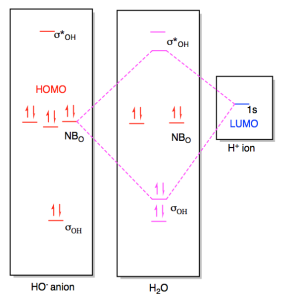
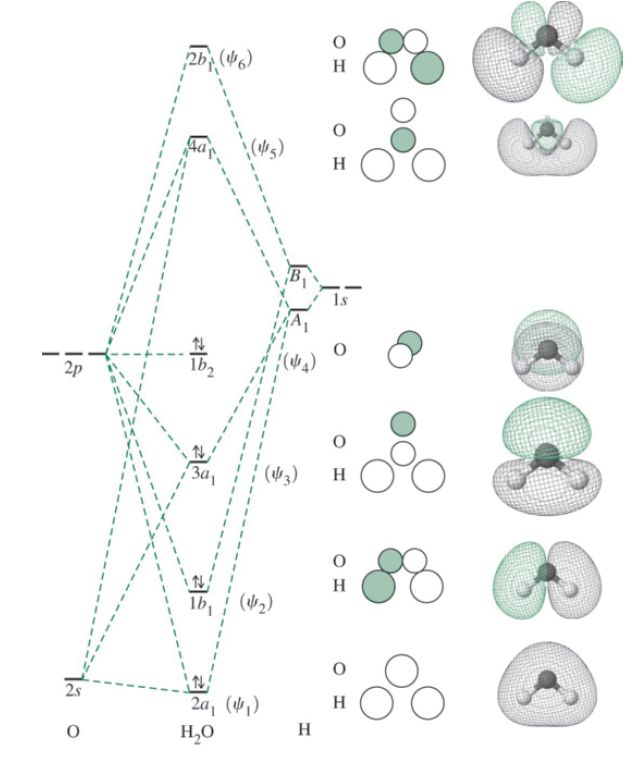
These two orbitals are called the e g orbitals (the symbol actually refers to the symmetry of the orbitals, but we will use it as a convenient name for these two orbitals in an octahedral complex). The other three orbitals, the d xy , d xz , and d yz orbitals, have lobes that point between the ligands and are called the t 2 g orbitals (again ... Orbitals of same symmetry and similar energy levels can then be mixed to form a new set of molecular orbitals with bonding, nonbonding, and antibonding characteristics. In the simple MO diagram of H 2 O , the 2s orbital of oxygen is mixed with the premixed hydrogen orbitals, forming a new bonding (2a1) and antibonding orbital (4a1). Using group theory to crate a qualitative MO diagram for water Molecular Orbitals for Larger Molecules 1. Determine point group of molecule (if linear, use D2h and C2v instead of D∞h or C∞v) 2. Assign x, y, z coordinates (z axis is principal axis; if non-linear, y axes of outer atoms point to central atom)3. Find the characters of the reducible representationfor the combination of
H20 Molecular Orbital Diagram. It uses 3-D pictorial presentations of molecular orbitals to elucidate organic reaction . As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals. General procedure for simple molecules that contain a central atom: build group orbitals using the outer atoms, then interact the group orbitals. (b) H20 (c) HI (d) H2S. Sol: (b) HC1, HI and H2S do not from H-bonds. Only H20 forms hydrogen bonds. One H20 molecule forms four H-bondin. g. Q12. If the electronic configuration of an element is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d2 4s2 , the four electrons involved in chemical bond formation will be . (a) 3p6 Answer (1 of 7): Oxygen is sp3 hybridised in H2O molecule. Two hybrid orbitals are occupied by lone pairs and two are used in bonding with Hydrogen atoms. Since lone pairs does not contribute to the geometry of a molecule, therefore H2O has an angular geometry. The lone pair-lone pair repulsion i... Predicting Reactions Using Frontier Orbitals • Here are two species you have never seen before. Using Frontier Molecular Orbital Theory (FMO Theory), predict the first step of the reaction between these two species. Draw the curved-arrow mechanism that shows how they react, and predict the immediate product of that reaction.
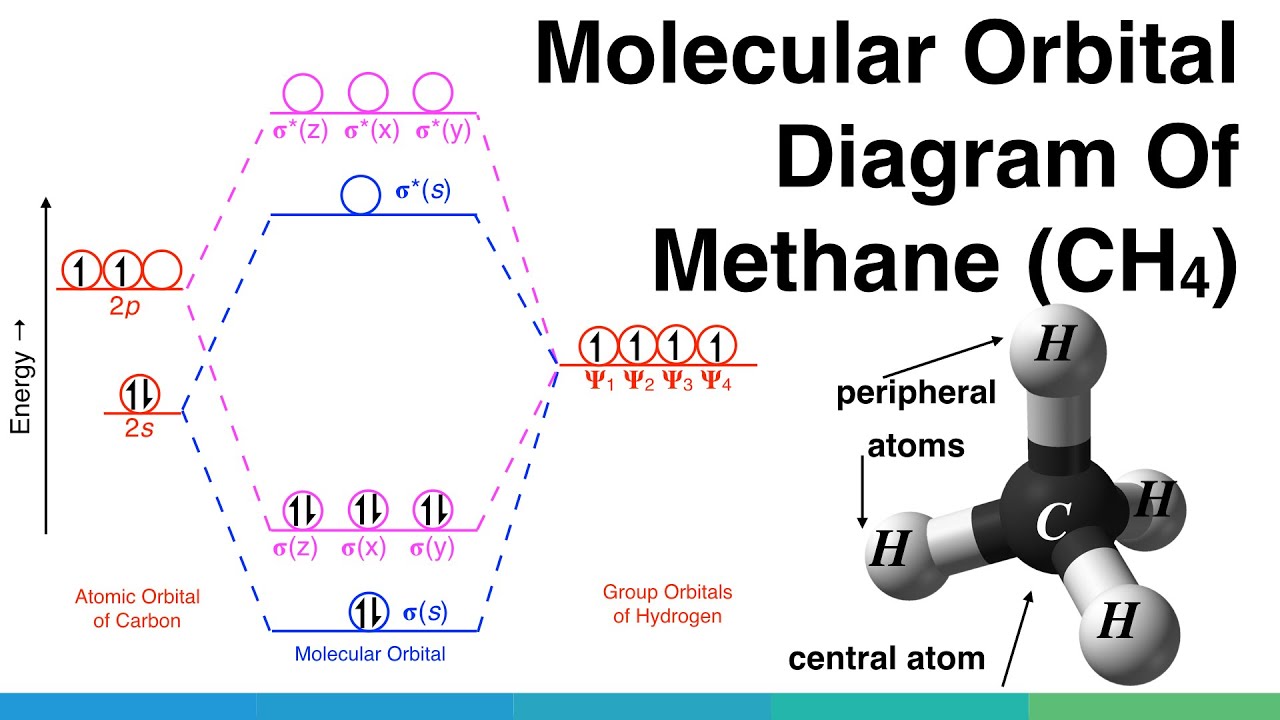
Molecular Orbital diagram of water (H2O) The molecular orbital diagram is a pictorial representation of determining chemical bonding between the molecules of a compound. Furthermore, the molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how two sigma bonds have been formed and the effect of the lone pairs on the structure.
molecular orbitals and a molecular orbital energy level diagram. These results are given below. You should compare these results with the traditional valence bond (Lewis structure) formulation of the bonding in H20. - 0.15ftP(Hl) + + 0.821Þ(02s) + = + 0.620 ) 2py = 02px 02py--- + 2px = - 2b2 1b 1b2 02.s 01s 0.5011J(02s) + 0.790 ) 2pz - 0.9911J(O )
In H 2 O hybridization orbitals having the same energy level will combine to form hybrid orbitals. The water molecule has two lone pairs and two bond pairs. Each O‒H covalent bond is called a sigma (σ) bond. H 2 O Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles. H 2 O has a tetrahedral arrangement of molecules or an angular geometry. This is mainly ...
An advanced molecular orbital diagram of H2O (water) for the inorganic or physical chemistry student.
Description. H2O-MO-Diagram.svg. English: MO diagram of water. Vectorized, simplified and corrected from File:Diagramme AH2.png. Quantitative calculations show bonding character in both the 3a 1 and 2a 1 levels. Date. 21 May 2015. Source. Own work.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
chemical bonding - chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can be introduced by considering the H2 molecule. Its molecular orbitals are constructed from the valence-shell orbitals of each hydrogen atom, which are the 1s orbitals of the atoms. Two superpositions of these two orbitals can be formed, one by summing the orbitals and the other by taking their difference.

Scielo Brasil Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built By Using Symmetry Principles Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built
H20 Molecular Orbital Diagram. It uses 3-D pictorial presentations of molecular orbitals to elucidate organic reaction . As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals. General procedure for simple molecules that contain a central atom: build group orbitals using the outer atoms, then interact the group orbitals.
d orbitals •l = 2, so there are 2l + 1 = 5 d-orbitals per shell, enough room for 10 electrons. •This is why there are 10 elements in each row of the d-block. σ‐MOs for Octahedral Complexes 1. Point group Oh 2. The six ligands can interact with the metal in a sigma or pi fashion.
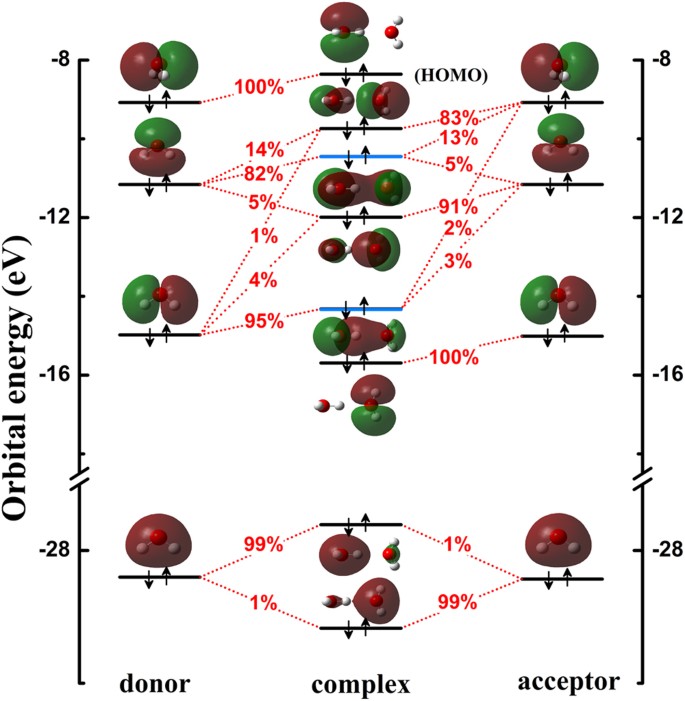
I I I I I I I I I I I -5.00 -3.67 -2.33 -1.00 0.33 1.67 3.00 X 4.33 Fig. 2. 3tg Molecular Orbital of [Fe(H20)6 12+, showing predominantly metal contributions. and ligand molecular orbitals are shown in brackets. The sequence of energy levels is similar for each complex, with only two changes in order.
Write the orbital diagram for sulfur and determine its number of unpaired electrons. Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4. Orbital diagram: 1s= 1 up 1 down. 2s= 1 up 1 down. 2p= 1 up 1 down 1 up 1 down 1 up 1 down. 3s= 1 up 1 down. 3p= 1 up 1 down 1 up 1 up. Two unpaired electrons. Write the electron configuration for Ge.
the respective electrons of each are displayed in their orbitals (not shown on the diagram but for oxygen you have 6 valence electrons, this constitutes 2x2s electrons, 4x2p electrons) for H 2 it is 2x 1s now effective molecular orbital formation is done by mixing and overlap of similar atomic orbitals.
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
In general, this mixing of n atomic orbitals always generates n molecular orbitals. The hydrogen molecule provides a simple example of MO formation. In the following diagram, two 1s atomic orbitals combine to give a sigma (σ) bonding (low energy) molecular orbital and a second higher energy MO referred to as an antibonding orbital.
Solved The Results Of A Molecular Orbital Calculation For H2o Are Shown Here Examine Each Of The Orbitals And Classify Them As Bonding Antibonding Or Nonbonding Assign The Correct Number Of Electrons To

Transparent Water Molecule Png H2o Molecular Orbital Diagram Png Download Transparent Png Image Pngitem














0 Response to "41 h20 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment