42 blank molecular orbital diagram
Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron. Jan 25, 2020 — Note that we have not added any electrons to that molecular orbital energy diagram yet, but when we do, we will just fill them in from the ...
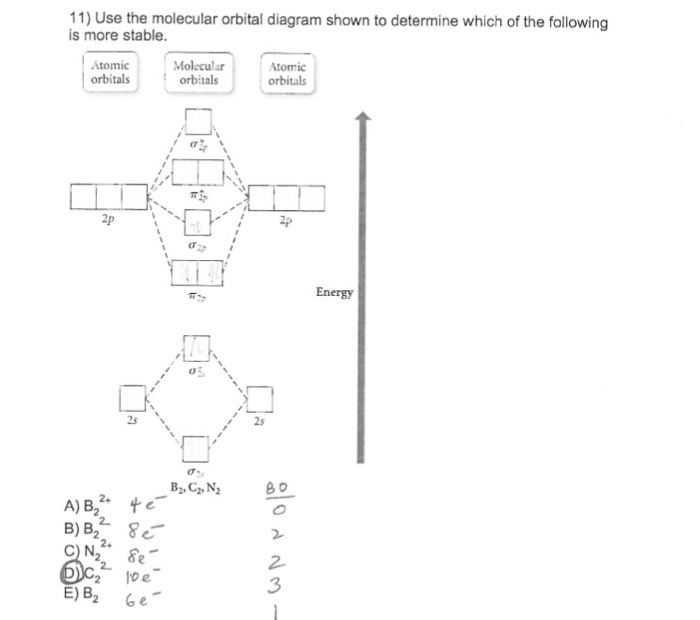
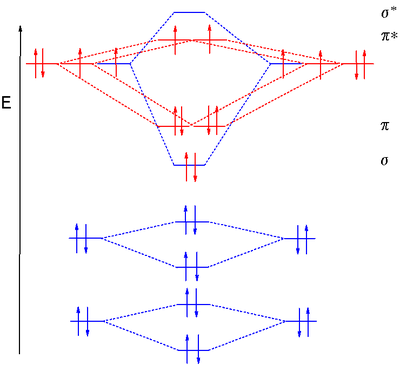
The blank molecular orbital diagram for #"O, F"#, and #"Ne"# is. Molecular orbitals for #"O"_2#. Each #"O"# atom has 6 valence electrons, so the #"O"_2# molecule has 12 valence electrons.. We use the Aufbau Principle and Hund's rule to place these electrons in the atomic and molecular orbitals.

Blank molecular orbital diagram
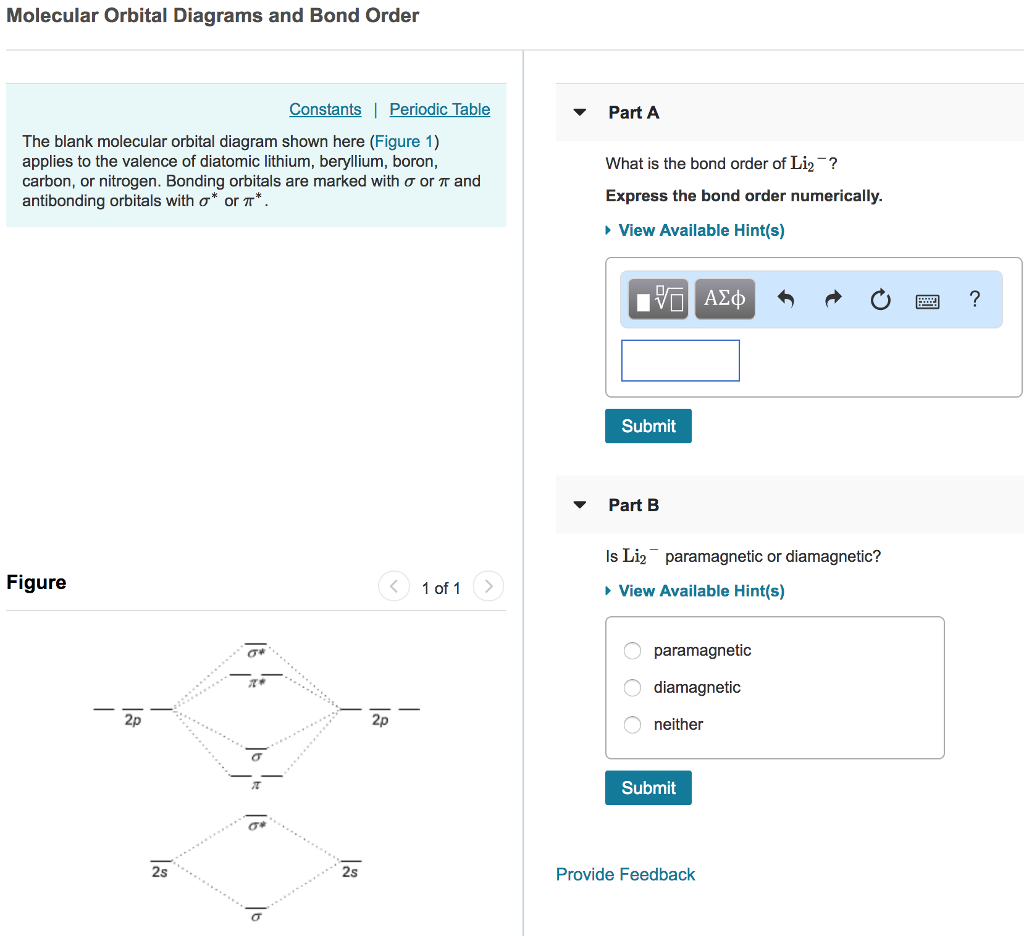
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 2) has been provided to help you. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. View Available Hint(s) ResetHelp Diamagnetic Paramagnetic . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Problem: The blank molecular orbital diagram shown here (Figure 1) applies to have valence of diatomic boron, carbon, or nitrogen. What is the bond order of ...1 answer · Top answer: [readmore]We’re being asked to determine the bond order of C2-. For this, we do the following:Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons ...
Blank molecular orbital diagram. A molecular orbital is a region of space in a covalent species where electrons are likely to be found. The combination of two atomic orbitals always forms two molecular orbitals; the bonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, and the antibonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy than the original atomic orbitals. The molecular orbital diagrams of , and are drawn in the attached image. There is no unpaired electron present in the MO diagram of and all the electrons are paired up so it is diamagnetic in nature. There is one unpaired electron present in the MO diagram of and therefore it is paramagnetic in nature. Procedure: draw Lewis Structure, determine Steric Number (SN), Molecular Geometry and Hybridization SN = # of atoms bonded to the central atom plus # of lone pairs on the central atom (SN = the effective number of electron pairs surrounding a central atom). Note: If one s and one p orbital hybridize, they form two sp hybrid orbitals. Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds.
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. A blank molecular orbital diagram (Part A 1 figure) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. To rank items as equivalent, overlap . Science. Based on Kepler's observations about planetary motion, what is the relationship between a planet's orbital ... Fill in the blank molecular orbital diagram, remembering the rules you know about filling orbitals with electrons (lowest energy first, fill with one electron/orbital in same energy level until the orbitals are all half full, then fill with the second electron) A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equilvalent, overlap them. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help F2 F2 Lowest bond energy Highest bond energy The correct ranking cannot be determined. Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. A blank molecular orbital diagram (Part A 1 figure) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. F2, F2+, F2-
Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from 180 o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram Water 104.5 ° X H H H O H Construct the molecular orbital diagram for dichlorine. x y z z y 3 x y z z y 4 Showing the p orbitals. Showing the s and p orbitals. ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION 11. CARBON ORBITALS Methane Ethane METHANE AND ETHANE C H H H H CH4 C C H H H H H H C2H6 1 2 Color conventions: Hydrogen atoms are shown in gray. Learn about the molecular orbital diagram for O2 using these free and printable molecular orbital diagram as your reference in understanding the MO of oxygen. A collection of printable MO diagram is available for you to help you study more about the topic. The following diagrams contain the MO of oxygen and you can get the picture by clicking on the image. which of the following diatomic species are paramagnetic and which are diamagnetic? a blank molecular orbital diagram (figure 2) has been provided to help you. Answers: 2 Show answers Another question on SAT. SAT, 27.06.2019 22:30. Compared with the cost of tuition, fees, and books for a traditional college course, the cost of a clep exam is: ...
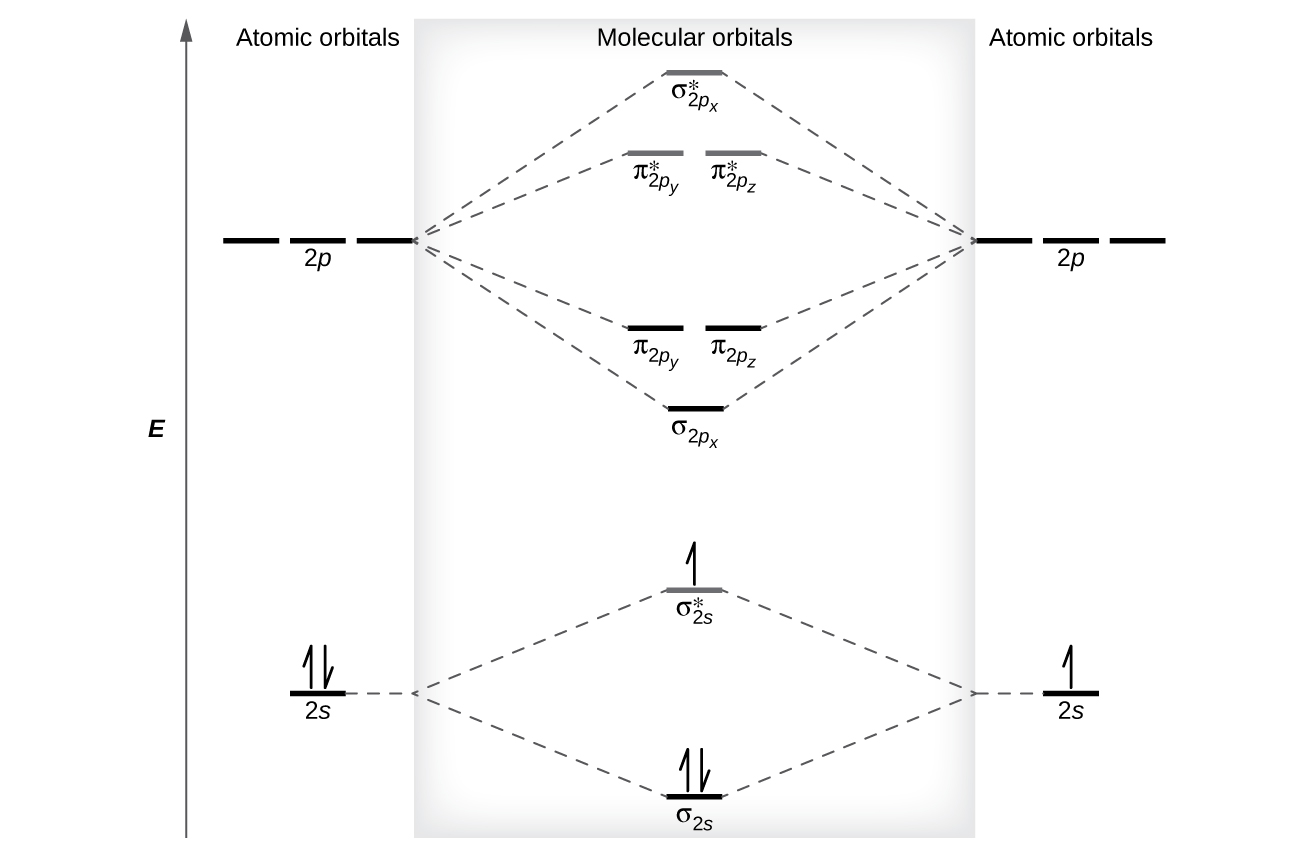
This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic orbitals.
Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in L a T e X by means of the package MOdiagram.For information about the more traditional molecular structure diagrams see our documentation about chemistry formulae.
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. A blank molecular orbital diagram (Part A 1 figure) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. F2, F2+, F2- Science
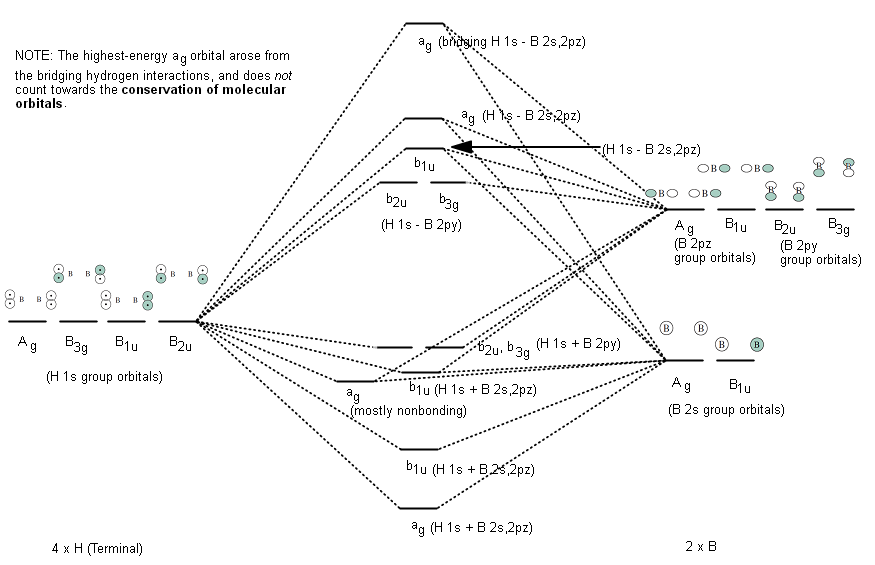
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic orbitals.
5.7 a. The energy level diagram for NO is on the right. The odd electron is in a π2p* orbital. b ...29 pages

2 A Molecular Orbital Diagram For A Tetrahedral Transition Metal Complex Is Shown Below Show How Homeworklib
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...

Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic Orbital Molecular Orbital Theory Dihydrogen Benzene Ring Angle White Text Png Pngwing
A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you. Rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in

Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For O 2 What Is Its Bond Order State Whether This Molecule Is Paramagnetic Or Diamagnetic From Chemistry Coordination Compounds Class 12 Cbse
A blank molecular orbital diagram has been provided to help you.Rank the fluorine species from highest to lowest bond energy. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.Molecular orbital (MO) theory is based in quantum mechanics and treats the orbitals found in a molecule in a manner similar to atomic orbitals in an atom.
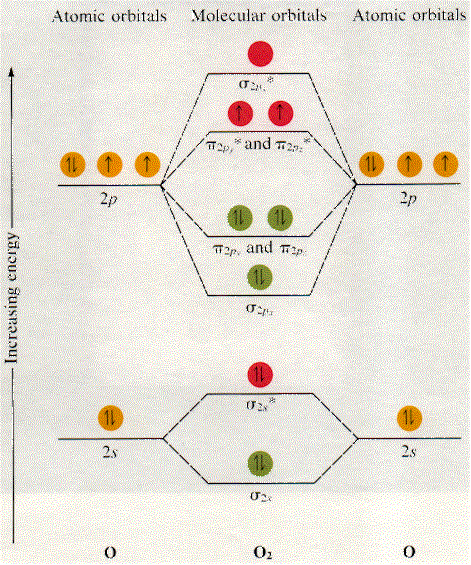
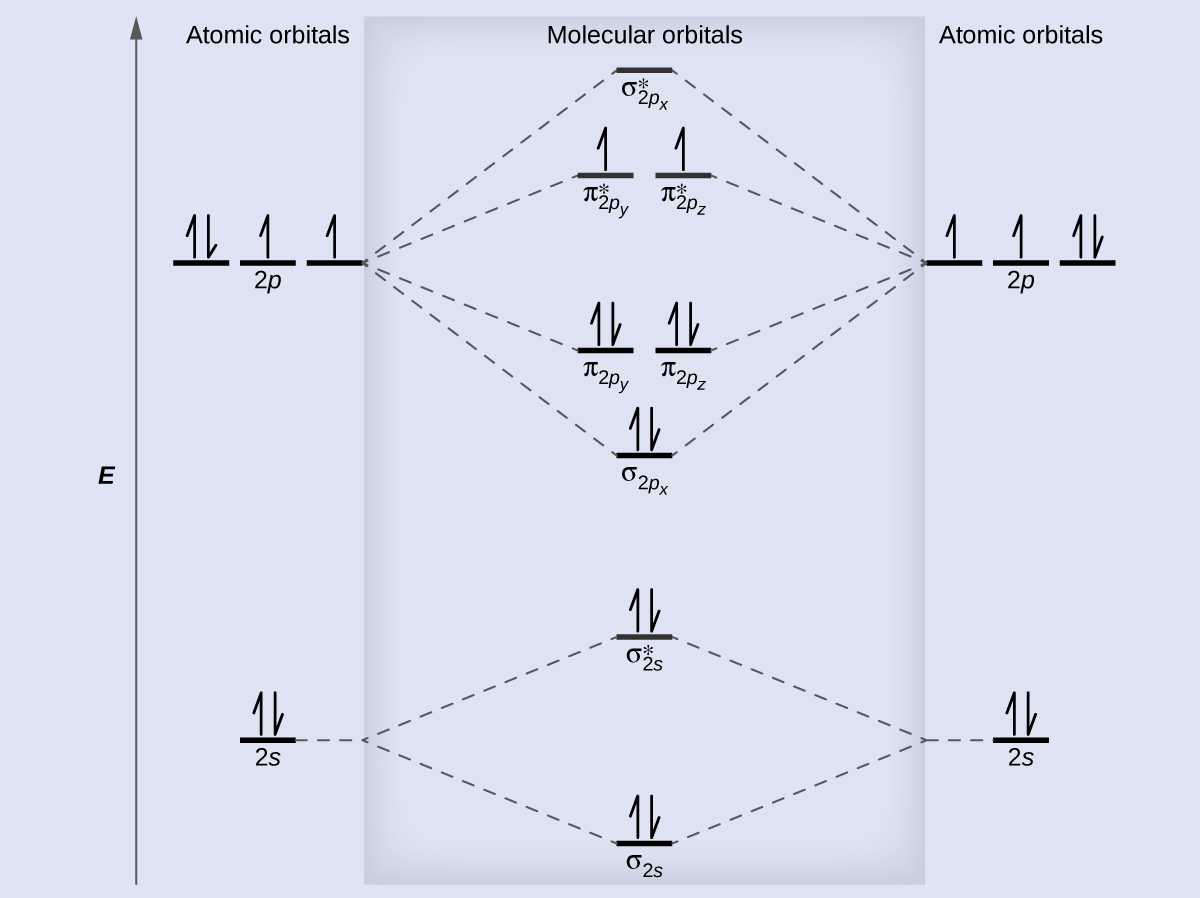
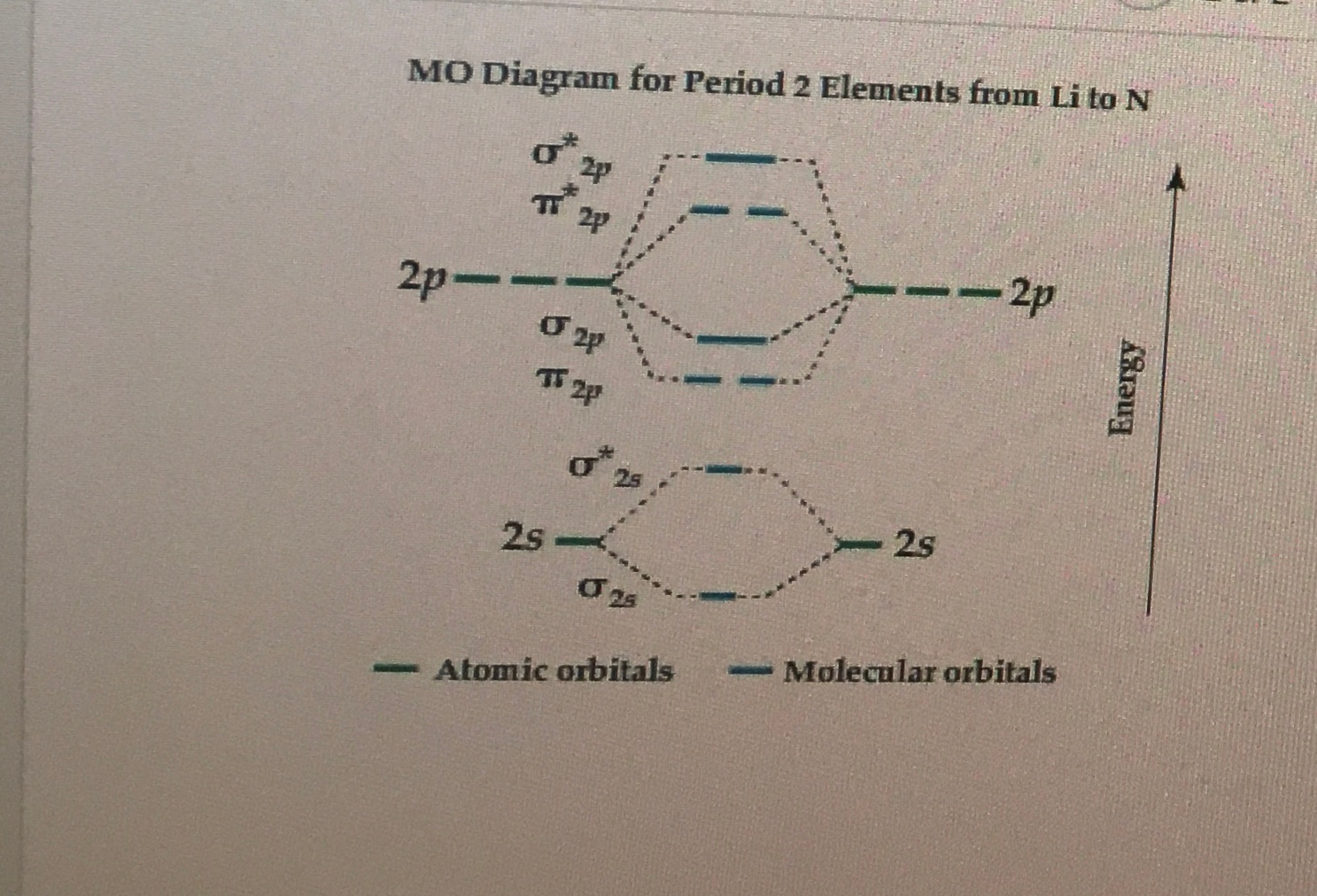
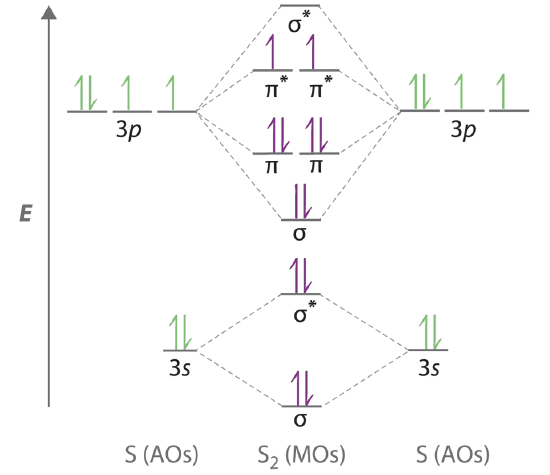
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
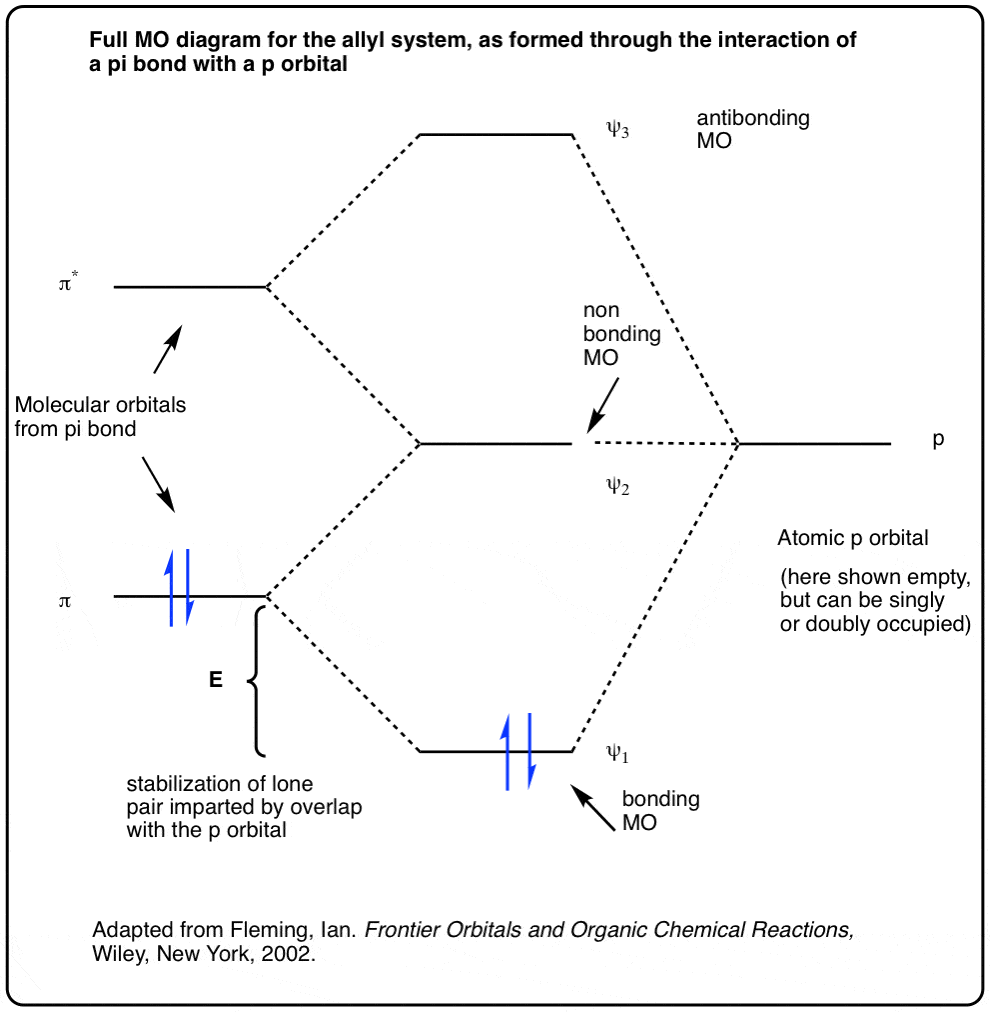
Six overlapping p orbitals must form six molecular orbitals . Three will be bonding, three antibonding . Lowest energy MO will have all bonding interactions, no nodes . As energy of MO increases, the number of nodes increases . System symmetric so 2 pairs of degenerate orbitals . 6 atomic orbitals - 6 molecular orbitals
Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. a blank molecular orbital diagram (part a 1 figure) has been provided to you. rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. to rank items as equivalent, overlap them. f2, f2+, f2-
Shells and Subshells of Orbitals. Orbitals that have the same value of the principal quantum number form a shell.Orbitals within a shell are divided into subshells that have the same value of the angular quantum number. Chemists describe the shell and subshell in which an orbital belongs with a two-character code such as 2p or 4f.The first character indicates the shell (n = 2 or n = 4).
Problem: The blank molecular orbital diagram shown here (Figure 1) applies to have valence of diatomic boron, carbon, or nitrogen. What is the bond order of ...1 answer · Top answer: [readmore]We’re being asked to determine the bond order of C2-. For this, we do the following:Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons ...
A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 2) has been provided to help you. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. View Available Hint(s) ResetHelp Diamagnetic Paramagnetic . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading.
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.

Which Of The Following Diatomic Species Are Paramagnetic And Which Are Diamagnetic A Blank Molecular Brainly Com















0 Response to "42 blank molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment