37 potential energy diagram physics
The term "potential energy" (energy due to position or configuration) is not necessary, but if one does want to use it then there are five potential forms of energy: gravitational, elastic, electromagnetic, chemical, and nuclear. The unqualified term "potential energy" can be ambiguous. Energy Flow Diagrams
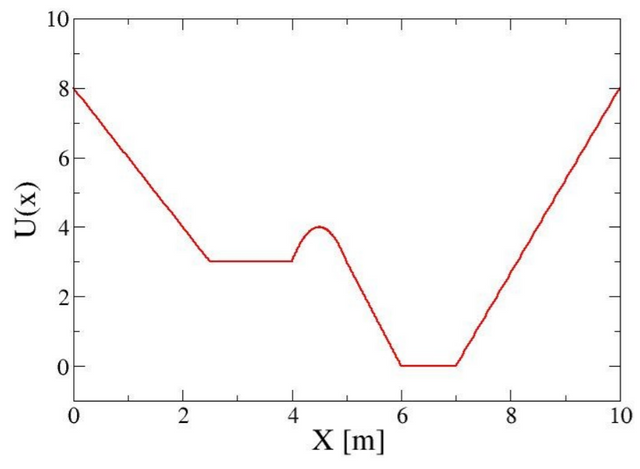
Quartic and Quadratic Potential Energy Diagram The potential energy for a particle undergoing one-dimensional motion along the x -axis is U ( x) = 2 ( x 4 − x 2), where U is in joules and x is in meters. The particle is not subject to any non-conservative forces and its mechanical energy is constant at
$\begingroup$ "why is the potential energy not defined as the difference between the energy level of the electron and the fermi level" It is the same thing. The energy level of the conduction band is just a way to talk about the energy the electrons in the conduction band may attain.

Potential energy diagram physics
How to solve the Potential energy function equilibrium Problems. (1) Potential energy function must be given for the problem. (2) Differentiate with respect to the variable. (3) To find the equilibrium points, put dU/dx=0 and solve for the values of x. (4) Perform second differentiation of the Potential energy function.
Energy flow diagrams. Diagrams can be used to show how energy is transferred from one store to another. Two examples are the transfer diagram and the Sankey diagram.
Work and Energy - Potential energy diagram. Problem Statement: The potential energy of a particle of mass m is represented in the figure below as a function of its position r. The particle begins its motion from rest at position r 0. what will be its speed at position 3r 0? If it were released without speed in position 2r 0, would it reach 3r 0?
Potential energy diagram physics.
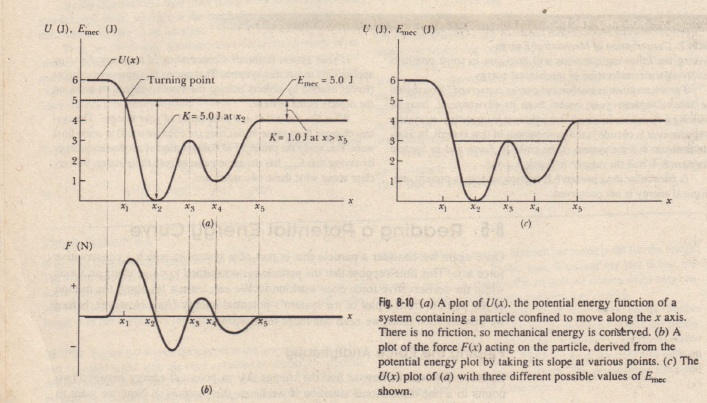
Physics. For the potential-energy diagram in (Figure 1), what is the maximum speed of a 5.0 g particle that oscillates between x = 2.0 mm and x = 8.0 mm? parabola starts at 5,2 and ends at 5,8 with the bottom at 1,4 ...
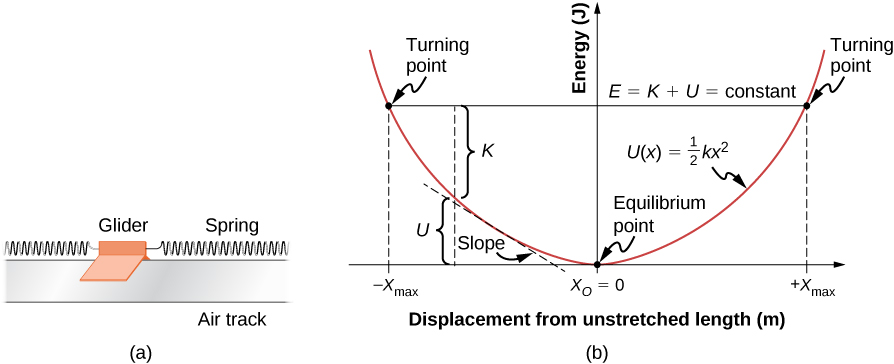
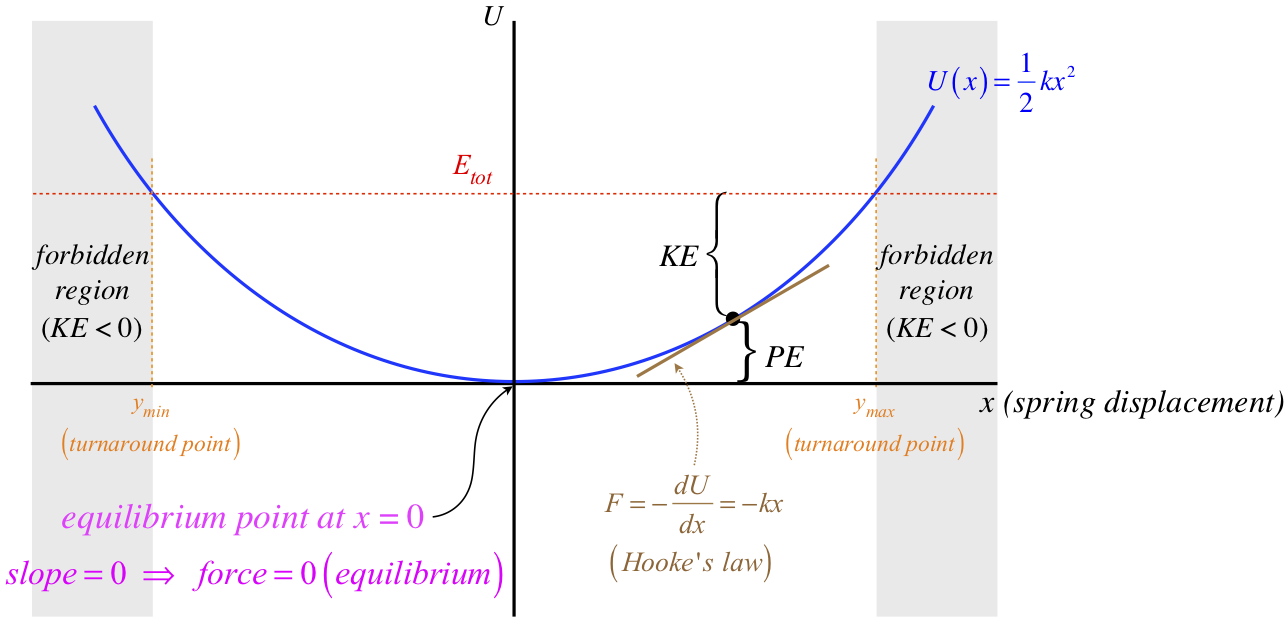
Elastic Force. We take precisely the same steps to draw the energy diagram for a mass on a spring, but there are some differences, such as two forbidden regions and a different slope for every position, and there is one additional feature for this potential that doesn't exist for the case of gravity: an equilibrium point.. Figure 3.7.3 – Energy Diagram for Object Influenced by Elastic Force
I. Kinetic energy Energy associated with the state of motion of an object. (7.1) 2 K 1 mv2 Units: 1 Joule = 1J = 1 kgm2/s2 = N m II. Work Energy transferred “to” or “from” an object by means of a force acting on the object. To +W From -W - Constant force: F x ma x d v v v v axd ax 2 2 2 0 2 2 0 2 Work done by the force = Energy
Potential-energy diagram help. I am given a potential-energy diagram with the vertical axis is potential-energy and the horizontal axis is x. The mass of the particle is 500g. They are asking the velocities of b, c, and d.
Energy Diagrams Identify system Identify state of system before interaction and state of final states. Draw energy diagrams for these states including: 1) Choice of zero point P for potential energy for each interaction in which potential energy difference is well-defined. 2) Draw speed of all objects in system
In physics, the use of the term mechanical energy usually involves three types of energies: potential gravitational energy, kinetic energy, and elastic potential energy. Although potential energy is often represented by the expression PE, in this lesson we will use the variable U; similarly, kinetic energy will be represented by the variable K.
The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds at B, C, and D? Learn this topic by watching Force & Potential Energy Concept Videos.
MIT 8.01 Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/8-01F16Instructor: Dr. Peter DourmashkinLicense: Creative Commons BY-NC-S...
Exponential potential energy state diagram. A particle of mass moves in one dimension. Its potential energy is given by where and are constants. (a) Draw an energy diagram showing the potential energy . Choose some value for the total mechanical energy such that . Mark the kinetic energy, the potential energy and the total energy for the ...
Explain the connection between stability and potential energy. Often, you can get a good deal of useful information about the dynamical behavior of a mechanical system just by interpreting a graph of its potential energy as a function of position, called a potential energy diagram. This is most easily accomplished for a one-dimensional system, whose potential energy can be plotted in one two-dimensional graph—for example, U ( x) versus x —on a piece of paper or a computer program.
Well, I was assuming that this ground was the H equals zero line. And we know that the gravitational potential energy is mgh. And where H equals zero, the potential energy is zero. So when this mass gets down to the final point, which I'm representing in this diagram, it no longer has any potential energy since the H would be zero.
B-6. Sketch the potential energy diagram of the car by subtracting it from the kinetic energy diagram. To maintain conservation of energy the potential energy must be negative in the region near the magnet. In fact, the shapes of the potential and kinetic energy diagrams turned out to be identical, although inverted.
1. Identify the general shape of the energy diagram Energy should conserve for any chemical reaction. The reaction in question is exothermic (releases heat) hence its products shall have chemical potential energies lower than that of its reactants- some of the potential energies have been converted to thermal energy during the reaction process.
gravitational potential energy ∆Ug = mg∆h acceleration due to gravity is nearly constant height change is small compared to the separation between centers the more general form will be dealt with later work-energy theorem, two possibilities conservative forces work done is independent of path W = ∮F · dr = 0
The mechanical energy of the object is conserved, E= K+ U, E = K + U, and the potential energy, with respect to zero at ground level, is U (y) = mgy, U ( y) = m g y, which is a straight line through the origin with slope mg m g. In the graph shown in Figure, the x -axis is the height above the ground y and the y -axis is the object’s energy.
Example 8.10: Quartic and Quadratic Potential Energy Diagram. The potential energy for a particle undergoing one-dimensional motion along the x-axis is U(x) = 2(x 4 − x 2), where U is in joules and x is in meters.The particle is not subject to any non-conservative forces and its mechanical energy is constant at E = −0.25 J. (a) Is the motion of the particle confined to any regions on the x ...
1 ) 𝐺𝑟𝑎𝑣𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑃𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝐸𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦 = 𝑈𝑔 = −𝐺𝑚1𝑚2/r, Here 𝑟 is the distance between the centers of two spherical bodies. 2 ) Potential energy due to the position of mass 𝑚 at a height ℎ above the earth's surface can be expressed as 𝑈𝑔 = mgh. Here, h<< Radius of the earth.
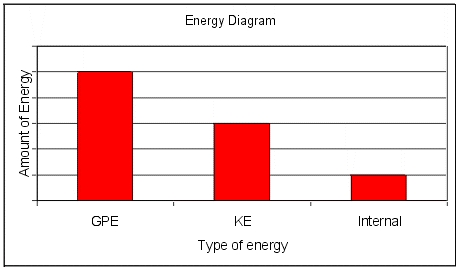
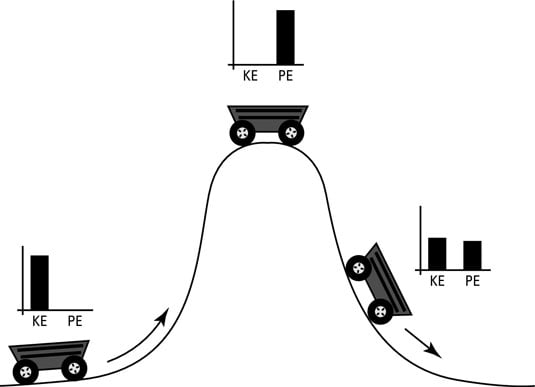
The diagram below depicts the conservation of total mechanical energy and the transformation of potential and kinetic energy for a roller coaster car at five positions along a track. In conclusion, bar charts are a useful tool for depicting the influence of external forces (if present) upon the total mechanical energy.
Force and Potential Energy. If the potential energy function U (x) is known, then the force at any position can be obtained by taking the derivative of the potential. (2.5.1) F x = − d U d x. Graphically, this means that if we have potential energy vs. position, the force is the negative of the slope of the function at some point.
Above is the potential energy formula. As per the law of conservation of energy, since the work done on the object is equal to m×g×h, the energy gained by the object = m×g×h, which in this case is the potential energy E.. E of an object raised to a height h above the ground = m×g×h. It is important to note that, the gravitational energy does not depend upon the distance travelled by the ...
The other issue with potential energy diagrams is that of accessibility. If an object has a particular initial kinetic energy , what points can the object get to?The object can get to any point with ; the graphical interpretation of this is that the object can get to any point below the line .A common follow-up takes the form “at a point with , what is the kinetic energy of the particle at a ...
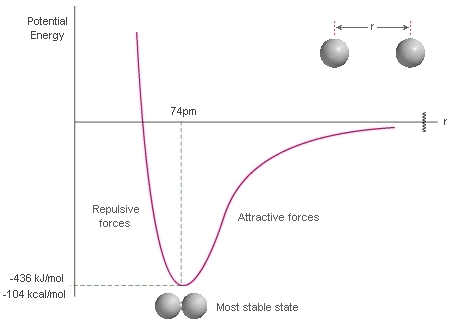
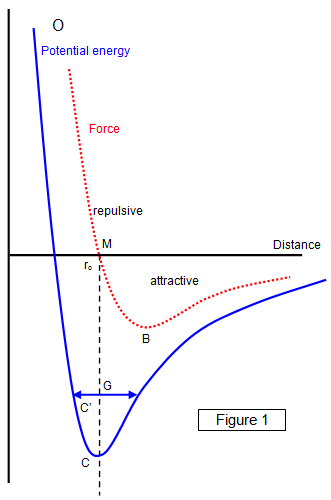
Potential Energy Diagram For The Formation Of An Ionic Bond. The point of greatest stability is r o, which gives the equilibrium spacing of the atoms. However, as the atoms approach each other from a large distance, the force is initially repulsive rather than attractive. The atoms require some additional energy, known as activation energy, to ...
A 800g ball is pulled up a slope as shown in the diagram. Calculate the potential energy it gains. 50cm 20cm Solution: In potential energy problems we are only interested in vertical distances Use E p = mgh, h = 20cm = 0.2m m = 800g = 0.8kg so E p = 0.8 x 10 x 0.2 = 1.6J remember to change units! The ball gains 1.6J of potential energy
Download English-US transcript (PDF) There's even a little bit more that we can learn about our energy diagram.. And I'd like to just clean this diagram up for a little second, because I want to work in this area. Suppose our system, because the work non-conservative is 0, tells us that the mechanical energy is constant. Now we don't know how much mechanical energy our system is.
Potential energy is one of several types of energy that an object can possess. While there are several sub-types of potential energy, we will focus on gravitational potential energy. Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in an object due to its location within some gravitational field, most commonly the gravitational field of the Earth.
The potential energy diagram is an important diagram because it depicts the potential energy function, often just called the potential. This terminology is unfortunate since it can lead to confusion with the electric potential.





















(251).jpg)
0 Response to "37 potential energy diagram physics"
Post a Comment