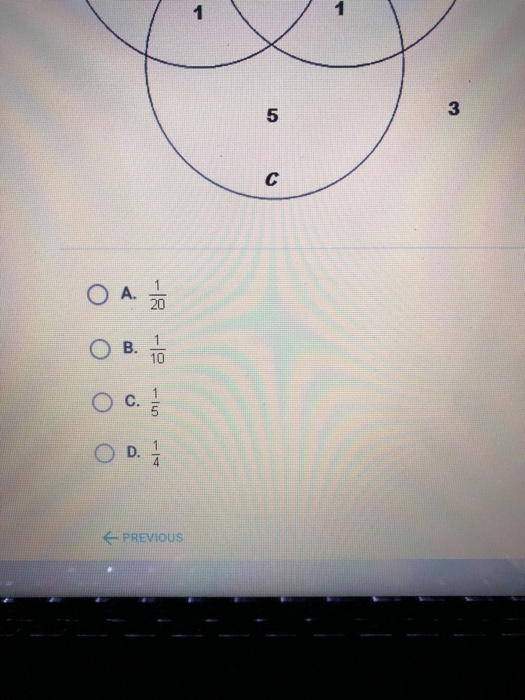
38 according to the venn diagram below what is p(a^b^c)
Venn Diagrams are a schematic way of representing the elements of a set or a group. In each Venn Diagram, we represent sets or groups of objects with the help of circles or ellipses. In the bank exams, the Venn Diagrams questions are of two types mainly. Let us learn these!
According to the Venn diagram below, what is (image below) A. 3/25 B. 4/25 C. 2/25 D. 1/25 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement Ashraf82 Ashraf82 Answer: P(A ∩ B ∩ C) is 1/25 ⇒ answer D. Step-by-step explanation: * Lets talk about the Venn diagram - There are three circles intersect each other
Calculation of P (B) Probability of B is represented as P (B) P (B) is calculated by adding all values of the set B. P (B) =0.05+0.05+0.01+0.03= 0.14 In venn diagram, P (B) is pictorially represented as.

According to the venn diagram below what is p(a^b^c)
Compare & Contrast. Based on what you have learned, complete the Venn diagram by using the statements below. (A) The defendant may have to pay money (B) The defendant may get jail time or loss of privileges (C) Deals with a crime that has committed (D) The case involves a problem between two individuals
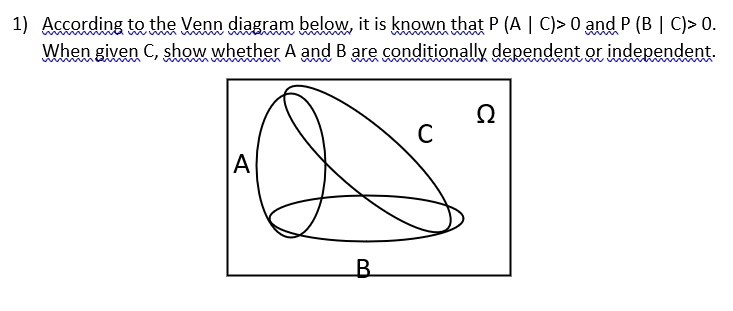
if P(A|B) = P(A) Ex) Probability that card drawn in event A is a Jack given event B was the drawing of a red card. Pr(A|B) = Pr(𝐴∩𝐵) Pr (𝐵) = 2 52 26/52 = 1/13 It was stated that if A and B are mutually exclusive -> (A∩B) = 0 then A and B are never independent. Various examples were then given to demonstrate independent events
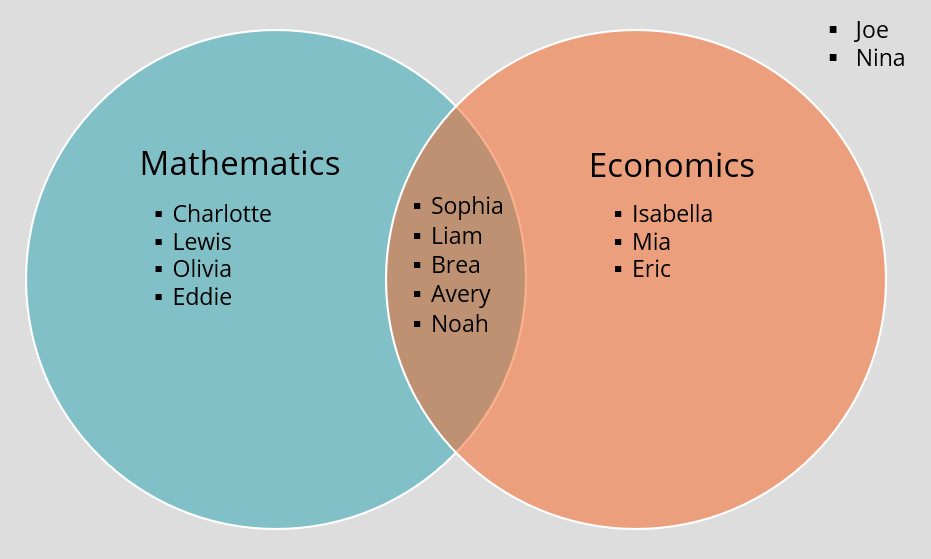
The students showed their preferences by writhing their initial in a portion of the Venn diagram below: "According to the diagram, what is the total number of students who like both math and science?" 2. The following four peoples are waiting in line at the post office:
According to the venn diagram below what is p(a^b^c).
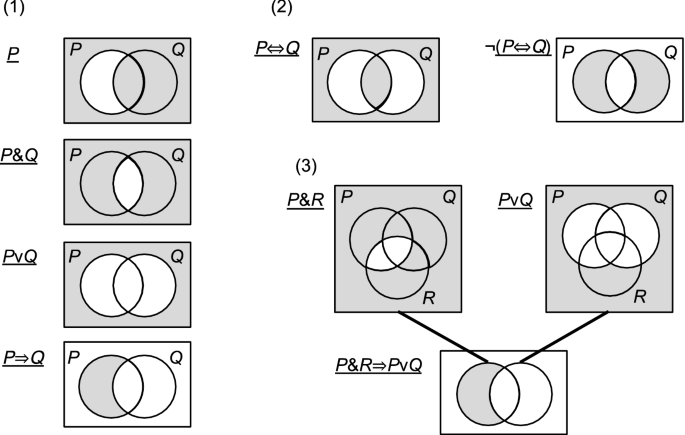
standard Venn diagram shown below. A B U 11. On a Venn diagram, shade the region(s) corresponding to A ∩ B. 12. On a Venn diagram, shade the region(s) corresponding to A ∪ B. 13. On a Venn diagram, shade the region(s) corresponding to A ∪ B′. 14. On a Venn diagram, shade the region(s) corresponding to A ∩ B′. 15.
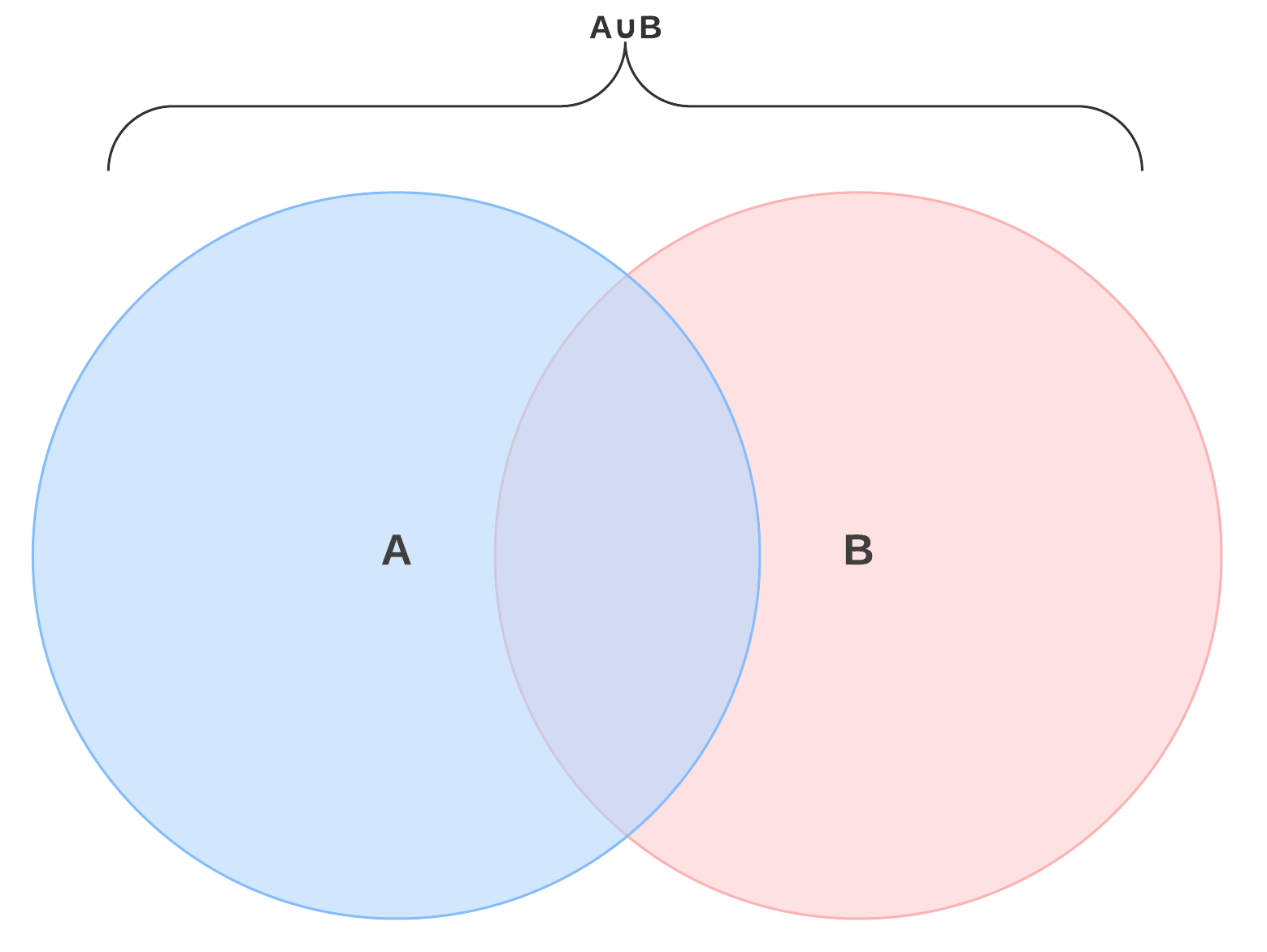
A U B Venn Diagram. The Venn diagram, is a convenient way to illustrate definitions within the algebra From the basic two circle Venn diagram above, it is easy to see that P (AUB). Thus, we conclude from the definition of union of sets that A ⊆ A U B, B ⊆ A U B.
Venn diagrams are used to determine conditional probabilities. The conditional probability is given by the intersections of these sets. Conditional probability is based upon an event A given an event B has already happened: this is written as P(A | B) (probability of A given B).. The probability of A, given B, is the probability of A and B divided by the probability of A:
A Venn diagram is a diagram that helps us visualize the logical relationship between sets and their elements and helps us solve examples based on these sets. A Venn diagram typically uses intersecting and non-intersecting circles (although other closed figures like squares may be used) to denote the relationship between sets.
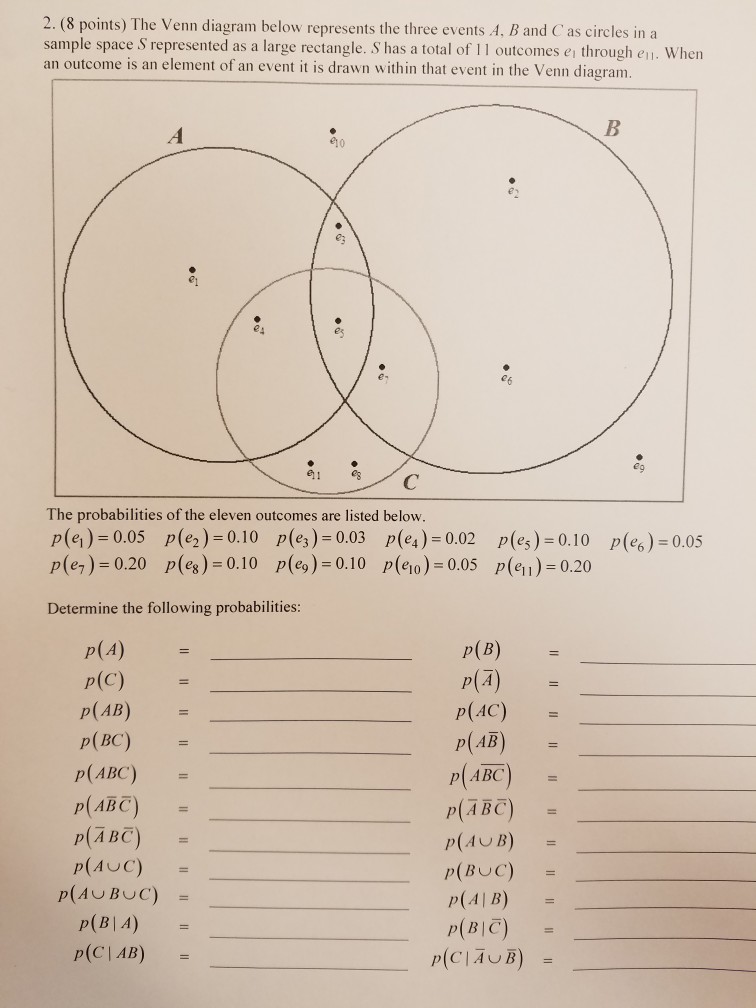
Best Answer. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. As per Venn diagram P (C) +P (A not B nor C) +P (A and B …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 2. Given the sample space and events A, B, and C as defined in the Venn Diagram below. What is the P (B)- (1 p) Not A nor B nor C 0.30 0.20 A and B 0.10 A and not B 0.30 ...
In the following Venn diagram, assume the events A, B, and C are about equally likely Complement Rule The probability that a bag of mixed vegetables selected is underweight, P(A), plus the probability that it is not an underweight bag, written P(∼A) and read "not A," must logically equal 1.
Testing Validity Using Venn's Diagrams. To test the validity of a categorical syllogism, one can use the method of Venn diagrams. Since a categorical syllogism has three terms, we need a Venn diagram using three intersecting circles, one representing each of the three terms in a categorical syllogism.
From the Venn diagram we can see that the probability of the three events together is simply the sum of their individual probabilities. So P ( A or B or C) = P ( A) + P ( B) + P ( C) . This will be true for any mutually exclusive events since they never overlap in the Venn diagram. Try the textbook questions.
Correct answers: 2 question: According to the Venn diagram below, what is P(AU BUC)? A B 10 N 8 8 4 5 6 7 с A. Glasila B. O C. D.
This is represented on a Venn diagram like this: The fact that the two circles do not overlap shows that the two events are mutually exclusive. This means that the probability of A or B happening =...
1.3.6 Solved Problems: Random Experiments and Probabilities. Problem. Consider a sample space S and three events A, B, and C. For each of the following events draw a Venn diagram representation as well as a set expression. Among A, B, and C, only A occurs. At least one of the events A, B, or C occurs. A or C occurs, but not B.
The following diagram shows a board which is divided into three regions \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\). A game consists of a contestant throwing one dart at the board. The probability of hitting each region is given in the following table.
try drawing a Venn diagram of A and B, their intersection will be 0.15, you want to find the probability outside of both circles 1. reply. shanks21 Badges: 2. Rep:? You'll earn badges for being active around the site. Rep gems come when your posts are rated by other community members.
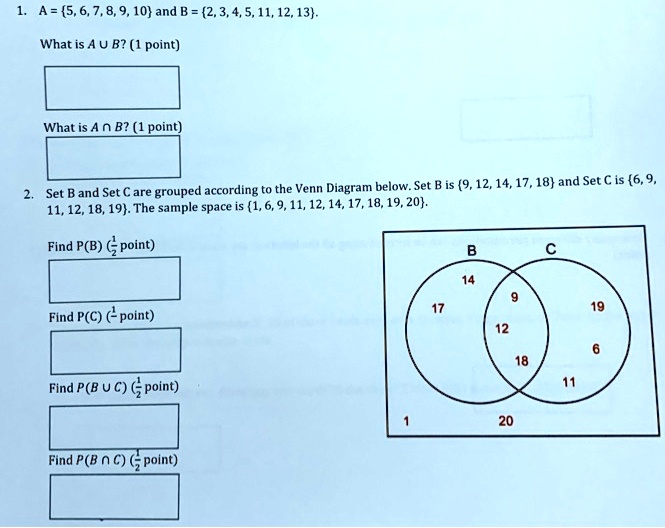
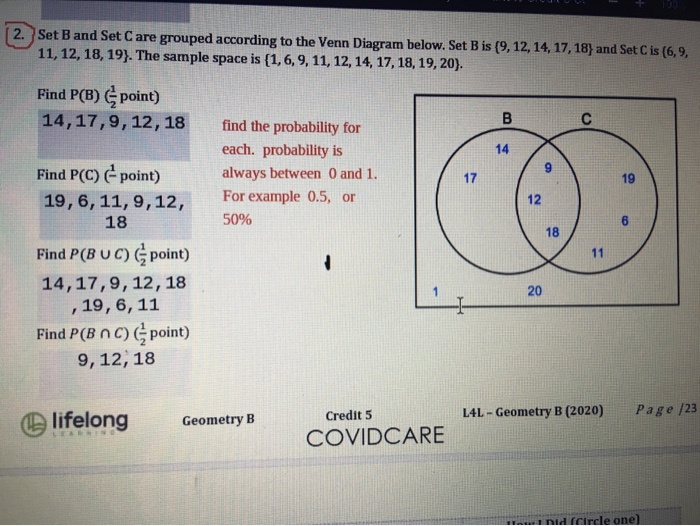
A sample space contains six sample points and events A, B, and C as shown in the Venn diagram. The probablities of the sample points are P(1) = 0:2; P(2) = 0:55; P(3) = 0:05; P(4) = 0:05; P(5)=0:05; P(6)=0:1: Use the Venn diagram and the probabilities of the sample points to find: (a) P(A) = (b) P(AjC) = (c) P(CjA) = Correct Answers: 0.2 0 0.75 2.
Point A is plotted 2 grid lines to the left of the y-axis and 4 grid lines above the axis. Point B is plotted at 1 grid line to the right of the y-axis and 4 grid lines above the x-axis. Point C is plotted at 1 grid line to the left of the y-axis and 4 grid lines below the x-axis.
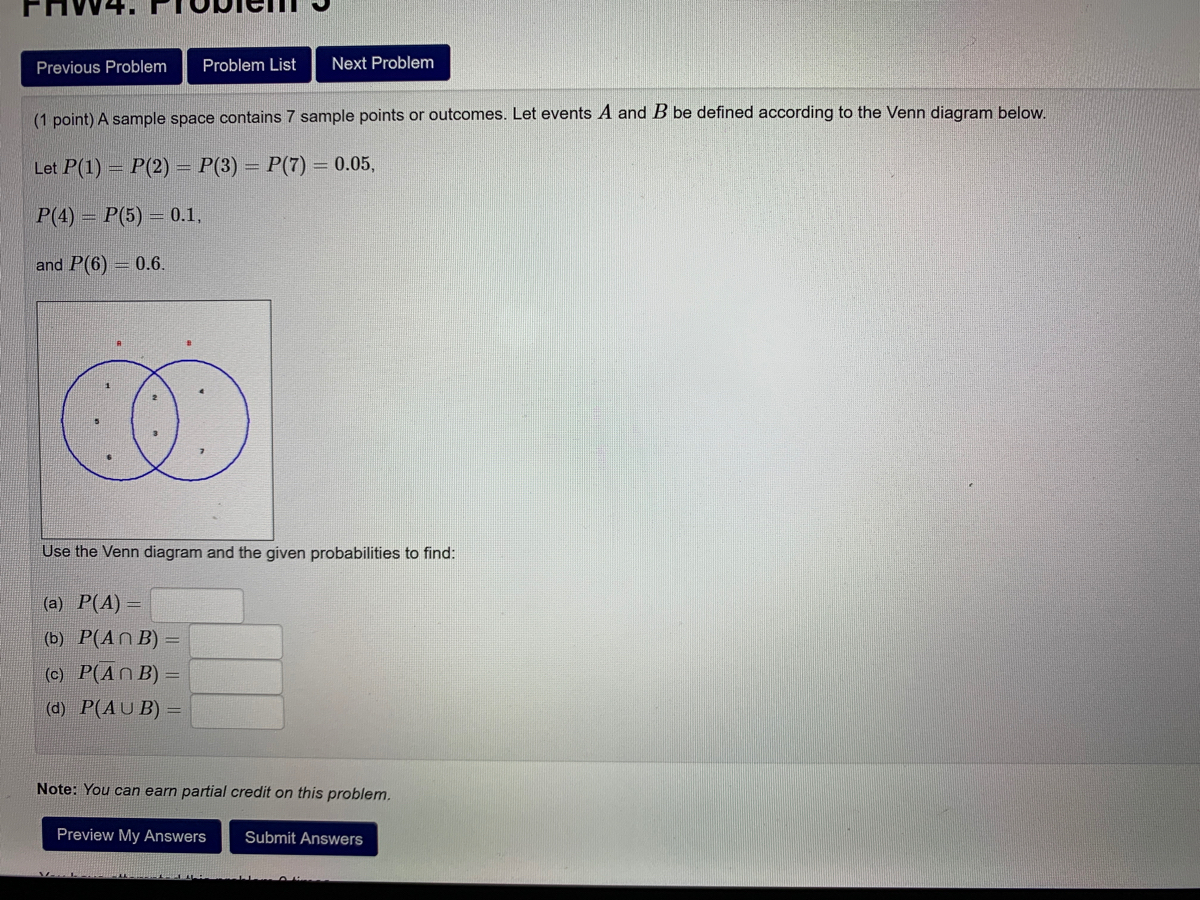
Let events A and B be defined according to the Venn diagram below. Let P(1) P(2) P(3) P(7) 0.1 P(4) P(5) 0.0 and P(6) 0.5. Use the Venn diagram and the given probabilities to find: (a) P(AU B) 0.23 (b) P(An B)0.15 (c) P(A)1-0.85 (d) P(An B)0.2
Venn Diagram Shading Calculator Or Solver. Enter an expression like (A Union B) Intersect (Complement C) to describe a combination of two or three sets and get the notation and Venn diagram. Use parentheses, Union, Intersection, and Complement. Try the free Mathway calculator and problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the ...
P(A and B) = P(both event A occurs and event B occurs) beginning with the multiplication rule for independent events. Using a Venn diagram, we can visualize "A and B," which is represented by the overlap between events A and B:
SOLUTION: according to the Venn diagram below what is p (a b c) a.3/25 b.2/25 c.1/25 d.4/25. Algebra: Probability and statistics. Section. Solvers.
Venn Diagrams We can visual subsets of a universal set, and how they interact/overlap, using Venn diagrams, as shown below. On the left, the brown shaded region is A\B. It is also (A 0[B )0. On the right, the shaded area is A\B.
The union of two sets is represented by ∪. (Don't confuse this symbol with the letter "u.") This is a two-circle Venn diagram. The green circle is A, and the blue circle is B. The complete Venn diagram represents the union of A and B, or A ∪ B. Feel free to click on the image to try this diagram as a template.
A Venn diagram is also called a set diagram or a logic diagram showing different set operations such as the intersection of sets, union of sets and difference of sets. It is also used to depict subsets of a set. For example, a set of natural numbers is a subset of whole numbers, which is a subset of integers.
Consider the following Venn diagram. The probability of \(A\) is the ratio between the number of outcomes in \(A\) and the number of outcomes in the sample space, \(S\). ... According to the definition, events are independent if and only if \[P(A\text{ and }B) = P(A) \times P(B)\] ... = P(A) \times P(B)\). See the exercises below for examples ...





![Solved] Consider the Venn diagram below, whereP(E1) = P(E2) = P(E3 ...](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.question.images/image/images10/766-M-S-P(7224).png)
/VennDiagram1_2-6b1d04d5b6874b4799b1e2f056a15469.png)



/VennDiagram1_2-6b1d04d5b6874b4799b1e2f056a15469.png)











0 Response to "38 according to the venn diagram below what is p(a^b^c)"
Post a Comment