38 ray diagram for nearsightedness
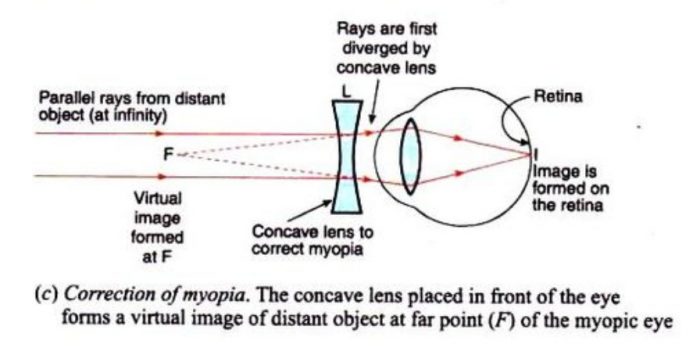
Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people to converge the parallel incoming rays and label where the image will be. Once the ray hits the lens bend it so that it goes directly away from the focal point on the near side of the lens. Nearsightedness and its correction. Since the nature of the problem of nearsightedness is that the light is ... What is the myopia (near sightedness) ? Draw a ray diagram to show how it can be corrected using a lens.Class:10Subject: PHYSICSChapter: THE HUMAN EYE AND CO...
Explain with the help of labelled ray diagram, the defect of vision called myopia and how it is corrected by a lens. asked Aug 30, 2018 in Physics by AbhinavMehra ( 22.5k points) the human eye and the colourful world

Ray diagram for nearsightedness
The power of lenses that correct nearsightedness is measured in units called diopters (D). The lens powers on an eyeglass prescription for myopia always begin with a minus sign. The higher the power number of the lens, the more myopia it corrects. For example, a -6.00 D lens corrects twice the amount of nearsightedness as a -3.00 D lens. Draw ray diagrams each showing (i) myopic eye and (ii) hypermetropic eye. Answer. Verified. 113.1k + views. Hint: Myopia is an eye disorder and commonly known as near-sightedness and it is otherwise known as short-sightedness. In myopia, the affected person can see the close object clearly, but the far object is blurry. A diverging lens ray diagram follows three basic rules: ... Diverging lens for correcting Nearsightedness. Refracting telescopes generally use a convex-concave lens combination to enable magnified viewing of far away objects. The study of the diverging lens has advanced the Optics branch of Physics in a multitude of ways. While it provides an ...
Ray diagram for nearsightedness. If the ray intersects the second medium with an angle of ... Figure 5 shows a schematic diagram of the human eye generated by a computer optics program. This optical model was developed initially by ... There are two main types of ametropia: myopia and hyperopia. Myopia. In the myopic eye, parallel rays come to focus in front of the retina as shown Ray diagrams help you to visualize how the lens bends the light and how your brain understands those light rays, and also to catch mathematical mistakes. In this case, you are able to focus on close objects (highly divergent rays) but not on distant ones (less divergent rays) and so you understand that your eye converges rays too much. Free MCAT Prep App: https://www.medschoolcoach.com/mcat-prep-appKen Tao is the MedSchoolCoach expert on MCAT, and will discuss how myopia is also called near... Nearsightedness and farsightedness are not eye diseases. Instead, they’re called refractive errors — slight abnormalities that affect the eye’s ability to focus light.. After light enters our eye through the pupil, it needs to be neatly focused on a thin layer of tissue in the back of the eye in order for us to see clearly.
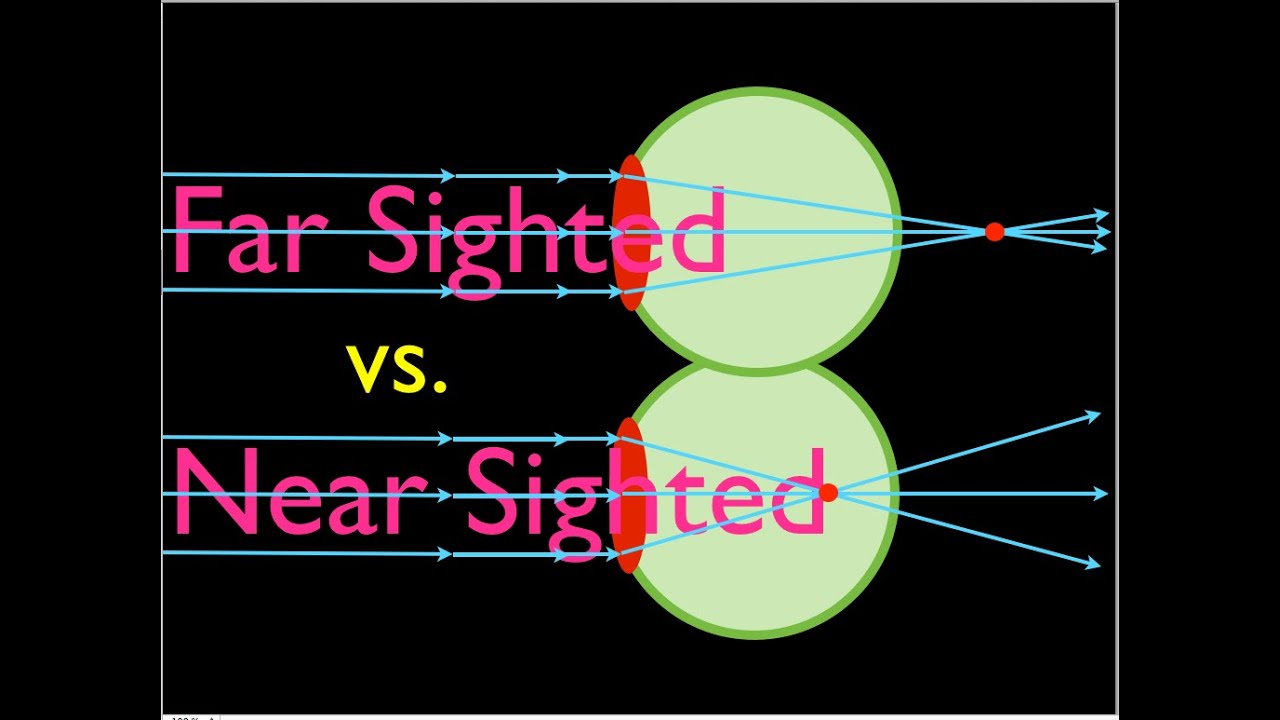
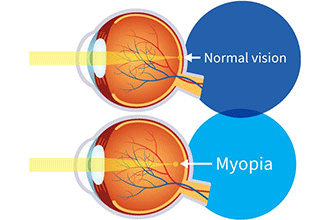
Myopia or Nearsightedness occurs when the eye loses its ability to focus on far-off objects as the lenses do not possess a long focal length. Objects that are near are clearly visible to patients of this defect. As we know, from the reference for countless ray diagrams describing the functioning of the eye, when the light suffers higher ... It's unusual, but a person can indeed be nearsighted in one eye and farsighted in the other. There are two medical terms used to describe this condition: anisometropia and antimetropia. Anisometropia is the condition where the two eyes have significantly different refractive (light-bending) powers. A draw a ray diagram for the following situation an object far from the lens involving a diverging lens. Start studying chapter 30 and 31. Nearsightedness And Its Correction Also draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted people. All of the above the wavy bright and dark lines ... Explain with the help of a labelled ray diagram the defect of myopia and how it is corrected. Hard. Open in App. Solution. Verified by Toppr. Myopia is a defect of vision in which a person clearly sees all the nearby objects, but is unable to see the distinct object comfortably and his eye is known as myopia eye. A myopic eye has its far pint ...
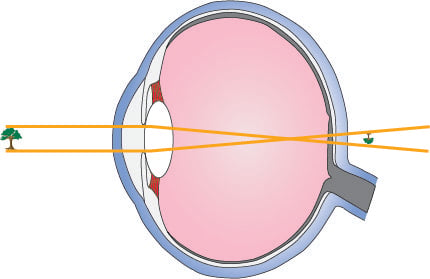
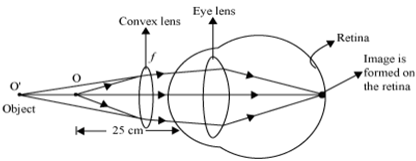
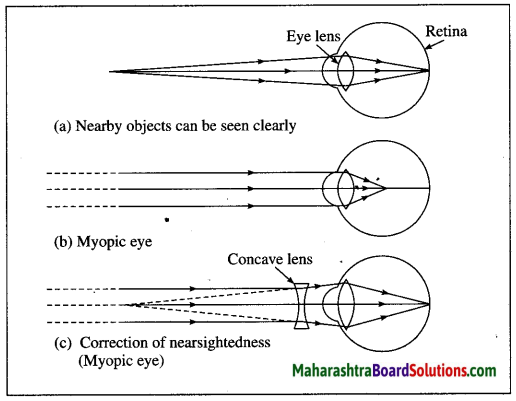
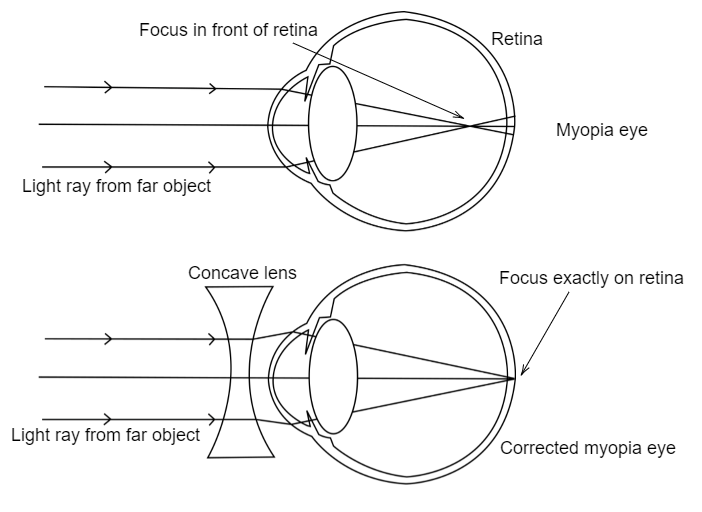
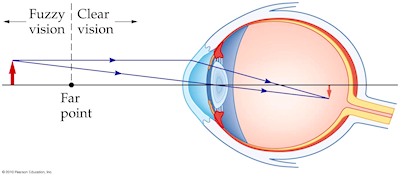
Myopia or shortsightedness: Myopia is the defect of eye in which a person can see only nearby objects, but fails to see the far away objects distinctly. This defect is due to (a) decrease in focal length of the eye lens. (b) spreading of the eye-sphere. Due to these reasons the image is formed in front of the retina. Converging Lenses Ray Diagrams How can 1. Draw the ray diagram for nearsighted. Draw a ray diagram to show a myopic eye. Draw a straight line from the top of your object parallel to the principal axis. The cure for the nearsighted eye is to equip it with a diverging lens. In drawing a ray diagram rays can be drawn. The power of lenses that correct nearsightedness is measured in units called diopters (D). The lens powers on an eyeglass prescription for myopia always begin with a minus sign. The higher the power number of the lens, the more myopia it corrects. For example, a -6.00 D lens corrects twice the amount of nearsightedness as a -3.00 D lens. i) Myopia is also known as near-sightedness. A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see distant objects distinctly. A person with this defect has the far point nearer than infinity. Such a person may see clearly up to a distance of a few meters. In a myopic eye, the image of a distant object is formed in front of the retina and not at the retina itself.
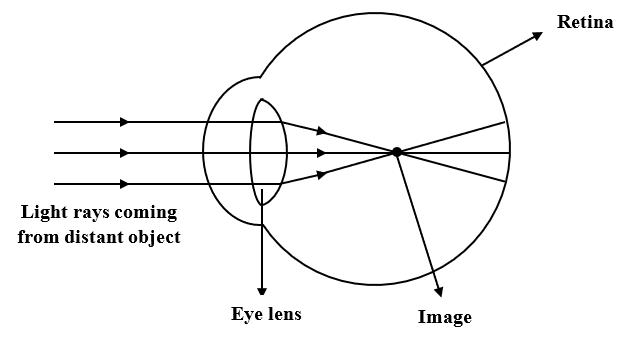
The ray diagram in Figure 16.33 shows image formation by the cornea and lens of the eye. The rays bend according to the refractive indices provided in Table 16.4 . The cornea provides about two-thirds of the magnification of the eye because the speed of light changes considerably while traveling from air into the cornea.
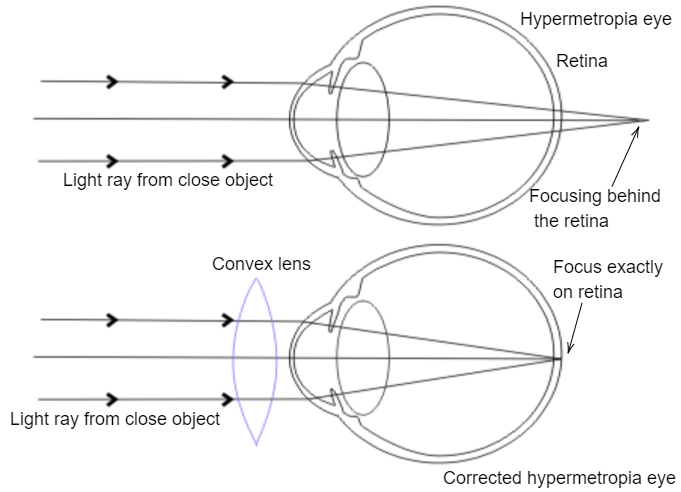
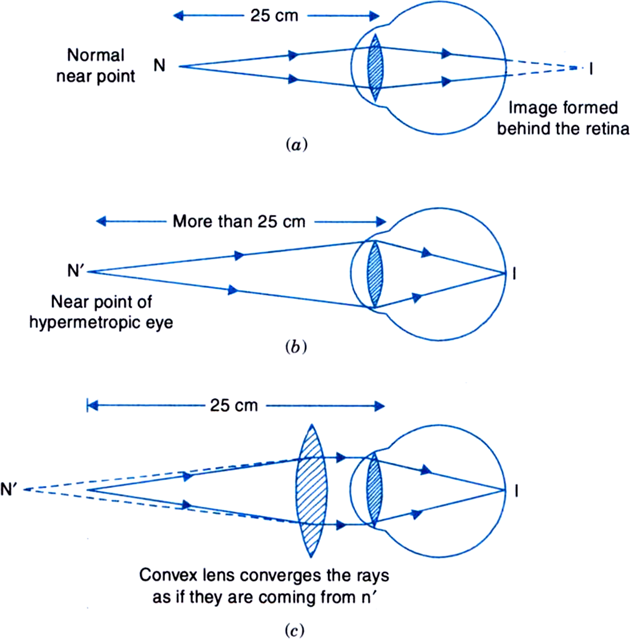
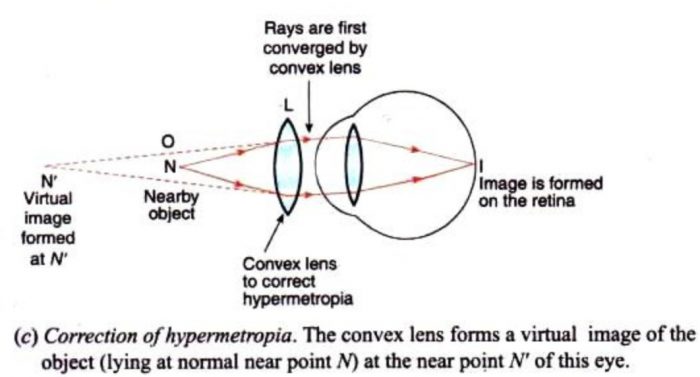
Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect? Assume that the near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.
The word myopia is the name of the condition and the word myopic is used to describe somebody with myopia. I.e., She has myopia, she is myopia. The more commonly used term for myopia is nearsightedness. I.e., She has nearsightedness, she is nearsighted. Here is an example of a ray diagram of myopia:
The above diagram decpicts a cross section of an eye with the focal point forming behind the retina. This is just a helpful way of visualizing hyperopia, but in reality, the focal point never actually has a change to form. The light rays are acutally stopped an absored as soon as they hit the retina.
Nearsighted Eye, Myopia Negative Lens Is Used to Correct Nearsightedness Positive Lens Is Used to Correct Farsightedness How Does a Microscope Work? Used to view small things nearby. Consists of two positive lenses, objective and eyepiece. Final image is magnified and inverted. Ray diagram can be used to illustrate the image formation.
Ques: What is myopia (near-sightedness)? Draw a ray diagram to show how it can be corrected using a lens. (3 Marks) Ans: Myopia is an eye defect in which a person is not able to view objects that are placed at a distance. In this case, the image is formed before the retina. For every myopic eye, there is a fixed far point beyond which a clear ...
In physics, ray diagrams show a ray of light's path from the object emitting light to a mirror, and then to a person's eye. Do this physics lab to learn about ray diagrams and lenses.
To solve ray Diagram questions related to Myopia We use lens equation: 1/f = 1/v - 1/u To correct myopia, a concave lens is used. So, focal length is negative Object distance (u) is taken as infinity (∞) And image distance (v) is person's far point Hypermetropia It is called long sightedness In Hypermetropia
Lenses and ray diagrams. Lenses are precisely shaped pieces of glass that have been developed and used in corrective glasses, telescopes, microscopes, binoculars, and magnifying glasses.
Explain with the help of labelled ray diagram the defect of vision called myopia and how it is corrected by a lens. 0 votes . 2.0k views. asked Aug 6, 2019 in Class X Science by navnit40 Expert (40.5k points) Explain with the help of labelled ray diagram, the defect of vision called myopia and how it is corrected by a lens. the human eyes and ...
Describe with a ray diagram how a person with myopia can be helped by spectacles. Answer. Myopia is also known as nearsightedness, which occurs when the eyeball is too long so it affects how the cornea and lens focus. This causes light rays to focus at a point in front of the retina , rather than directly on its surface. For, the correction of ...
The ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; Snell's law and refraction principles are used to explain a variety of real-world phenomena; refraction principles are combined with ray diagrams to explain why lenses produce images of objects.
Myopia runs in families and will probably start in childhood. Multifocal lens (glasses or contacts) and eye drops such as atropine, pirenzepine gel, or cyclopentolate can help slow the progression.
A diverging lens ray diagram follows three basic rules: ... Diverging lens for correcting Nearsightedness. Refracting telescopes generally use a convex-concave lens combination to enable magnified viewing of far away objects. The study of the diverging lens has advanced the Optics branch of Physics in a multitude of ways. While it provides an ...
Draw ray diagrams each showing (i) myopic eye and (ii) hypermetropic eye. Answer. Verified. 113.1k + views. Hint: Myopia is an eye disorder and commonly known as near-sightedness and it is otherwise known as short-sightedness. In myopia, the affected person can see the close object clearly, but the far object is blurry.
The power of lenses that correct nearsightedness is measured in units called diopters (D). The lens powers on an eyeglass prescription for myopia always begin with a minus sign. The higher the power number of the lens, the more myopia it corrects. For example, a -6.00 D lens corrects twice the amount of nearsightedness as a -3.00 D lens.















0 Response to "38 ray diagram for nearsightedness"
Post a Comment