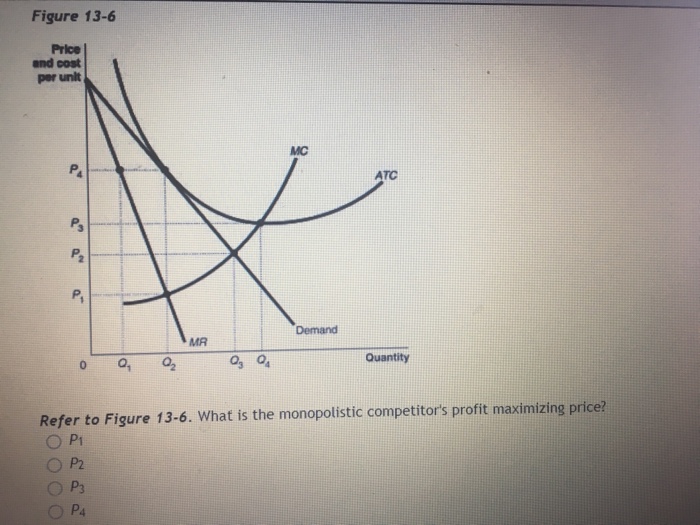
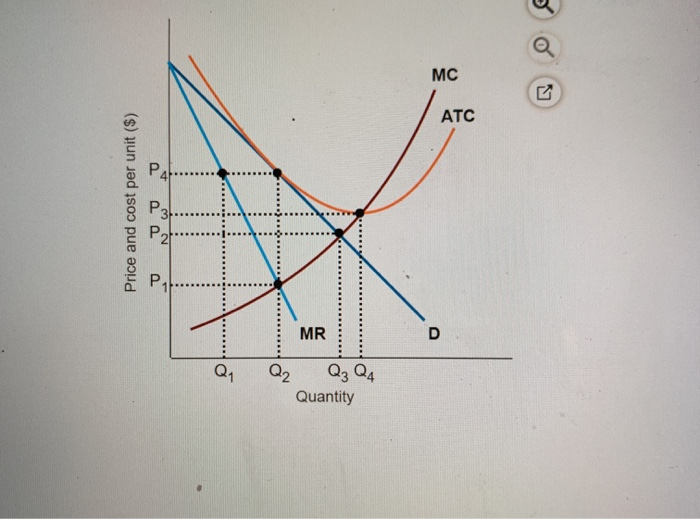
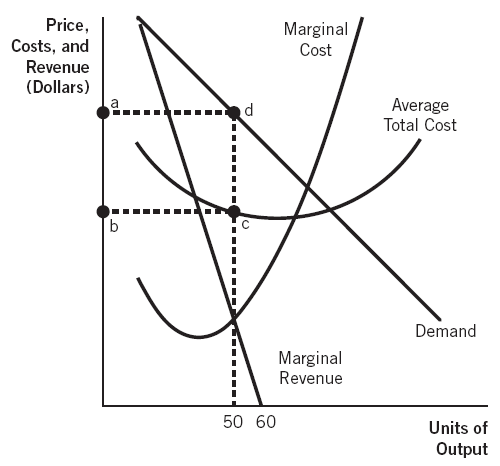
40 refer to the diagram to the right. what is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output?
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A monopolistically competitive industry that earns economic profits in the short run will. A) continue to earn economic profits in the long run. B) experience the exit of old firms out of the industry in the long run.
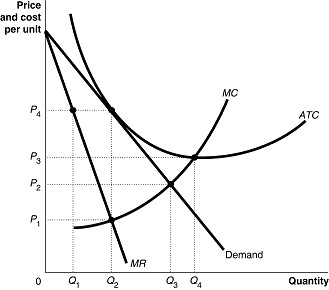
Refer to the diagram to the right which shows short run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches. If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units, what is the price charged?
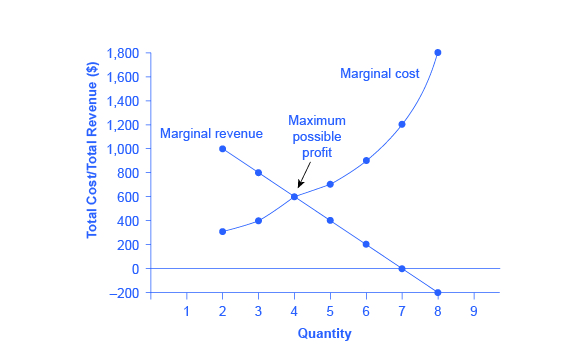
A monopolist produces 14,000 units of output and charges $14 per unit. Its marginal revenue is $8, its marginal cost is $7 and rising, its average total cost is $10, and its average variable cost is $9. The monopolist should. a. increase output, which will result in an increase in the firm's positive economic profit.

Refer to the diagram to the right. what is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output?
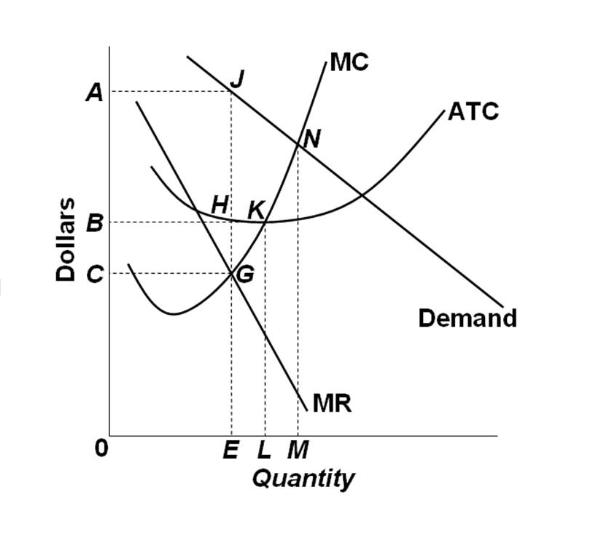
Refer to the diagram to the right. What is the productively efficient output for the firm represented in the diagram? A. Q_1 units B. Q_2 units C. Q_3 units O_4 units ; Question: Refer to the diagram to the right. What is the productively efficient output for the firm represented in the diagram? A. Q_1 units B. Q_2 units C. Q_3 units O_4 units
Each firm chooses the optimal, profit-maximizing output level given the other firm's output. This will result in a Nash Equilibrium, since each firm is holding the behavior of the rival constant. Firm One maximizes profits as follows. max π 1 = TR 1 - TC 1. max π 1 = P(Q)Q 1 - C(Q 1)[price depends on total output Q = Q 1 + Q 2] max π 1 ...
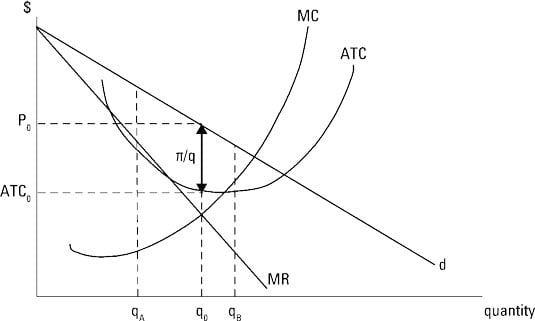
At the profit maximizing quantity of 400, average total cost is $6. This means that the firm is making an economic (above-normal) profit. Average profit is $7 minus $6, or $1. This means that total profit is $400 (400 times $1). Because there are low barriers to entry into monopolistic competition, a firm is not expected to make economic (above ...
Refer to the diagram to the right. what is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output?.
11) Refer to Figure 13-6. What is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing price? 12) Refer to Figure 13-6. The firm represented in the diagram. A) makes zero economic profit. B) makes zero accounting profit. C) should exit the industry. D) should expand its output to take advantage of economies of scale. 13) Refer to Figure 13-6.
21)In monopolistic competition, in the short run a firm maximizes its profit by selecting an output at which marginal cost equals A)price. B)marginal revenue. C)zero. D)average total cost. 21) 22)If a monopolistically competitive firm's marginal cost curve shifts upward, then its level of output A)will decrease.
A) The profit maximizing output is the one at which marginal revenue and marginal cost are equal. B) Average revenue equals price. C) The profit maximizing output is the one at which the difference between total revenue and total cost is largest. D) The monopolist's demand curve is the same as the market demand curve.
firm's profit depends on every firm's actions. Cartel: A cartel is an illegal group of firms acting together to limit output, raise price, and increase profit. Firms in oligopoly face the temptation to form a cartel, but aside from being illegal, cartels often break down. What is Oligopoly? Examples of Oligopoly An HHI that exceeds 1800
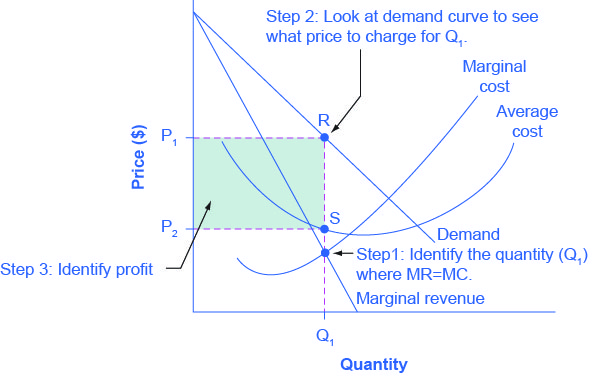
Then the firm decides what price to charge for that quantity. Step 1. The monopolistic competitor determines its profit-maximizing level of output. In this case, the Authentic Chinese Pizza company will determine the profit-maximizing quantity to produce by considering its marginal revenues and marginal costs.
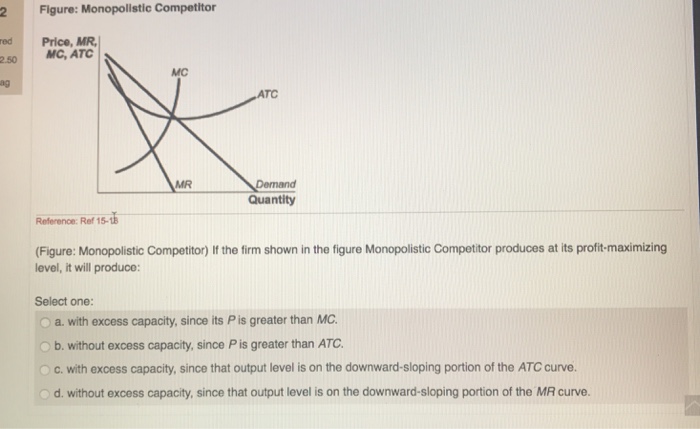
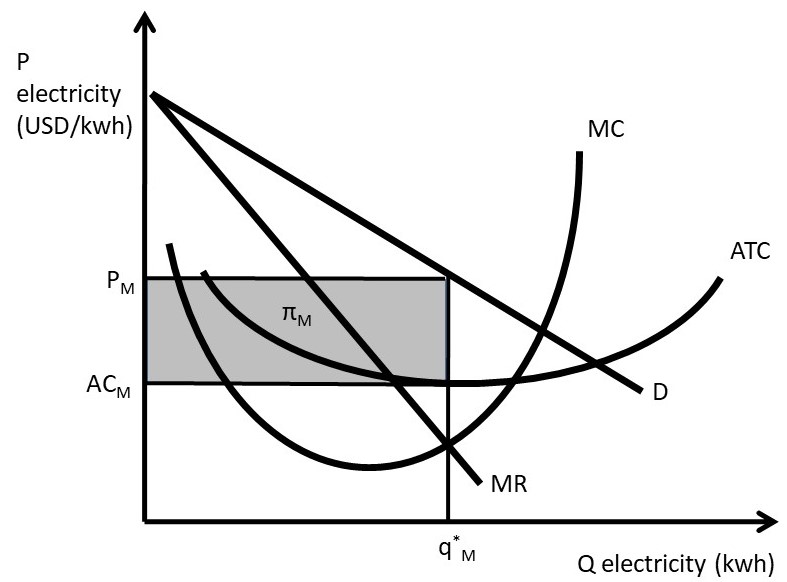
The monopolistically competitive firm's long‐run equilibrium situation is illustrated in Figure .. The entry of new firms leads to an increase in the supply of differentiated products, which causes the firm's market demand curve to shift to the left. As entry into the market increases, the firm's demand curve will continue shifting to the left until it is just tangent to the average total ...
A perfectly competitive firm produces 3,000 units of a good at a total cost of $36,000. The price of each good is $10. Calculate the firm's short run profit or loss. Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the cost and demand curves for a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market.
The level of output that maximizes a monopoly's profit is calculated by equating its marginal cost to its marginal revenue. Key Takeaways A monopolistic market is where one firm produces one product.
Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 13-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules. Refer to Table 13-2. What is the output (Q) that maximizes profit and what is the price (P) charged?
The monopolistic competitor determines its profit-maximizing level of output. … If the firm is producing at a quantity of output where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, then the firm should keep expanding production, because each marginal unit is adding to profit by bringing in more revenue than its cost.
11) Refer to Figure 13 -5. The candy store represented in the diagram is currently selling Q a units of candy at a price of P a . Is this candy store maximizing its profit and if it is not, what would you recommend to the firm? 11) A) Yes, it is maximizing its profit by charging the highest price possible.
monopolistic competitor depends on the number of rival firms and the firm's ability to differentiate its product. • Marginal Revenue Equals Marginal Cost: Monopolistic competition maximizes profit in the short run just as a monopolist does. Profit maximizing quantity is where
Question 1 Refer to the table that shows the demand schedule for a firm that has a monopoly in the sale of personla computers at 2,000.00 Question 2 Refer to the Graph. if this monopolist were forced to set price equal to average cost, i would charge a price of: $2, $3, $8 or $12 Question 3 Refer to the graph.
15) In the short run, for a firm in monopolistic competition, A) the firm's economic profit must equal zero. B) marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost. C) price exceeds marginal cost. D) the firm is a price taker. Answer: C . 16) In monopolistic competition, firms can make an economic profit in . A) the short run and in the long run.
Monopolists: Profit Maximization. An illustration of the monopolistically competitive firm's profit‐maximizing decision is provided in Figure . The firm maximizes its profits by equating marginal cost with marginal revenue. The intersection of the marginal cost and marginal revenue curves determines the firm's equilibrium level of output ...
A) a patent on a firm's product. B) a legal right to position a firm's product in high-traffic public areas such as airports and post offices. C) a distinguishing attribute such as a sign or logo that allows a firm to uniquely identify its product. D) a legal instrument which grants a firm the right to differentiate its product.
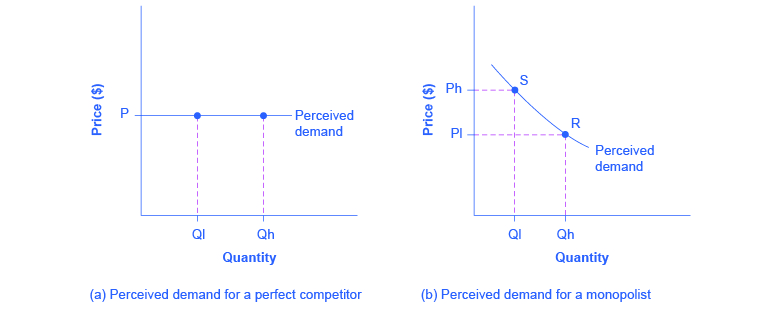
In Step 1, the monopoly chooses the profit-maximizing level of output Q 1, by choosing the quantity where MR = MC. In Step 2, the monopoly decides how much to charge for output level Q 1 by drawing a line straight up from Q 1 to point R on its perceived demand curve. Thus, the monopoly will charge a price (P 1 ).
Refer to the diagram to the right which shows short run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches. If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units, what is the price charged?
A)means that the monopolistic competitor's product is a close but not perfect substitute for the products of its competitors. B)is why a monopolistic competitor faces a downward-sloping demand curve. C)enables the monopolistic competitor to compete in product quality. D)All of the above answers are correct. 4)
First, although both a monopolist and a monopolistic competitor face downward-sloping demand curves, the monopolist’s demand curve is the market demand curve, while the perceived demand curve for a monopolistic competitor is based on the extent of its product differentiation and how many competitors it faces. Second, a monopolist is ...
a highly inelastic demand curve and the monopolistic element from advertising and product promotion. 3. ... Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: ... The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be: A. 210. B. 180. C. 160. D. 100. 6.
a short-run loss. a normal profit. an economic profit. -Consider the diagram below depicting the revenue and cost conditions faced by a monopolistically competitive firm, and then answer the following questions. Image transcription text. $70 $65 MC $60 $55 $50 $45 540 ATC $40 $35 532.50 Price and.




















0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram to the right. what is the monopolistic competitor's profit maximizing output?"
Post a Comment