41 orbital diagram for as
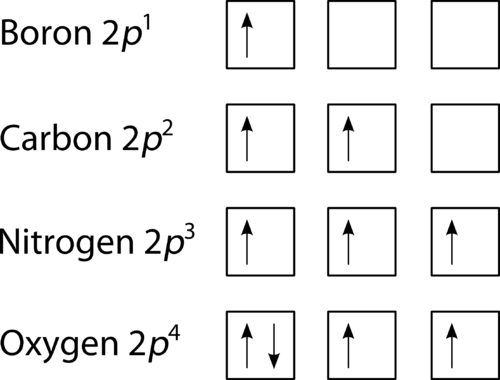
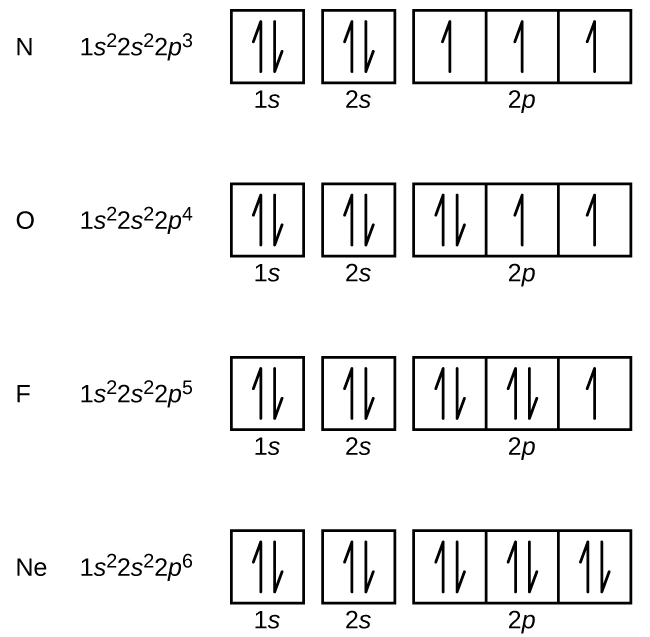
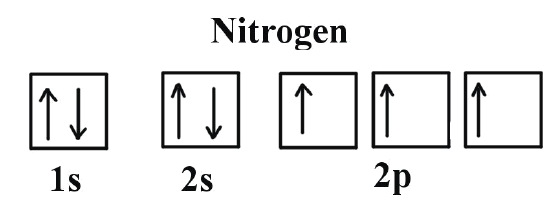
Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8. Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9. Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10. Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11. Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na)
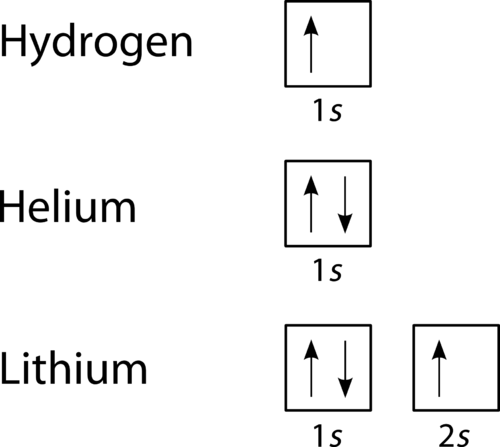
The orbital filling diagram for helium. The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there's a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. This represents the second electron in the 1s orbital, and ...
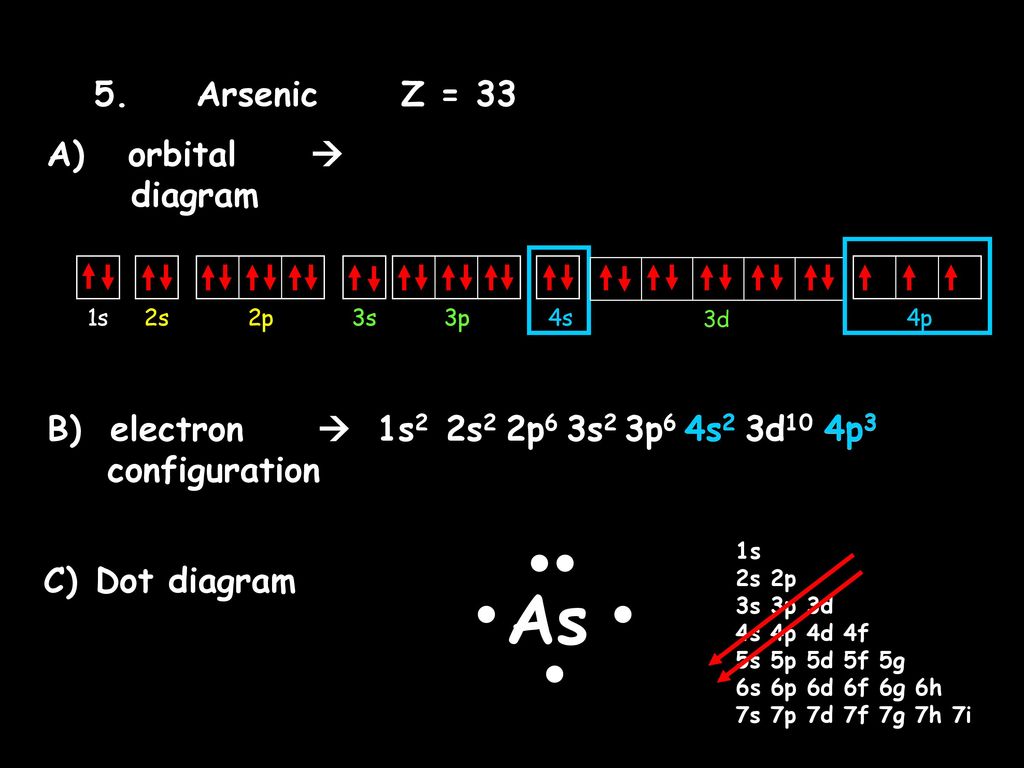
Orbital Diagram For Arsenic. Because the 4p section has 3 orbitals, but Arsenic ends with 4p3. It'll want to leave as few orbitals empty, so you have three arrows pointing up. The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. Arsenic has 33 electrons, including 3 in itsoutermost shell. schematron.org!

Orbital diagram for as
An orbital diagram is similar What is the orbital diagram for. For example, write the electron configuration of scandium, Sc: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 1. So for scandium the 1 st and 2 nd electron must be in 1s orbital, the 3 rd and 4 th in the 2s, the 5 th through 10 th in the 2p orbitals, etc. 6/14/ Ch 8 4/18 Correct Part B Complete ...
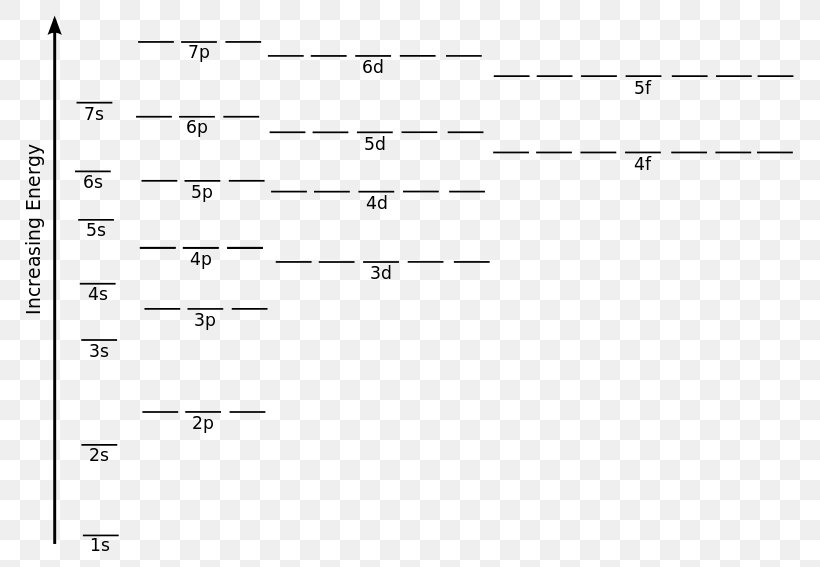
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s → 2s → 2p x 2p y 2p z → 3s → 3p x 3p y 3p z →
January 27, 2021 - Here you can check out the Sulfur Electron Configuration (S) with Orbital Diagram as well as the Valence Electrons of other elements.
Orbital diagram for as.
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Orbital filling diagrams for hydrogen, helium, and lithium. According to the Aufbau process, sublevels and orbitals are filled with electrons in order of increasing energy. Since the \(s\) sublevel consists of just one orbital, the second electron simply pairs up with the first electron as ...
Simple pictures showing orbital shapes are intended to describe the angular forms of regions in space where the electrons occupying the orbital are likely to be found. The diagrams cannot show the entire region where an electron can be found, since according to quantum mechanics there is a non-zero probability of finding the electron (almost ...
An orbital diagram, or orbital filling diagram, is a type of notation which illustrates an atom's electron distribution and electron spin within orbitals.
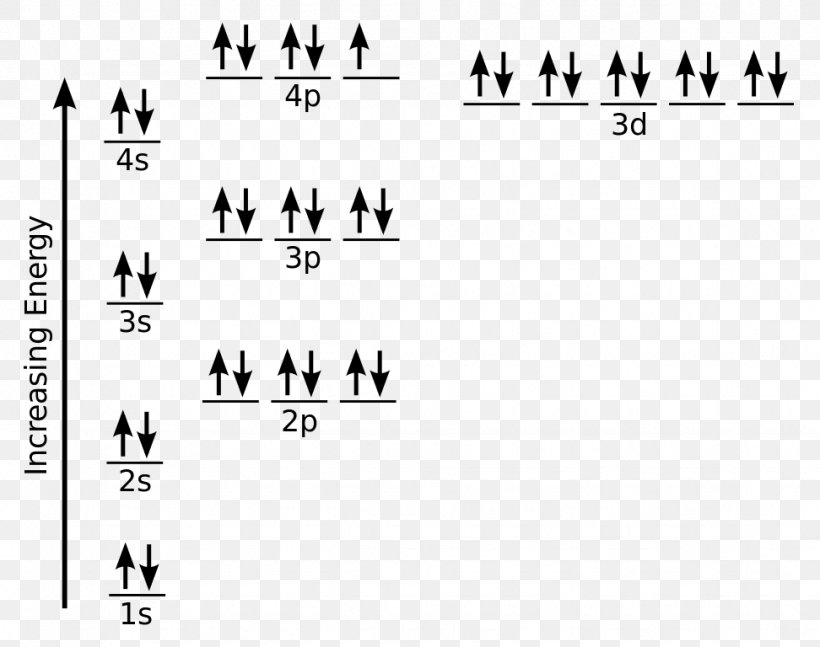
The 1s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2s and then 2p, 3s, and 3p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms.
An orbital diagram is similar to electron configuration, except that instead of indicating the atoms by total numbers, each orbital is shown with up and down arrows to represe nt the electrons in each orbital. Refer to the related link to see an illustration of an orbital diagram for aluminum. Periodic Table of Elements Element Xenon - Xe.
Just as with atomic orbitals, we create an energy-level diagram by listing the molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy. We then fill the orbitals with the required number of valence electrons according to the Pauli principle. This means that each molecular orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins.
Show the orbital-filling diagram for Br (bromine). Stack the subshells in order · This problem has been solved! ... Who are the experts?Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
BISD affirms its commitment to ensure that people with disabilities have an equal opportunity to access online information and functionality. For assistance accessing any online information or functionality that is currently inaccessible, contact Michelle DoPorto, District Webmaster, 817-547-5799, ...
August 21, 2017 - Well, we use the "aufbau principle", and for sulfur, Z=16.... And thus.....1s^(2)2s^(2)2p^(6)3s^(2)3p^4; this distributes the 16 electrons appropriately. Given this configuration, sulfur commonly forms sulphide anion, i.e. S^(2-). Can you give the electronic description for S^(2-). What other ...
Construct the orbital diagram for As. First, we need to determine the electron configuration for As (arsenic). The electron configuration depends on the number of electrons an atom or ion has. Since As is neutral (uncharged), we can say that Z (atomic number) = number of protons = number of electrons. Arsenic has an atomic number of 33, so it ...
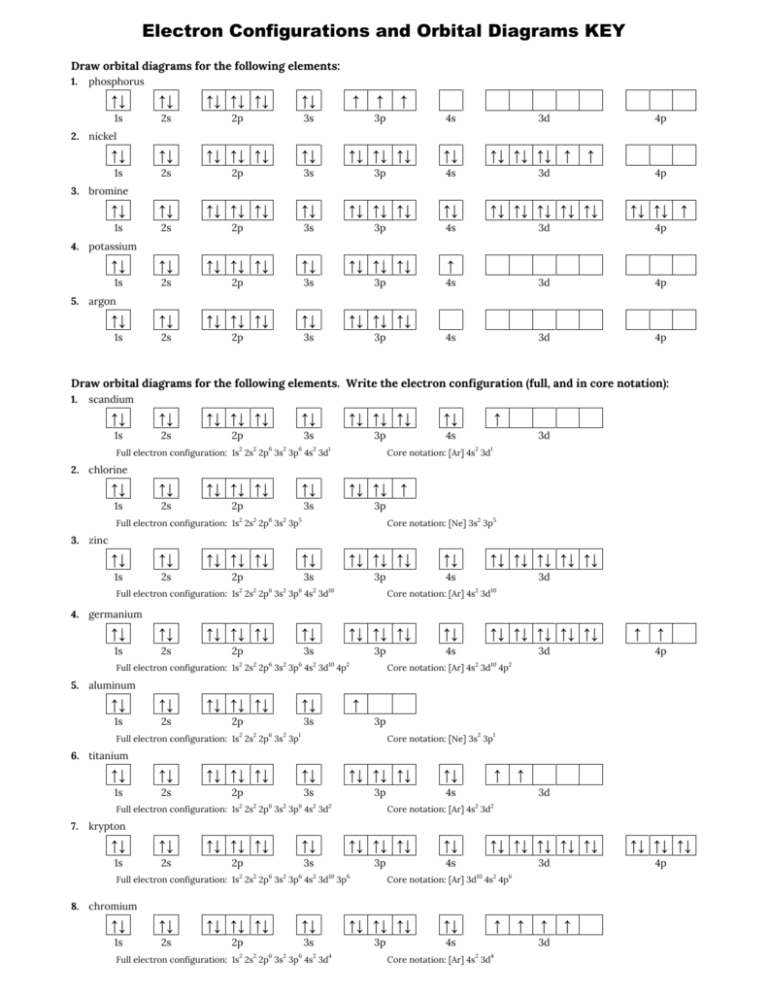
Write the electron configuration for phosphorus and draw the orbital diagram.
The S orbital energies are -22.7 eV (3s) and -11.6 eV (3p); the 1s of H has an energy of -13.6 eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of
How to Write Electron Configurations. Step-by-step tutorial for writing the Electron Configurations.
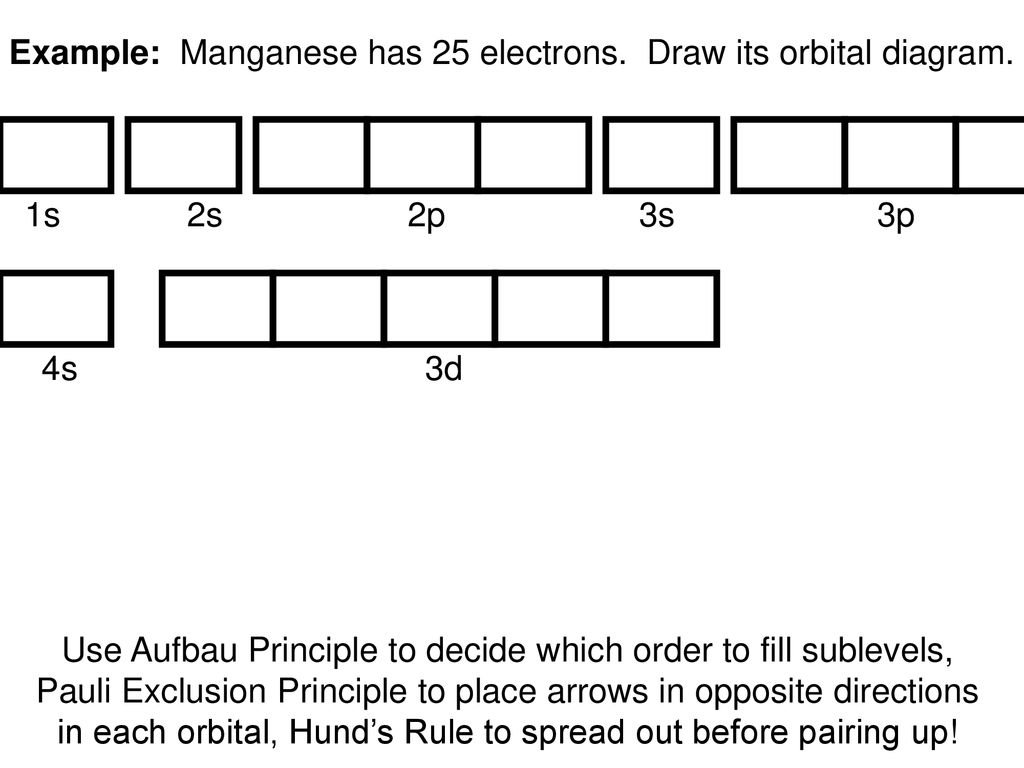
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal –each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for “build up” •Electrons are notated with an arrow –Up arrow goes first then, down arrow –Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
So the electron configuration of potassium will involve 19 electrons. The full electron configuration of potassium is "1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^6"3s"^2"3p"^6"4s"^1". The noble gas notation is "[Ar]4s"^1". The following orbital diagram shows the increase in energy from one energy sublevel to the next, but you can write them on the same level horizontally,
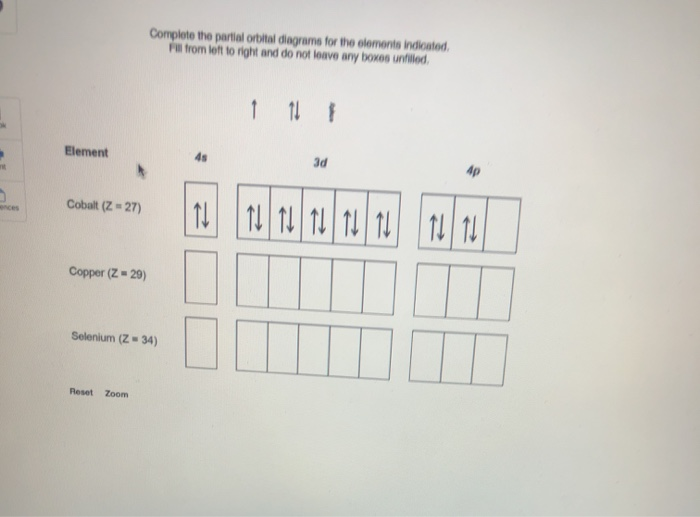
Table 8.3 Partial Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configurations * for the Elements in Period 4. * Colored type indicates the sublevel to which the last electron is added. 8-26. Figure 8.10 A periodic table of partial ground- state electron configurations. 8-27. Figure 8.11.
Molecular-orbital diagrams as obtained by the ROHF method. Dashed lines indicate MOs dominated by the metal d-orbitals, the solid lines stand for doubly occupied or virtual ligand orbitals. Orbitals which are close in energy are presented as degenerate the average deviation from degeneracy is approximately 0.01 a.u.
To see this video, other videos, chemistry education text, and practice problems visit my website. Website is 100% FREE to use. http://scientifictutor.org/
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
What is the correct orbital diagram for arsenic? Electrons & Oxidation. Oxidation States. ±3,+5. Electrons Per Shell. 2 8 18 5. Electron Configuration. [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3.
Oxidation States, ±3,+5. Electrons Per Shell, 2 8 18 5. Electron Configuration, [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p3. Orbital Diagram.Atomic Number: 33Atomic Weight: 74.9216 Isotopes
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...
Orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom. In order to figure out where electrons go in an atom we have to follow 3 main rules. The first one being the Auf Bau Principle, the Auf Bau Principle states that each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available. Then we have to think okay with the sublevels, I mean ...
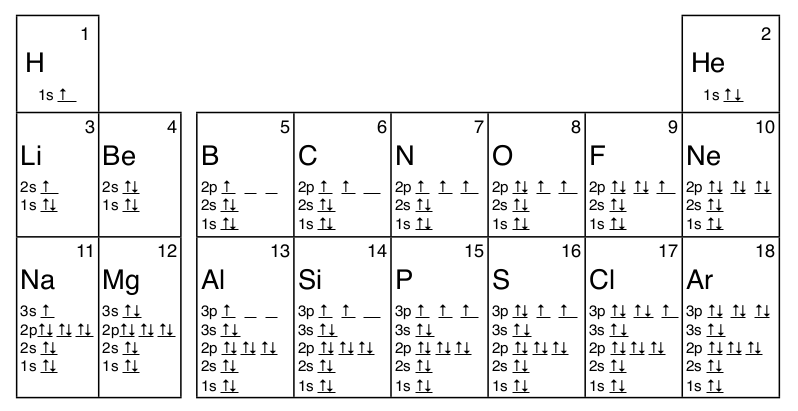
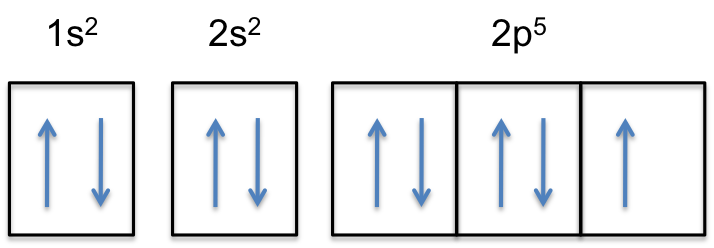
An orbital box diagram can be written as well. Boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin-one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing down. The orbital box diagrams are listed for the first 20 elements in the figure below.
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
What does an orbital diagram tell about a given element? An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally.
What is an orbital energy diagram? Orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom. In order to figure out where electrons go in an atom we have to follow 3 main rules. The first one being the Auf Bau Principle, the Auf Bau Principle states that each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available.
The orbital diagram for hydrogen can be represented in the following way. This notation uses a box to represent the orbital, the label for the orbital and an arrow to represent the electron. The electronic configuration for hydrogen can be written as 1s 1. This is a short-hand notation which identifies the level, the sublevel and the number of ...
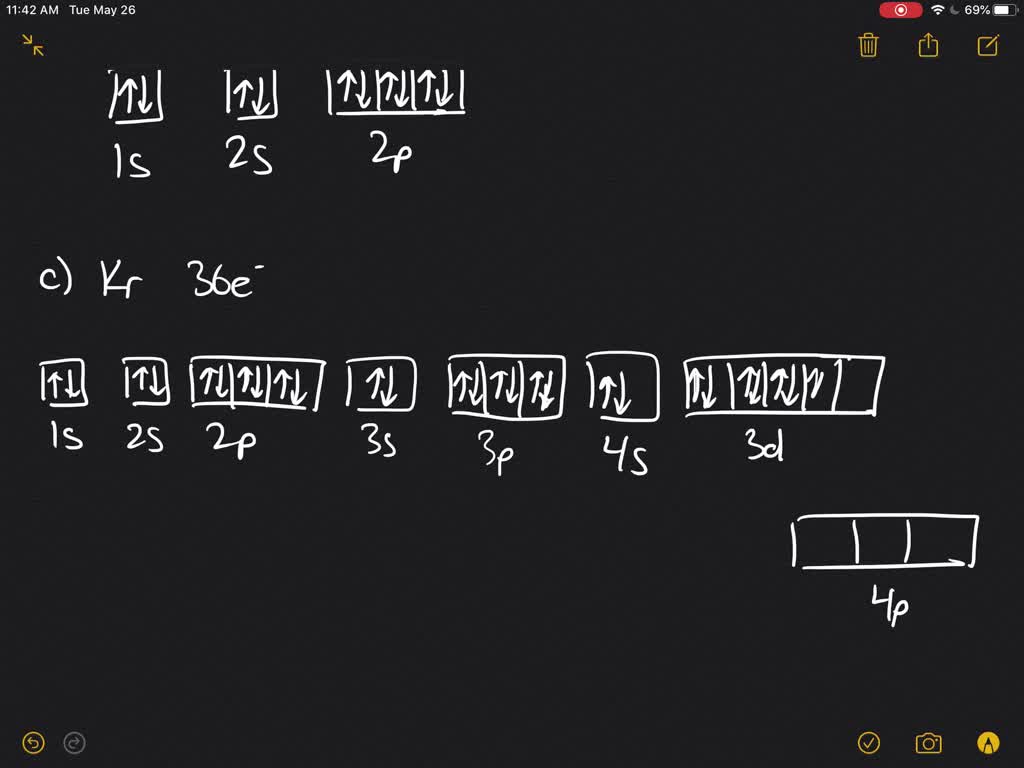
Write the complete orbital diagram for each of the following elements using boxes to represent orb 2
Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau...
This is a test designed to evaluate students skills with orbital diagrams and electron configurations. It is all editable and is broken down in the following way:Part 1: Orbital Diagrams- Correct/Incorrect, explain why it may be incorrect, then draw correct diagram.- Create diagrams based off given
Find expert-verified textbook solutions to your hardest problems. Our library has millions of answers from thousands of the most-used textbooks. We’ll break it down so you can move forward with confidence.
Steps to Draw Hybrid Orbital Diagrams for a Molecule. Step 1: Read through the provided information, and sketch the Lewis dot diagram of the provided compound. Step 2: Determine the steric number ...
An orbital diagram, or orbital filling diagram, is a type of notation which illustrates an atom's electron distribution and electron spin within orbitals.
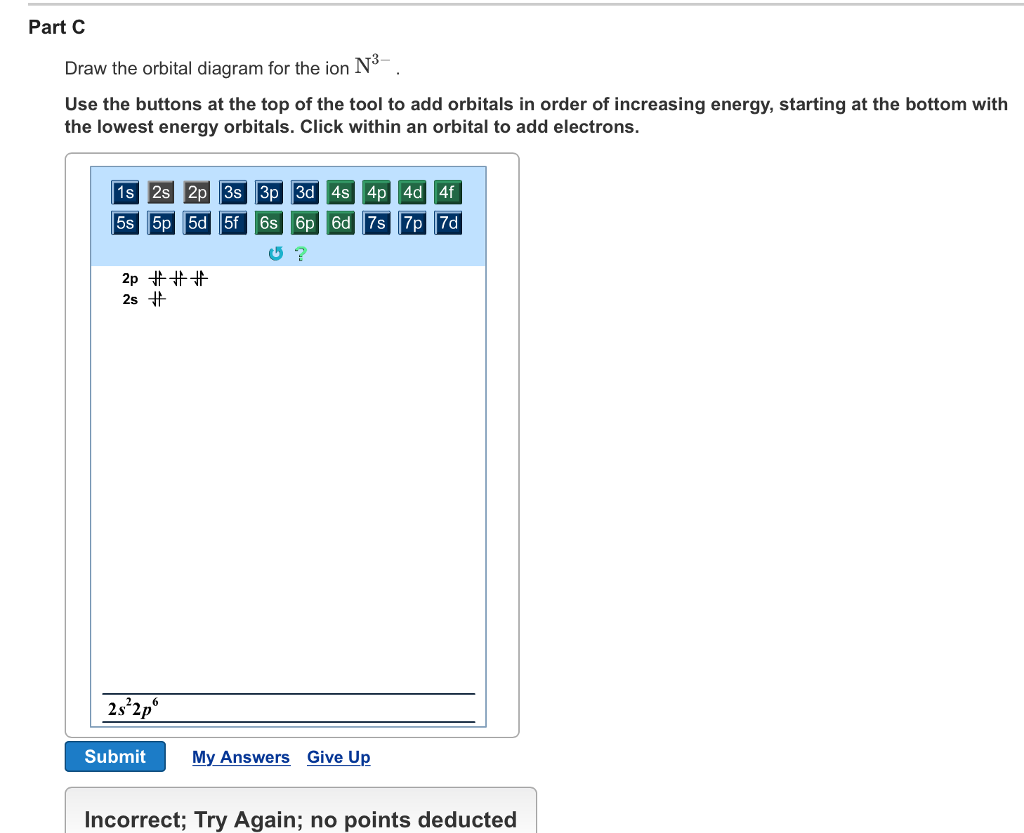
Part C Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s22s22p1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As).
Molecular orbital diagrams are complex, involving two additional orbitals, electronegativity, atomic symmetries and atomic energies. Although more complex, these diagrams reveal a more realistic case for bonding, allowing electrons to travel about a molecule, rather than in between one.
Answer (1 of 3): Orbital Diagrams Many times it is necessary to see all the quantum numbers in an electron configuration, this the purpose of the orbital diagram. In addition to listing the principle quantum number, n, and the subshell, ℓℓ, the orbital diagram shows all the different orientation...
February 3, 2019 - Before you look at the next section, why don't you try to draw the orbital diagrams for the atoms in each Period first, then compare your orbital diagrams with the orbital diagrams below. If your orbital diagram is not the same as the one given below, read through the explanation and try again.
The electron configuration for oxygen is: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^4 This video will walk you through the step of writing orbital diagram. The video uses Kr as an example, but the process is exactly as the same as what you need to do for oxygen. Hope this helps!
November 7, 2021 - In addition to listing the principle quantum number, n, and the subshell, \(\ell\), the orbital diagram shows all the different orientations and the spin of every electron. The diagram shows the number of subshell by using boxes or lines for electrons (use three for p-orbitals, five for d-orbitals, ...












![Molecular orbital diagram of [Co(salen)] À , [Co(salen)-CO 2 ...](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334704704/figure/fig4/AS:784907114672129@1564147847056/Molecular-orbital-diagram-of-Cosalen-A-Cosalen-CO-2-A-and-CO-2-The-figure.png)








0 Response to "41 orbital diagram for as"
Post a Comment