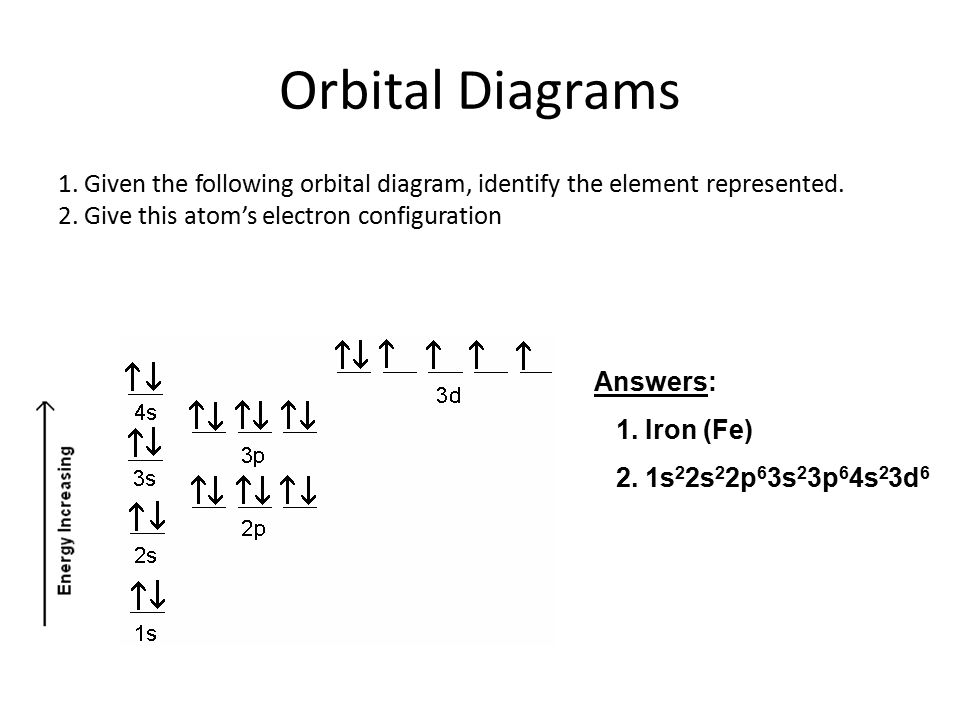
42 orbital diagram for iron
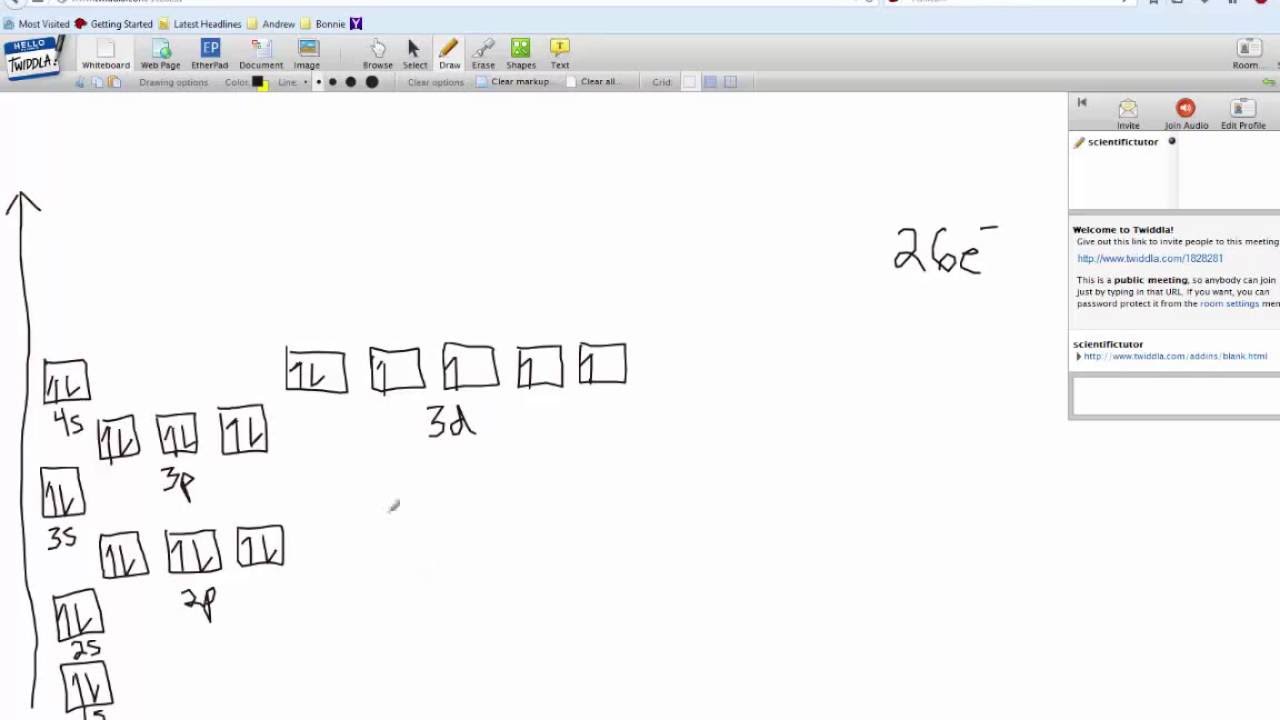
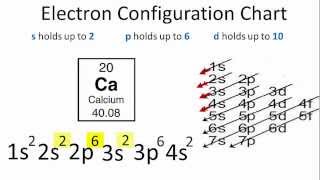
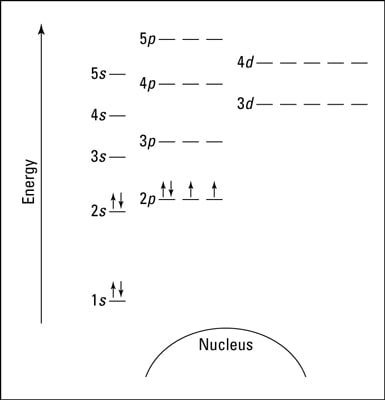
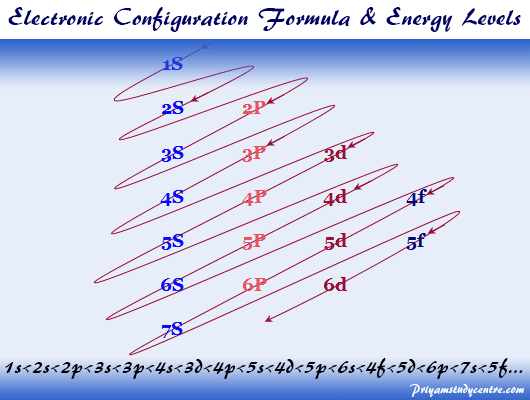
Okay let's do the orbital diagram for iron, iron we know is on its ground state of 26 electrons, so we know the first electrons are going to go into the 1s orbital and we said 2 electrons can fall into the 1s orbital. After the 1s orbital is a 2s, 2 electrons are going to go in there as well, then you have the 2p and don't forget the p ... From the periodic table, iron has atomic number 26 , meaning that there are 26 electrons in each ground state iron atom. 2⋅5=10 electron in each d orbital, and so on so forth. Electron orbitals fill according to the Aufbau (Build-up) Principle.
(In other iron-based superconductors, AFe 2 As 2 systems (A = Ba, Sr, and Ca), the phase diagrams and T c have been investigated from the viewpoints of local structural parameters and carrier ...

Orbital diagram for iron
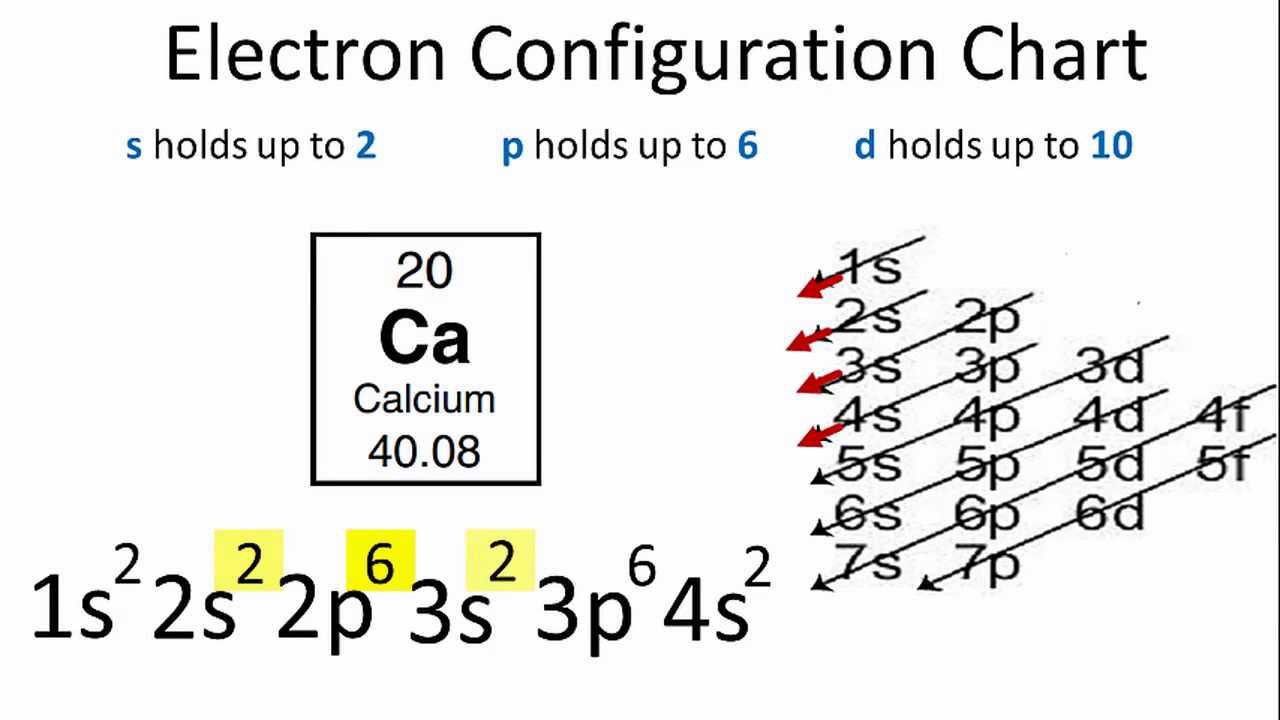
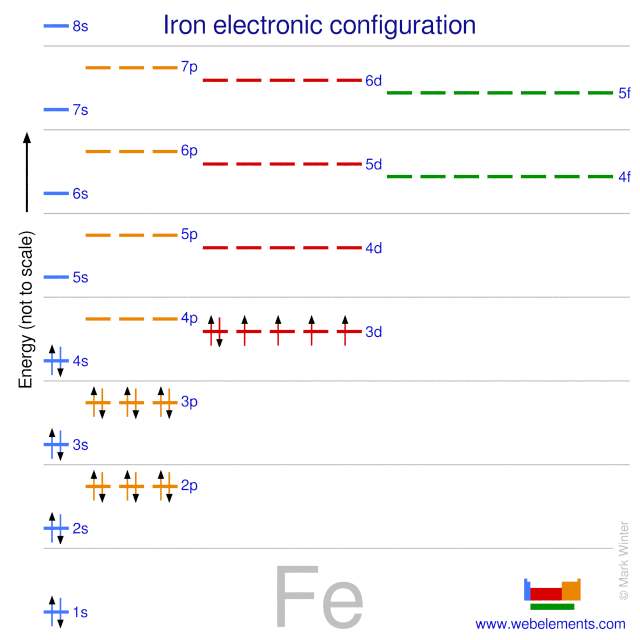
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics. Fe or iron has the atomic number of 26. Its full orbital diagram is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6. We have chosen to show the full unabbreviated configurations to provide more practice for students who want it but listing the core abbreviated electron configurations is also. An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. →. 2s.
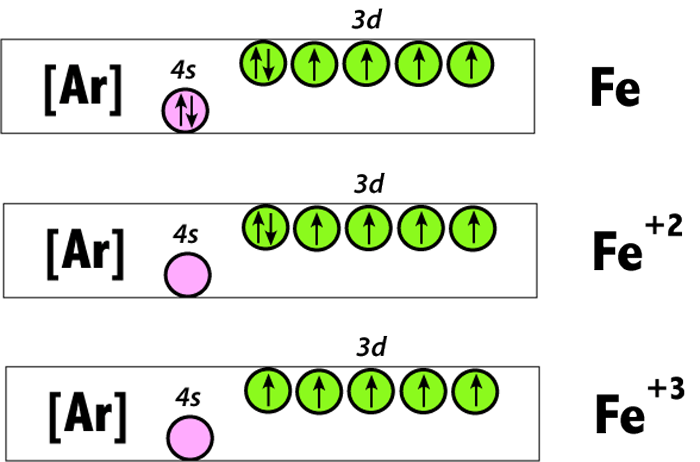
Orbital diagram for iron. Example: Constructing MOs for Titanium Tetraiso propoxide, Ti(OiPr) pp , 4 • The OiiPrSALCs are compridised of fill dfilled p d bit l th O t x an p y orbitals on e a oms. • Ti bonding AOs E: (3dz 2, 3dx2‐y ) T 2: (4p x , 4p y, 4p z) (3dxy, 3dxz, 3dyz) • The T 1 SALC is non‐bonding. • Significant overlap occurs between the E SALC 2and the e AOs on Ti (3dz2, 3dx2‐y ) Chemistry questions and answers. 10. Write the electron configuration and draw the orbital diagram for iron (Fe), atomic number 26. Use the Noble core abbreviation. Electron Configuration of neutral iron: Orbital Diagram: Write the electron configuration and draw the orbital diagram for the chloride ion, (CI+), atomic number 17. Iron has 26 electrons so its normal electron configuration would be: Fe 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6. When we make a 3+ ion for Iron, ... Orbital Diagrams. Another way to represent the order of fill for an atom is by using an orbital diagram often referred to as "the little boxes": Transition Fe3+ ions and draw the orbital box diagrams for both ions. Using this. There for 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 is the electronic configration for Fe3+. half of electrons (there must be one electron in each orbital, and d has 5 orbitals). That's for filling up orbitals for ground state atoms.
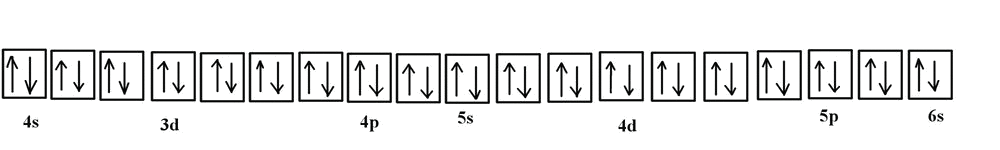
Fe orbital Diagram. what is the orbital diagram for fe answers fe or iron has the atomic number of 26 its full orbital diagramis 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 electron configuration orbital diagram iron electron configuration orbital diagram iron how to write electron configurations and orbital diagrams duration fe fe2 & fe3 Orbital diagram of Iron (Fe) 27: Orbital diagram of Cobalt (Co) 28: Orbital diagram of Nickel (Ni) 29: Orbital diagram of Copper (Cu) 30: Orbital diagram of Zinc (Zn) 31: Orbital diagram of Gallium (Ga) 32: Orbital diagram of Germanium (Ge) 33: Orbital diagram of Arsenic (As) 34: Orbital diagram of Selenium (Se) 35: Orbital diagram of Bromine ... An orbital box diagram can be written as well. Boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin-one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing down. The orbital box diagrams are listed for the first 20 elements in the figure below. After the 4s is full we put the remaining six electrons in the 3d orbital and end with 3d6. Therefore the Iron electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6. Note that when writing the electron configuration for an atom like Fe, the 3d is usually written before the 4s. Both of the configurations have the correct numbers of ...
Orbital Notation for Iron (Fe). Mr. Causey shows you step by step how to write the orbital notation for iron (Fe).http://yourCHEMcoach.comSUBSCRIBE for more ... Electron configurations and orbital diagrams can be determined by applying For example, gallium (Ga, atomic number 31) has the electron.Write the electron configuration and draw an orbital diagram, showing the electrons and labeling the sublevels for each of the following elements. ... Iron 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 4. Titanium 1s2 2s2 2p6 ... Orbital Diagram for Iron. what is the orbital diagram of iron answers iron has an atomic number of 26 the orbital diagram for its shellsis 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6 electron orbital diagram for iron 56 mr gerbe goes over the electron orbital diagram for iron 56. Write the complete orbital configuration for iron (Fe). Orbital Configuration: Orbital configuration is the arrangement of electrons present in the atomic structure.
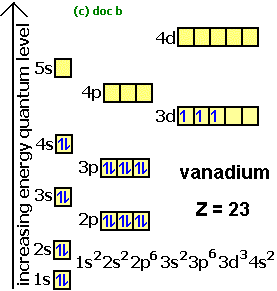
Each orbital holds 2 electrons. Next element is vanadium so we do the same thing. Construct the orbital diagram (using the arrow-in-box notation) for iron, showing the electrons in the and energy levels only and label each sub-level on the diagram. For the last three lines, it is arrow pointing up (line 1) arrow pointing up (line 2) and arrow pointing up (line 3).
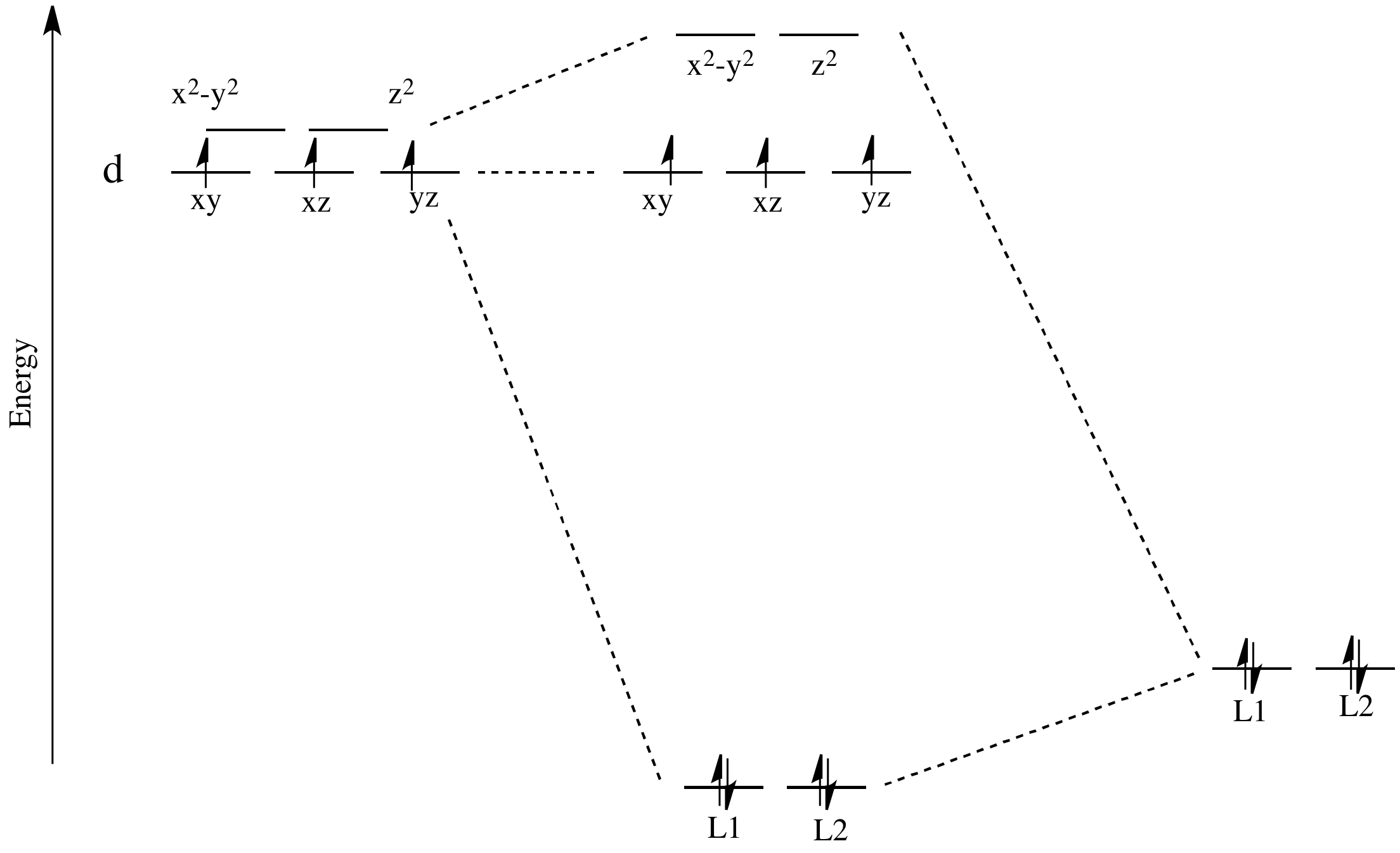
The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for σ-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Figure 10. The formation of σ-molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding and non-bonding) in octahedral complexes of transition metals. Buy the complete book with TOC navigation,
1g SALC orbital can in theory overlap with the Fe 4s and 3dz2orbitals as they are also of a 1g symmetry. This interaction gives rise to the bonding and anti‐bonding molllecularorbi lbitalsof thecomplex a d * il 1g an a 1g * respectively. • Each combination of ligand molecular orbitals and metal molecular orbitals leads to a bonding ...
To see this video, other videos, chemistry education text, and practice problems visit my website. Website is 100% FREE to use.http://scientifictutor.org/
Below are partial MO diagrams for metal-ligand -bonding in Oh. The orbitals responsible for -bonding are not shown. The energy scale is expanded relative to the -complex MO diagram. Determine which diagram is for the -donor and -acceptor cases. Label the MOs with the appropriate symmetry labels and the o.
Fe2+ Orbital Diagram. For midterm question Q5C, why the electron configuration for Fe2+ is not [Ar]3d^5 4S^1? The outermost shell, in this case, is the 4s orbital. You're removing 2 electrons from it to generate the Fe2+ ion, which are removed from the 4s orbital first (this is always the case in transition chemistry - as far as.
Orbital Diagram. 1s ... Obtained from iron ores. Pure metal produced in blast furnaces by layering limestone, coke and iron ore and forcing hot gasses into the bottom. This heats the coke red hot and the iron is reduced from its oxides and liquified where it flows to the bottom
Iron is on the fourth row of the periodic table, sixth column of the transition metals, atomic number 26. What we have is: Its core orbitals are the 1s, 2s, 2p's, 3s, and 3p's. Its valence orbitals are the 4s and 3d's. Writing the electron configuration, you really only need the valence orbitals, and you can omit the core orbitals by notating it via the noble gas shortcut.
Iron has an atomic number of 26. The orbital diagram for its shells is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6.
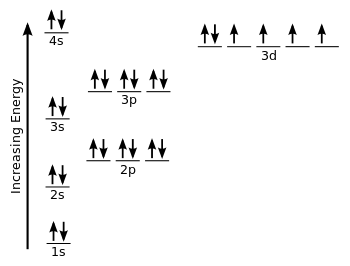
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history ...
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. →. 2s.
Fe or iron has the atomic number of 26. Its full orbital diagram is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6. We have chosen to show the full unabbreviated configurations to provide more practice for students who want it but listing the core abbreviated electron configurations is also.
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
















/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)

0 Response to "42 orbital diagram for iron"
Post a Comment