38 refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is
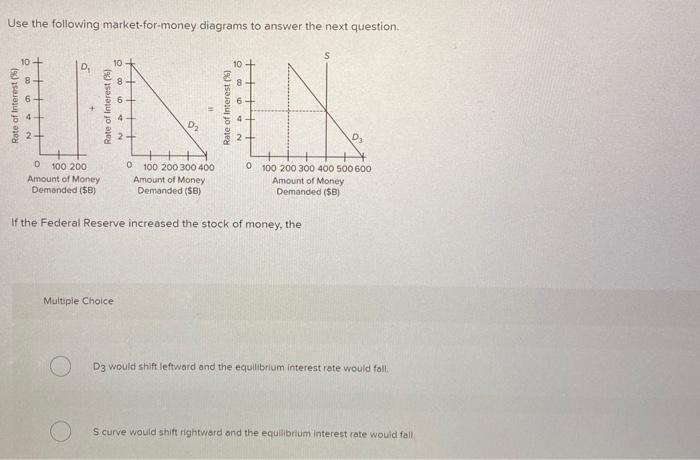
Refer to the above market for money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the: S curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. D 3 would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. May 08, 2019 · Economics questions and answers. 27) 2 Quantity of Money Refer to the diagram of the market for money. The equilibrium interest rate is A) /3. C) /2. D) not determinable without additional information. 28) Which of the following is an asset on the consolidated balance sheet of the Federal Reserve Banks?
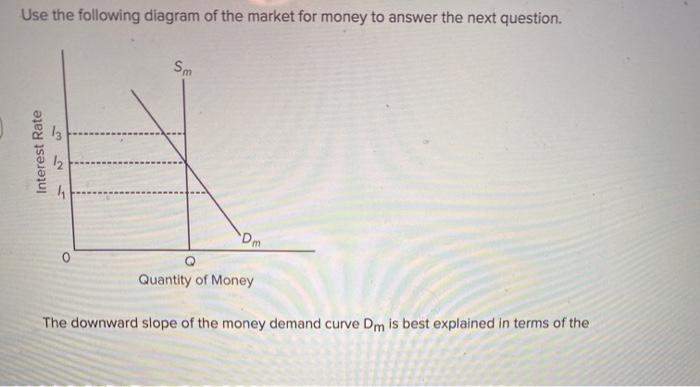
Refer to the diagram of the market for money. The vertical money supply curve Sm reflects the fact that: the stock of money is determined by the Federal Reserve System and does not change when the interest rate changes.

Refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is
Refer to the diagram of the market for money. Given Dm and Sm, an interest rate of I3 is not sustainable because the: demand for bonds in the bond market will rise and the interest rate will fall. The real money demand function with GNP level Y $ 1 intersects with real money supply at point G 1 in the money market diagram determining the interest rate i $ 1. The interest rate in turn determines RoR $ 1, which intersects with RoR £ at point G 2, determining the equilibrium exchange rate E $/£ 1. Figure 15-8 Effect on the Dollar/Euro Exchange Rate and Dollar Interest Rate of an Increase in the U.S. Money Supply Given and when the money supply rises from to the dollar interest rate declines (as money market equilibrium is reestablished at point 2) and the dollar depreciates against the euro (as foreign exchange market equilibrium is ...
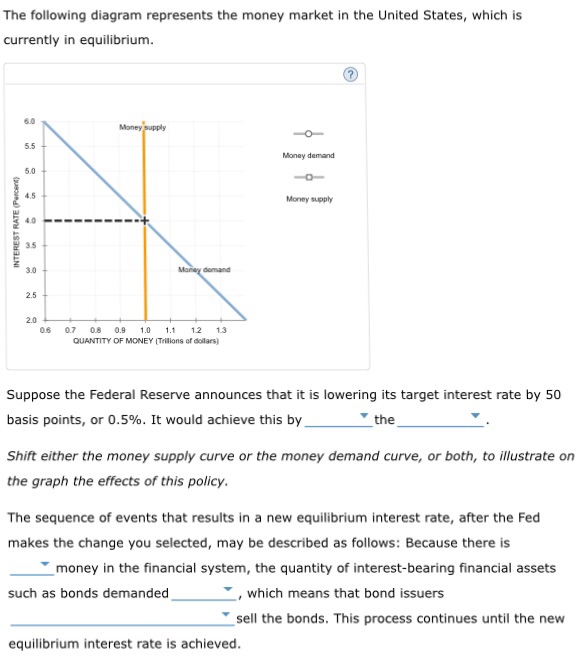
Refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is. Refer to the above diagram of the market for money. The vertical money supply curve Sm reflects the fact that: the stock of money is determined by the Federal Reserve System and does not change when the interest rate changes. Since the interest rate is identical to the rate of return on dollar assets from a U.S. dollar holder's perspective (i.e., RoR $ = i $), we can now place the RoR diagram directly on top of the rotated money market diagram as shown in Figure 7.8 "Money-Forex Diagram".The equilibrium interest rate (i′ $), shown along the horizontal axis above the rotated money market diagram, determines the ... The following diagram represents the money market in the United States, which is currently in equilibrium, as indicated by the grey star. Suppose the Federal Reserve (the Fed) announces that it is raising its target interest rate by 25 basis points, or 0.25%. The real money demand function with GNP level Y $ 1 intersects with real money supply at point G 1 in the money market diagram determining the interest rate i $ 1. The interest rate in turn determines RoR $ 1, which intersects with RoR £ at point G 2, determining the equilibrium exchange rate E $/£ 1.
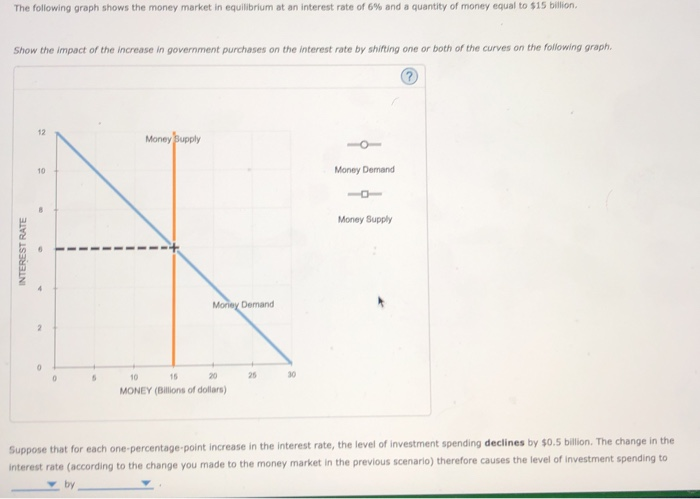
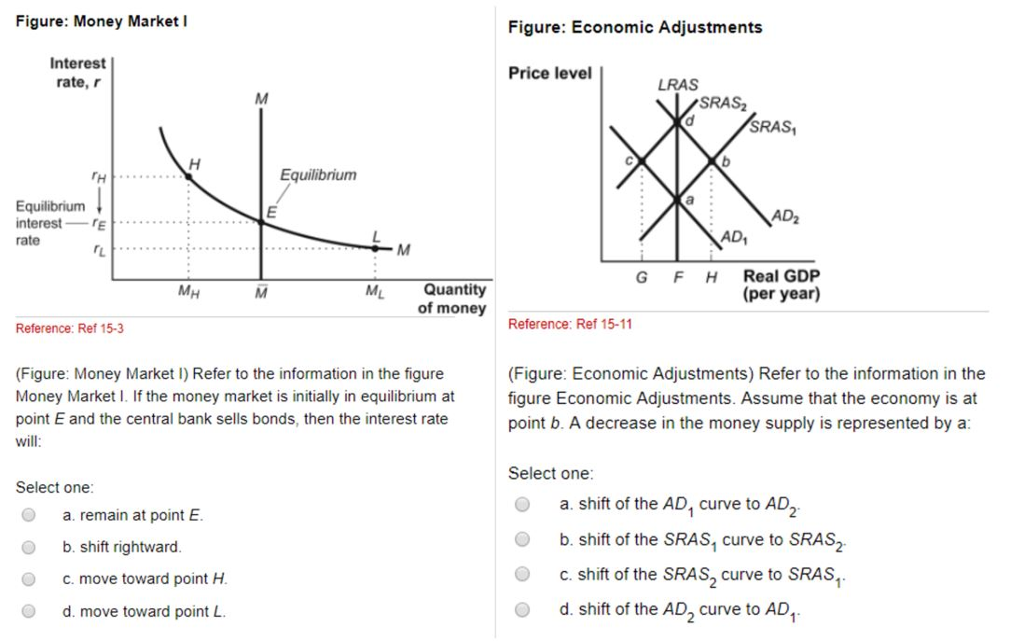
Solution for Refer to the graph. If the initial equilibrium interest rate was 5 percent and the money supply increased by $100 billion, then the new interest… Result: People will sell bonds and thus asset price will fall leading to rise in interest rate. Thus, due to increase in demand for money the interest rate will increase and, thus, move up on the LM 1 curve till a new equilibrium point is reached. This is at point E 2.. Thus, At point E 2: both product and money market is in equilibrium (IS = LM,). D) increase the equilibrium interest rate and decrease equilibrium money holdings. 32) Refer to Figure 11.3. At an interest rate of 6%, there is a 32) A) surplus of money and the interest rate will decline. B) shortage of money and the interest rate will decline. C) surplus of money and the interest rate will rise. Refer to the above diagram of the market for money. Given Dm and Sm, ... The equilibrium interest rate in this economy is: 4 percent. Refer to the above ...
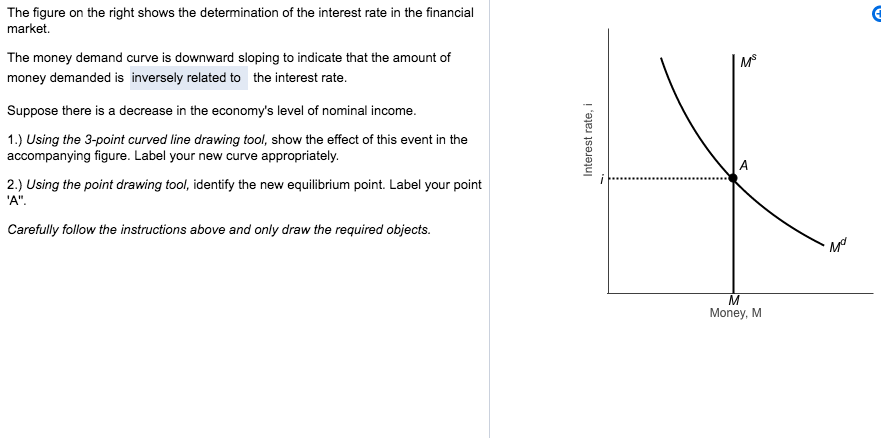
Refer to the given market-for-money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the D3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. S curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. Refer to the diagram of the market for money. Given Dm and Sm, an interest rate of i3 is not sustainable because the: demand for bonds in the bond market will rise and the interest rate will fall. Refer to the diagram for a private closed economy. the equilibrium level of gdp is: saving equals planned investment only at the equilibrium level of gdp. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: the equilibrium price and | chegg . refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: a. $1.00 and 200. Jan 07, 2022 · Refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is. the money market, with the price level is normalized to 1: MD = Y L(i) M = MS = MD On the graph, show what happens if income increases. In terms of the new equilibrium, what is the effect of the increase in Y on the interest rate i?
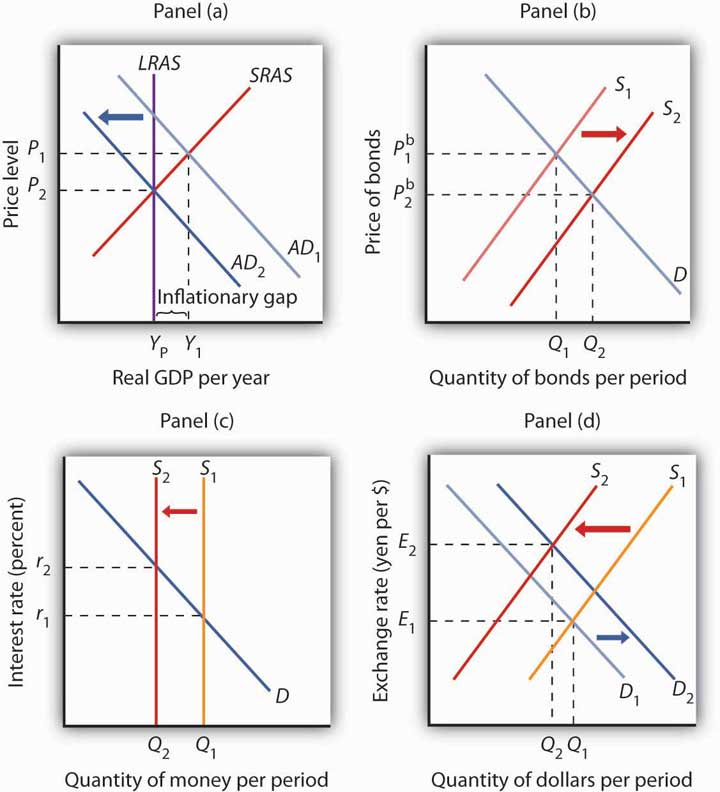
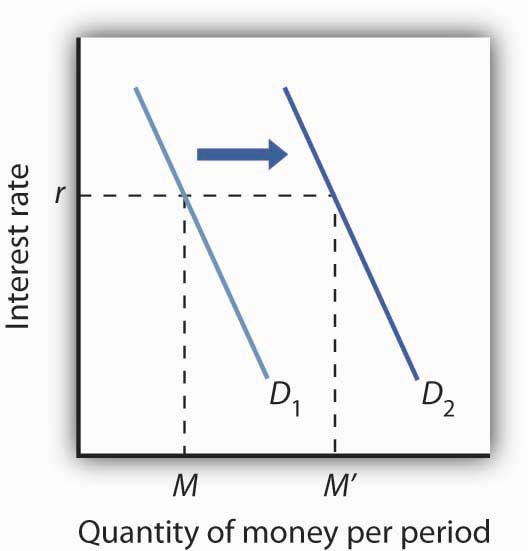
Figure 25.12 An Increase in the Money Supply. The Fed increases the money supply by buying bonds, increasing the demand for bonds in Panel (a) from D1 to D2 and the price of bonds to Pb2. This corresponds to an increase in the money supply to M ′ in Panel (b). The interest rate must fall to r2 to achieve equilibrium.
Refer to the given market-for-money diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the D3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. D3 curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall.
Jul 31, 2019 · Economics questions and answers. Dm Quantity of Money Refer to the diagram of the market for money. The equilibrium interest rate is: i3. can't be determined without additional information. i2. Oi1. SA ey Interest Rate. Question: Dm Quantity of Money Refer to the diagram of the market for money.
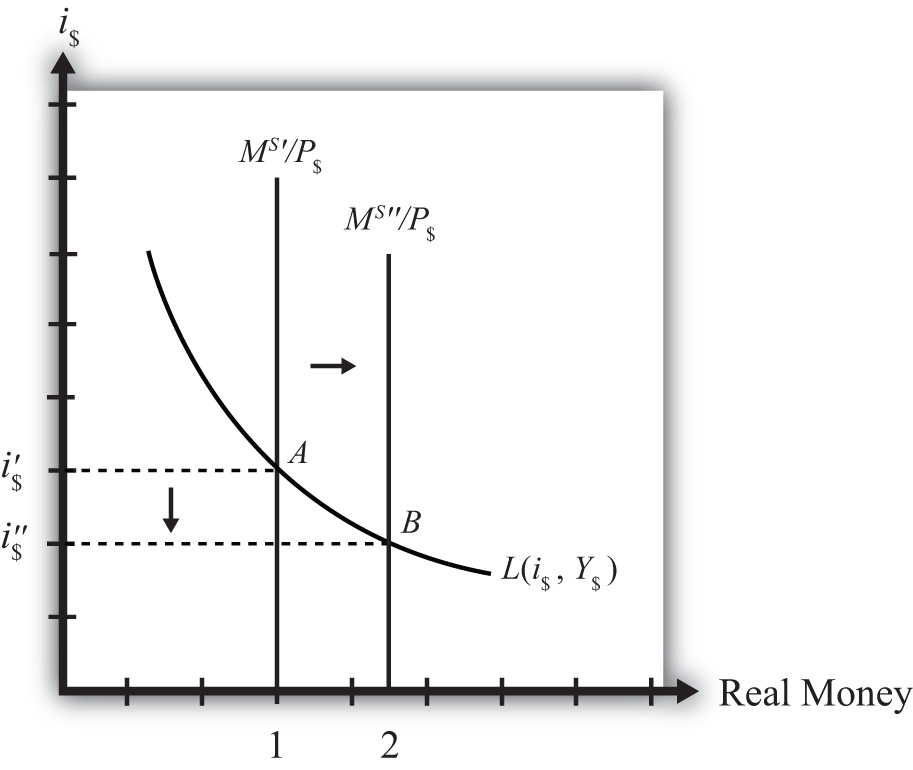
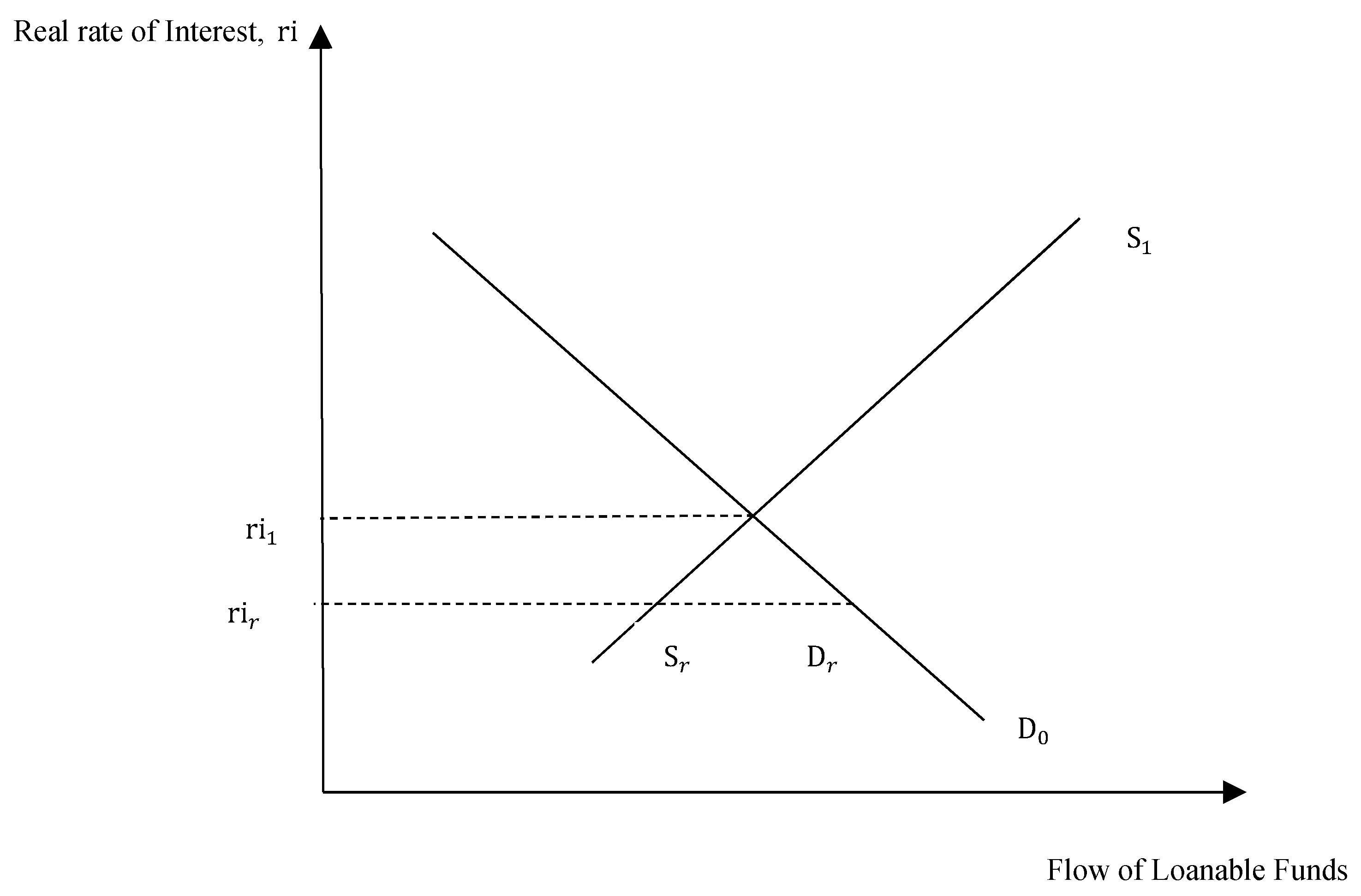
The LM curve represents the combinations of income and the interest rate at which the money market is in equilibrium. If money demand does not depend on the interest rate, then we can write the LM equation as M/P = L(Y). For any given level of real balances M/P, there is only one level of income at which the money market is in equilibrium. Thus,
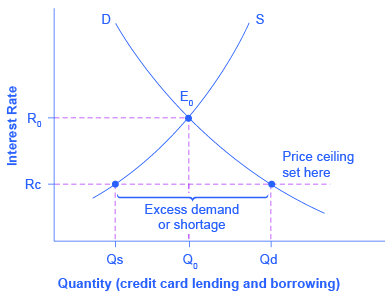
In this market for credit card borrowing, the demand curve (D) for borrowing financial capital intersects the supply curve (S) for lending financial capital at equilibrium €. At the equilibrium, the interest rate (the "price" in this market) is 15% and the quantity of financial capital being loaned and borrowed is $600 billion.
Refer to the above diagram of the market for money. The equilibrium interest rate is: i2.
A surplus of 160 units would be encountered if the price was: $1.10, that is, $1.60 minus $.50. *{$1.60.} $1.00. $0.50. Refer to the diagram. A shortage of 160 units would be encountered if price was: Money market equilibrium occurs at the interest rate at which the quantity of money demanded equals the quantity of money supplied.
Figure 1. Refer to this diagram of the open-economy macroeconomic model to answer the questions below. (see notes) Refer to Figure 1. At an interest rate of 4 percent, the diagram indicates that. a. there is a surplus in the market for foreign-currency exchange. b. national saving equals domestic investment.
Refer to the above diagram of the money market. The equilibrium interest rate is: A. i *B 1. B. ... R-1 F13072: Refer to the above diagram of the money market. Other things equal, the money demand curve in the diagram would shift leftward if: A. the asset demand for money increased. B. the transactions demand for money increased. C. nominal GDP ...
The money market is a variation of the market graph. Be cautious with labels use only standard abbreviations if you decide to use abbreviate: "n.i.r." for nominal interest rate, " " for the money supply curve, "D_m" for the money demand curve, and " " for the quantity of money. Always label equilibrium interest on the vertical ...
Explain why the equilibrium interest rate changes the way it does. Provide a graphical illustration using the appropriate diagram(s). (10 points) b. Discuss the effects of the policy on equilibrium output and interest rate in the economy using the ISLM-ADAS model in the short run. Explain which market (or markets) is (or are) affected and which ...
If the interest rate is above the equilibrium rate, there will be an _____ money and the interest rate will _____. A. excess demand for; rise B. excess supply of; fall C. excess demand for; fall D. excess supply of; rise E. excess supply of; remain the same 35. Use the “Money Market II” Figure 28-1. If the rate of interest is below the ...
The equilibrium real interest rate is a crucial concept in the new Keynesian class of models. This rate represents the real rate of return required to keep the economy's output equal to potential output, which, in turn, is the level of output consistent with flexible prices and wages and constant markups in goods and
164. Refer to the above money market diagrams. If the Federal Reserve increased the stock of money, the: A) S curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. B) S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. C) D3 would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall.
The money market diagram showing liquidity preference and money supply intersect at an equilibrium level of interest rate, but what interest rate is it? Is it the base rate (I presume this is the rate at which commercial banks lend out loans to borrowers) or FED Funds Rate/LIBOR? Or does it simply refer to interest rates in general?
Refer to the diagram of the market for money. Given Dm and Sm, an interest rate of i3 is not sustainable because the: demand for bonds in the bond market will rise and the interest rate will fall.
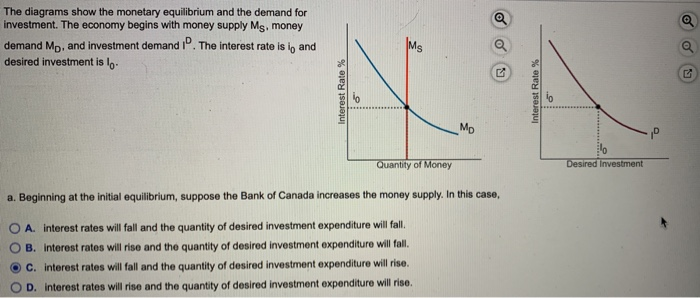
Refer to the market for money diagram below.Other things being equal, if the Bank of Canada increases the stock of money, the: 11eacf22_e8a2_7529_aab5_51eae88d9e9b_TB6686_00 A)S curve would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would rise. B)S curve would shift rightward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall. C)D would shift leftward and the equilibrium interest rate would fall.
Figure 15-8 Effect on the Dollar/Euro Exchange Rate and Dollar Interest Rate of an Increase in the U.S. Money Supply Given and when the money supply rises from to the dollar interest rate declines (as money market equilibrium is reestablished at point 2) and the dollar depreciates against the euro (as foreign exchange market equilibrium is ...
The real money demand function with GNP level Y $ 1 intersects with real money supply at point G 1 in the money market diagram determining the interest rate i $ 1. The interest rate in turn determines RoR $ 1, which intersects with RoR £ at point G 2, determining the equilibrium exchange rate E $/£ 1.
Refer to the diagram of the market for money. Given Dm and Sm, an interest rate of I3 is not sustainable because the: demand for bonds in the bond market will rise and the interest rate will fall.














:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash-INV-final-Why-Are-Price-and-Quantity-Inversely-Related-According-to-the-Law-of-Demand-Mar-2021-01-2f00c44178804aaa9f7889c367ab0223.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/human-hand-giving-paper-money-to-iron-clip-with-conveyor-belt-depicting-investment-170886383-59f0db1d9abed500108ee1ac.jpg)



0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram of the market for money. the equilibrium interest rate is"
Post a Comment