42 p2 molecular orbital diagram
1 answerThe electronic configuration of phosphorus is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3. The Molecular Orbital Diagram of P2 can be shown as: So number of electrons... For chem videos, quizzes and more download Chemistry X for free on the App Store! Correlation Diagrams - by considering the positions and energies of electr...
(i) Be2 molecule: The electronic configuration of Be(Z = 4) is: 4 Be 1s 2 2s 1 Be 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. Number of valence electrons in Be atom = 2 Thus in the formation of Be 2 molecule, two outer electrons of each Be atom i.e. 4 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies.
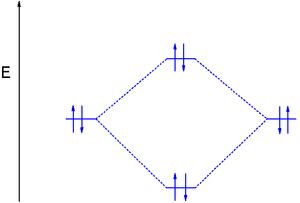
P2 molecular orbital diagram
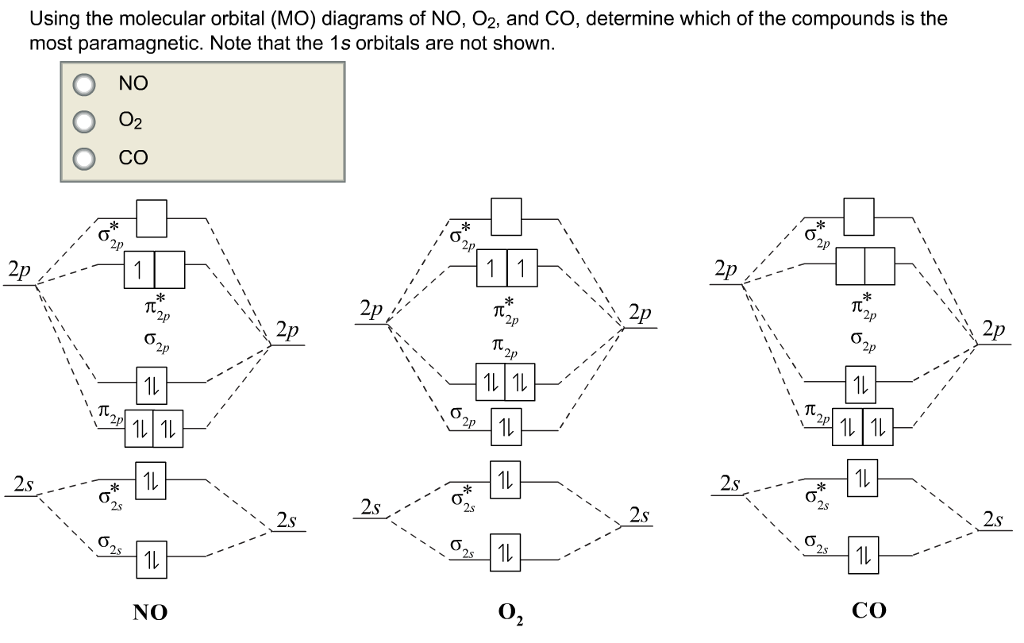
Also, the molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide reveals that s-p mixing must be occurring since the $3\sigma$ orbital is higher in energy than the $1\pi$ orbital. This also seems to contradict the idea that the s and p orbitals mix on the same atom because in $\ce{O_2}$ there is no s-p mixing so why would oxygen mix its s and p orbitals ... molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the Molecular orbitals were first introduced by Friedrich Hund and Robert S. Mulliken in 1927 and 1928. The linear combination of atomic orbitals or "LCAO" approximation for molecular orbitals was introduced in 1929 by Sir John Lennard-Jones. His ground-breaking paper showed how to derive the electronic structure of the fluorine and oxygen molecules from quantum principles.
P2 molecular orbital diagram. Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or... Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals ( σ σ, σ σ *, π π, π π *)
Molecular Weight: 61.94752400: Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.08.13) XLogP3-AA-0.2: Computed by XLogP3 3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count: 0: Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count: 0: Computed by Cactvs 3.4.8.18 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) Rotatable Bond ... Consider the molecular orbitals of the P2 molecule. Assume that the MOs of di-atomics from the third row of the periodic table are analogous to those from the second row. (a) Which valence atomic orbitals of P are used to construct the MOs of P2? (b) The figure that follows shows a sketch of one of the MOs for P2.What is the label for this MO? ... Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory (continued 1) • Filling of MOs with electrons is governed by the same rules as for atomic orbitals • Aufbau principle - Fill MOs beginning with the lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital • Pauli exclusion principle - No more than two electrons can be accommodated in a MO, and their spins must be paired Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: 5. Draw the Molecular Orbital Diagram for P2, P2*, and P2". Rank these in terms of increasing bond strength. Use evidence to support your answer. (Hint determine the bond order).
This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, . electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the Li2 molecule to be . Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Step-by-step solution. 100% (3 ratings) for this solution. Step 1 of 5. (A) Contain 30 electrons and if it behaves like then the valence atomic orbital of P that are used to construct the for are. Molecular Orbital Diagram - Cl2, Br2, I2 3s & 3p and higher atomic orbitals are not so widely separated in energy and allow significant mixing (hybridization) to occur. This mixing causes the inversion of the σσand πmolecular orbitals' energy. σσσ ππ σ* π* 3,4,5 p 3, 4,5 s σ* σ 3,4,5 s 3,4,5 p Interhalogens Br Br F F Br F F F F. Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below.
The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be.
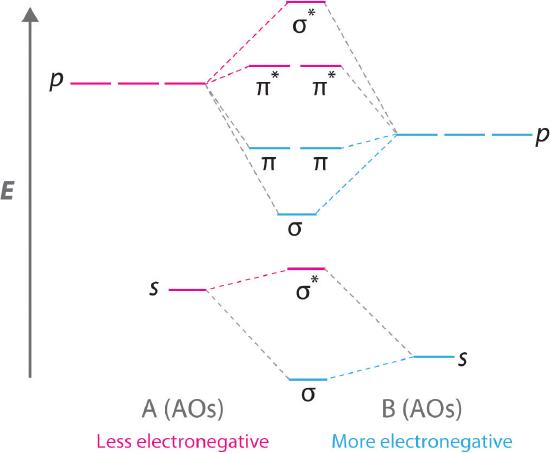
Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds.
The iodine bromide molecule, IBr, is an interhalogen compound.Assume that the molecular orbitals of IBr are analogous to the homonuclear diatomic molecule F 2.(a) Which valence atomic orbitals of I and of Br are used to construct the MOs of IBr?(b) What is the bond order of the IBr molecule?(c) One of the valence MOs of IBr is sketched here.Why are the atomic orbital contributions to this MO ...
We're being asked to determine the bond order of P2. For this, we need to do the following steps: Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Step 3: Calculate the bond order of the molecule/ion. Recall that the formula for bond order is: B o n d O r d e r = 1 2 [ # of e - in ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram of O 2 Chapter 9 Section 6 When filling the MO levels, you have to: Count the number of valence electrons, Start with the lower energy orbitals first, Follow Hund's rule, and Pt t th t Dr. A. Al-Saadi 19 Put not more than two electrons in one MO. Molecular Orbital Diagram of N 2 Chapter 9 Section 6
Li2 is more stable than Li+ 2, because the bond is (hypothetically) stronger (probably gas-phase). Here we consider the molecular orbital diagram (MO) of Li2: The bond order can be calculated in a simple manner. Just take electrons that are in each MO, and. for each electron in a bonding MO, it adds 0.5 to the bond order, because more bonding ...
Molecular orbitals in Nitrogen. Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. There are four molecular orbitals derived from the 1s and 2s orbitals. Use the buttons to display the 1s and 2p atomic orbitals that make up the molecular orbitals. The p orbitals combine to produce a sigma and two ...
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Sigma pi bond formation Orbital overlap concept ncert
To calculate the bond order, it's one half the number of valence electrons in bonding molecular orbital's minus those in an anti bonding molecular orbital. This ...4 answers · Top answer: to construct the molecular orbital diagram for HE two. Plus, we need to follow the conventions. ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
The pi bond between the carbon atoms perpendicular to the molecular plane is formed by 2p-2p overlap. Formation of sp2 hybrid orbitalsThis illustration shows how an s-orbital mixes with two p orbitals to form a set of three sp 2. hybrid orbitals. Notice again how the three atomic orbitals yield the same number of hybrid orbitals.
Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbitals and transitions for P2 ; similar orbitals and transitions have been obtained for other dyes. from publication: Photophysical, electrochemical and ...
Sigma (σ) bonding molecular orbital - Shared electron density is directly between the ... show one MO diagram and you can imagine doing it a second time.13 pages
Jul 20, 2016 — four key points to remember when drawing molecular orbital diagrams: The number of molecular orbitals produced is the same as the number of ...
For the problem, we have to determine which valence atomic orbitals of P are used to construct the MOs of P2. In this case, we will pattern the MO of P using N (from the second row) since they belong in the same group. Consider the molecular orbitals of the P2 molecule. Assume that the MOs of diatomics from the third row of the periodic table ...
O sp2 sp C sp s p2 s p2 p s p2 p pp molecular shape: linear 211 sp3d hybridization • sp3d hybridization is the mixing of 1 s orbital, 3 ... Valence orbital diagram; O ground state : 2s 2p O excited state : 2s 2p O hybrid : sp3 F ground state : 235 2s 2p Answer Orbital Overlap: Molecular Shape : V- shaped s p3
Molecular orbitals were first introduced by Friedrich Hund and Robert S. Mulliken in 1927 and 1928. The linear combination of atomic orbitals or "LCAO" approximation for molecular orbitals was introduced in 1929 by Sir John Lennard-Jones. His ground-breaking paper showed how to derive the electronic structure of the fluorine and oxygen molecules from quantum principles.
molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the
Also, the molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide reveals that s-p mixing must be occurring since the $3\sigma$ orbital is higher in energy than the $1\pi$ orbital. This also seems to contradict the idea that the s and p orbitals mix on the same atom because in $\ce{O_2}$ there is no s-p mixing so why would oxygen mix its s and p orbitals ...


























0 Response to "42 p2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment