38 oh molecular orbital diagram
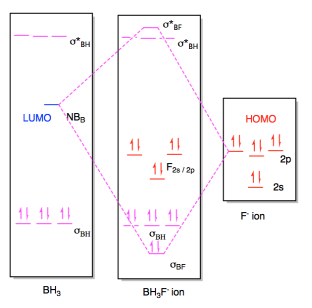
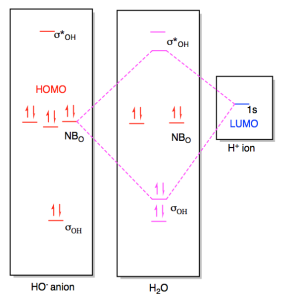
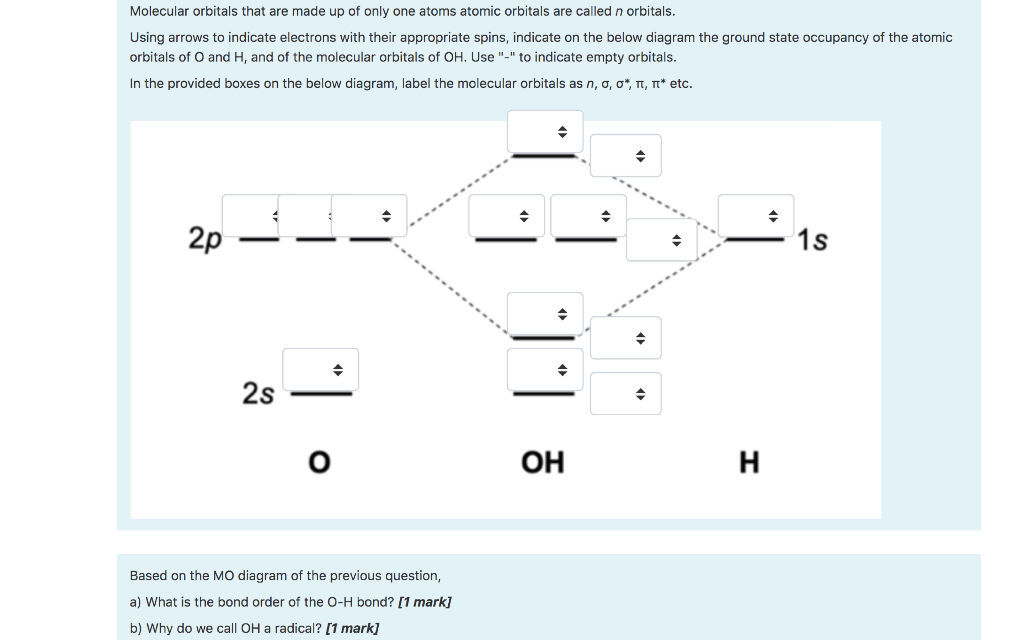
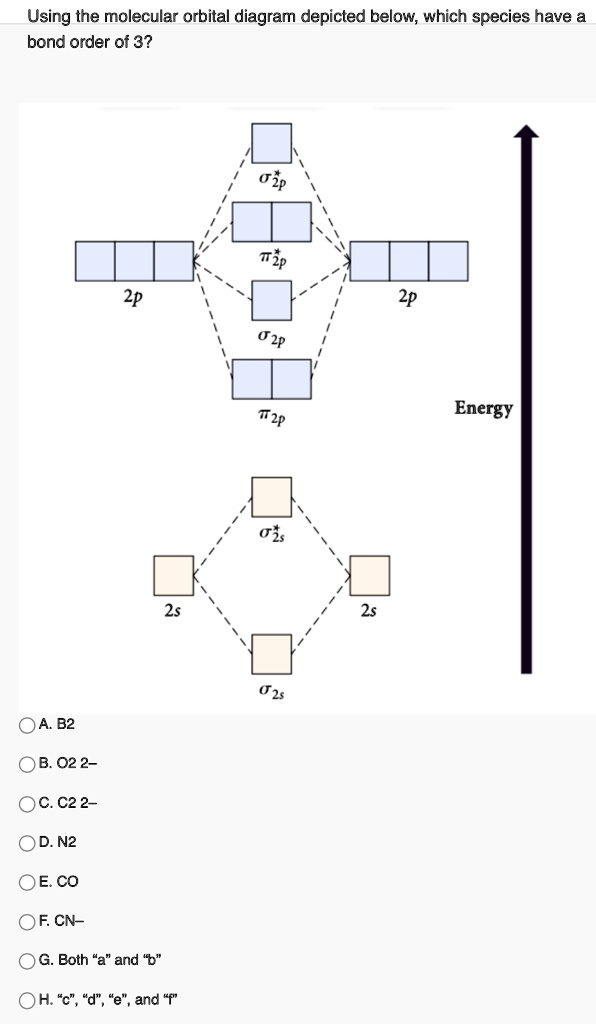
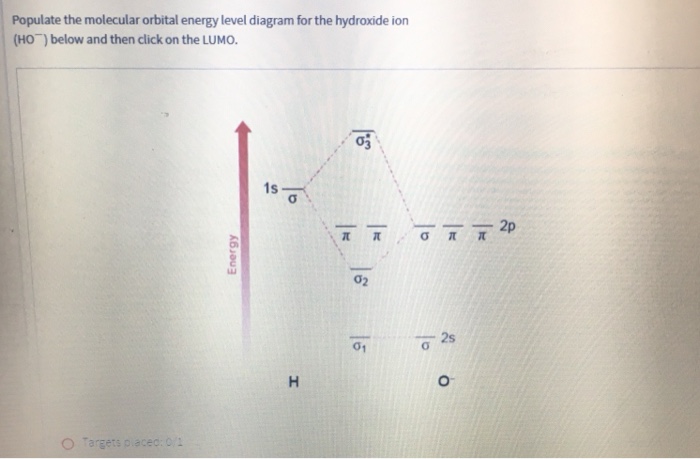
A molecular orbital interaction diagram shows how atomic or molecular orbitals combine together to make new orbitals. Sometimes, we may be interested in only the molecular orbital energy levels themselves, and not where they came from. A molecular orbital energy level diagram just shows the energy levels in the molecule. Energy level diagram for the molecular orbitals of OH ). H and O atom orbitals, which combine to form the molecular orbitals, are on the left and right side of the figure, respectively.
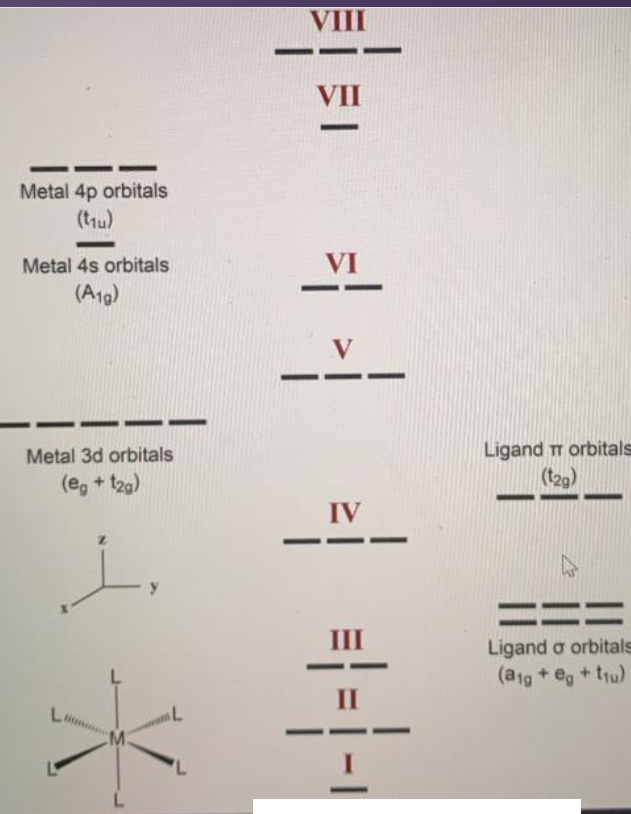
d orbitals •l = 2, so there are 2l + 1 = 5 d-orbitals per shell, enough room for 10 electrons. •This is why there are 10 elements in each row of the d-block. σ‐MOs for Octahedral Complexes 1. Point group Oh 2. The six ligands can interact with the metal in a sigma or pi fashion.

Oh molecular orbital diagram
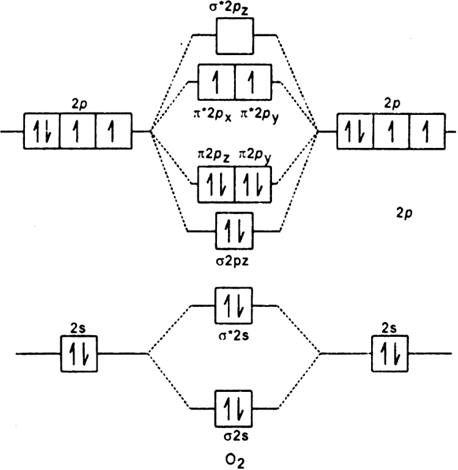
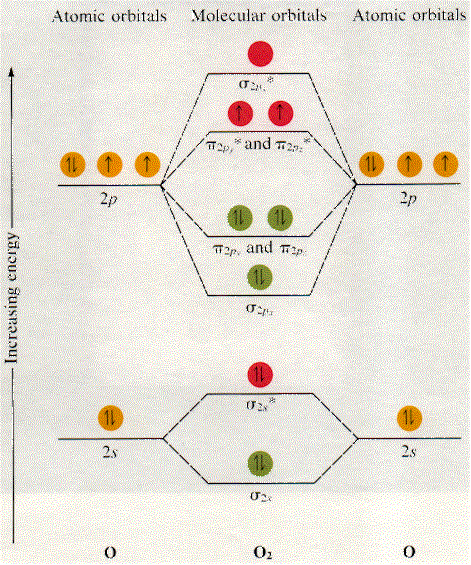
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Oxygen Gas (O2).Fill from the bottom up, with 12 electrons total.Bonding Order is 2, and it is Paramagnetic.sigma2s(2),sigma2s*... MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY OF COORDINATION COMPOUNDS OCTAHEDRAL COMPLEXES σ-Bonding In the valence shell of transition metals, there are 9 atomic orbitals (5 d + 1 s + 3 p). For octahedral ML 6 complex, the point group is O h. The symmetry of the nine valance orbitals is found from the Oh point group character table as a 1g (1s), t 1u (p x, p y ... • The energy increase of the e g orbitals and the energy decrease of the t 2g orbitals must be balancedrelative to the energy of the hypotheticalsphericalfield(aka the barycenter).• The energy of each of the two orbitals of the e g set rises by +3/5 o (+6 Dq) while the energy of eachof the three t 2g orbitalsfallsby ‐2/5 o(‐4Dq). • Thisresults inno netenergy changefor the system:
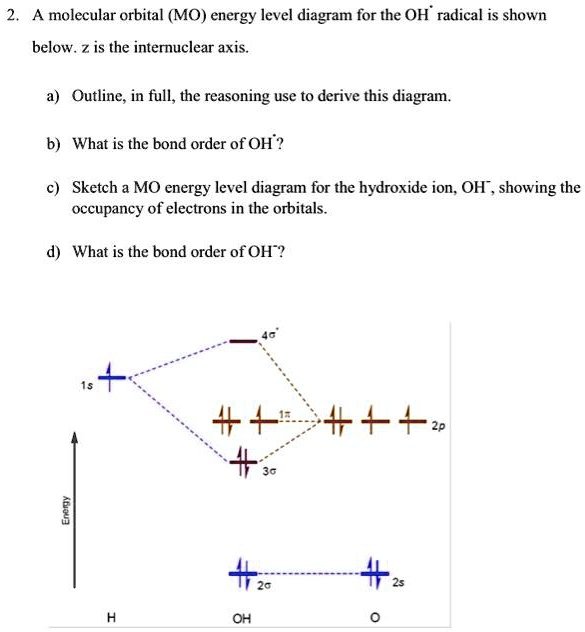
Oh molecular orbital diagram. Core orbitals are omitted. Marks 8 Using arrows to indicate electrons with their appropriate spin, indicate on the above diagram the ground state occupancy of the atomic orbitals of O and H, and of the molecular orbitals of OH. In the provided boxes on the above diagram, label the molecular orbitals as n, σ, σ∗, π, π∗, etc. Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Consider the hydroxide ion, OH and do the following: a. Prepare a molecular orbital diagram and fill with electrons given the following atomic orbital potential energies: (2s) = -32.3 eV, O(2p) =-15.8 eV, H(18)=-13.6 eV. Be sure to label each molecular orbital (bonding, anti-bonding, non-bonding). b. Molecular orbital diagram for the Fe3*Mn2*O,o clus-ter in the (a) ferromagnetic and (b) antiferromagnetic configu-rations. Orbitals indicated with a dashed line are unoccupied. Note that the orbital energies correspond to "orbital electronega-tivities" . Dec 05, · Upload failed.
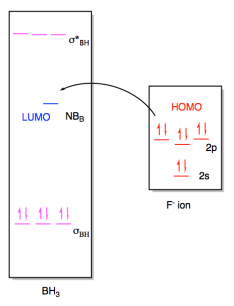
Molecular orbitals for Octahedral complexes The combination of the ligand and metal orbitals (4s, 4p x, 4p y, 4p z, 3d z2, and 3d x2-y2) form six bonding and six antibonding with a 1g, e g, t 1u symmetries. The metal T 2g orbitals do not have appropriate symmetry - nonbonding Electron in bonding orbitals provide the potential energy that holds ... Nov 04, 2008 · Molecular orbital of the hydroxyl radical with unpaired electron Skeletal formulae of 1-hydroxy-2(1H)-pyridinethione and its tautomer The hydroxyl radical, OH, is the neutral form of the hydroxide ion. Hydroxyl radicals are highly reactive and consequently short-lived; however, they form an important part of radical chemistry. Most features of molecular orbital theory for metal complexes are as follows: 1.The atomic orbital of the metal center and of surrounding ligands combine to form new orbitals, known as molecular orbitals. 2.The number of molecular orbitals formed is the same as that of the number of atomic orbitals combined. Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
are combined. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2molecule would therefore ignore the 1selectrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2sand 2pvalence orbitals. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level The 2sorbitals on one atom combine with the 2sorbitals on another to form a 2sbonding and a 2s* Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. This orbital corresponds to the LUMO for a proton. The molecular orbital diagram for hydroxide ion is not much more complicated. This molecule is diatomic; it comes from the combination of an oxygen atom with a hydrogem atom, with the addition of an extra electron to provide the negative A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory ...
Where is the energy difference (Between which orbitals) that corresponds to o (10Dq)? Label o on the MO diagram. What type of orbitals (bonding, non-bonding, antibonding) are the "crystal field" orbitals? Explain why. Calculate the o for [Co(NH3)6]3+, then determine if it is low- or high-spin. Fill in the MO diagram accordingly.
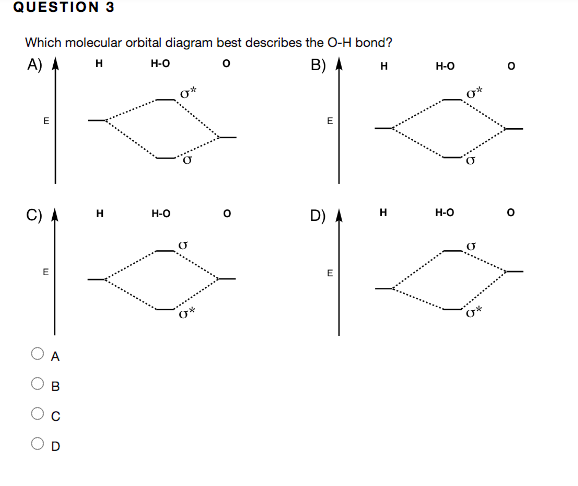
Dec 30, 2019 · I would like to understand how to create a molecular orbital diagram for the hydroxide ion from scratch. This includes understanding the shape of the molecular orbital. Here is an attempt I have come up with: Where the top MO is sigma* and the bottom is simply sigma. But this makes no sense.
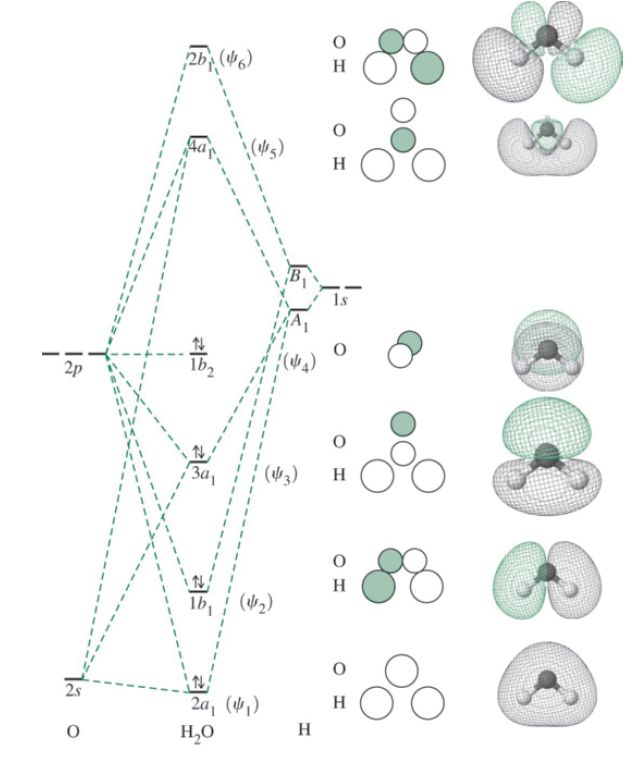
Oh- molecular orbital diagram FIG. 1: Two molecular orbital s of water that have bonding ˙ OH character, 2a 1 and 1b 1. Their combined contribution leads to 2 single OH bonds: (2a 1)2(1b 1)2!(˙ OH1)2(˙ OH2)2 ˙ orbital s are oriented along the bonds, whereas ˇ- orbital s are oriented perpendicular to the molecular plane.
Consider the hydroxide ion, OH and do the following: a. Prepare a molecular orbital diagram and fill with electrons given the following atomic orbital potential energies: O(2s) = -32.3 eV, O(2p) =-15.8 eV, H(1s) = -13.6 eV. Be sure to label each molecular orbital (bonding, anti-bonding, non-bonding). b. Sketch each molecular orbital's shape in ...
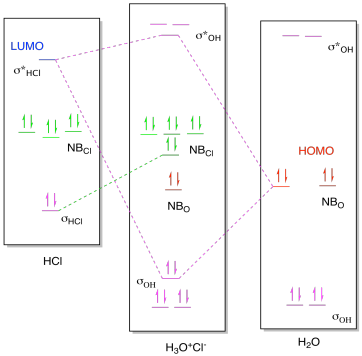
Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagram of O2, H2O, and OH⁻. from publication: Spin‐Related Electron Transfer and Orbital Interactions in Oxygen Electrocatalysis | Oxygen ...
#MOT #BMO #ABMO #HF #CO #NO #CN #OHHello everyoneThis is shivam here To follow me on instagram search - Sshivam898To join telegram group click on the given l...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Compare the bond order in H 2 + and H 2 using the molecular orbital energy diagram for ...
Property Name Property Value Reference; Molecular Weight: 17.007: Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) XLogP3-AA-.6: Computed by XLogP3 3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07)
• The energy increase of the e g orbitals and the energy decrease of the t 2g orbitals must be balancedrelative to the energy of the hypotheticalsphericalfield(aka the barycenter).• The energy of each of the two orbitals of the e g set rises by +3/5 o (+6 Dq) while the energy of eachof the three t 2g orbitalsfallsby ‐2/5 o(‐4Dq). • Thisresults inno netenergy changefor the system:
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY OF COORDINATION COMPOUNDS OCTAHEDRAL COMPLEXES σ-Bonding In the valence shell of transition metals, there are 9 atomic orbitals (5 d + 1 s + 3 p). For octahedral ML 6 complex, the point group is O h. The symmetry of the nine valance orbitals is found from the Oh point group character table as a 1g (1s), t 1u (p x, p y ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Oxygen Gas (O2).Fill from the bottom up, with 12 electrons total.Bonding Order is 2, and it is Paramagnetic.sigma2s(2),sigma2s*...


















0 Response to "38 oh molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment