39 myosin and actin diagram
PDF 03Gusev Sliding of two types of filaments formed by actin and myosin is basic mechanism of muscle contraction. Contraction is regulated by special Ca-binding proteins located on either actin or myosin filaments. muscle - Actin-myosin interaction and its regulation | Britannica The myosin-actin interaction also changes the physical properties of the mixture. If the concentration of ions in the solution is low, myosin molecules aggregate into filaments. As myosin and actin interact in the presence of ATP, they form a tight compact gel mass; the process is called superprecipitation.
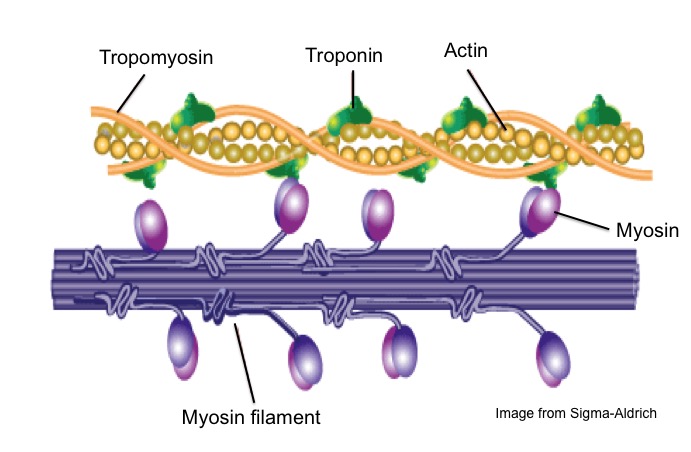
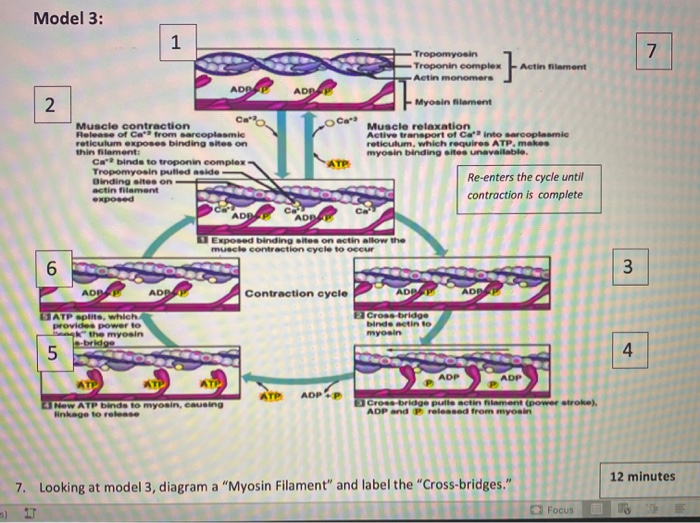
Lecture 3 Sarcomere, Myosin, Actin, etc. Flashcards | Quizlet Troponin, tropomyosin, g-actin. G-actin is a globular protein aranged in strands that form a double helix. Tropomyocin is a tube shaped protein that twists around the actin Troponin is a globular protein that is attached at regular intervals to both tropomyosin and actin and has a negative charge.

Myosin and actin diagram
› en › librarySmooth muscle: Structure, function, location | Kenhub Oct 28, 2021 · The actin filaments are stretched between dense bodies in the cytoplasm and attachment plaques at the cell membrane. The myosin filaments lie between the actin filaments. Furthermore intermediate filaments such as desmin and vimentin support the cell structure. Actin and Myosin | Biology Dictionary Actin and myosin are both proteins that are found in all types of muscle tissue. Myosin forms thick filaments (15 nm in diameter) Actin and myosin work together to produce muscle contractions and, therefore, movement. First, a motor neuron delivers an electrical signal to the muscle cell from the brain. PDF Polarity sorting drives remodeling of actin-myosin networks Since actin-myosin remodeling is rather fast, we develop an 95 open chamber assay that allows us to capture the initial steps of myosin-mediated 446 In the phase diagrams (Figs. 7d,e and 8a,b), the boundary between the Polarity Sorting (PS) and Filament 447 Buckling (FB) mechanisms was...
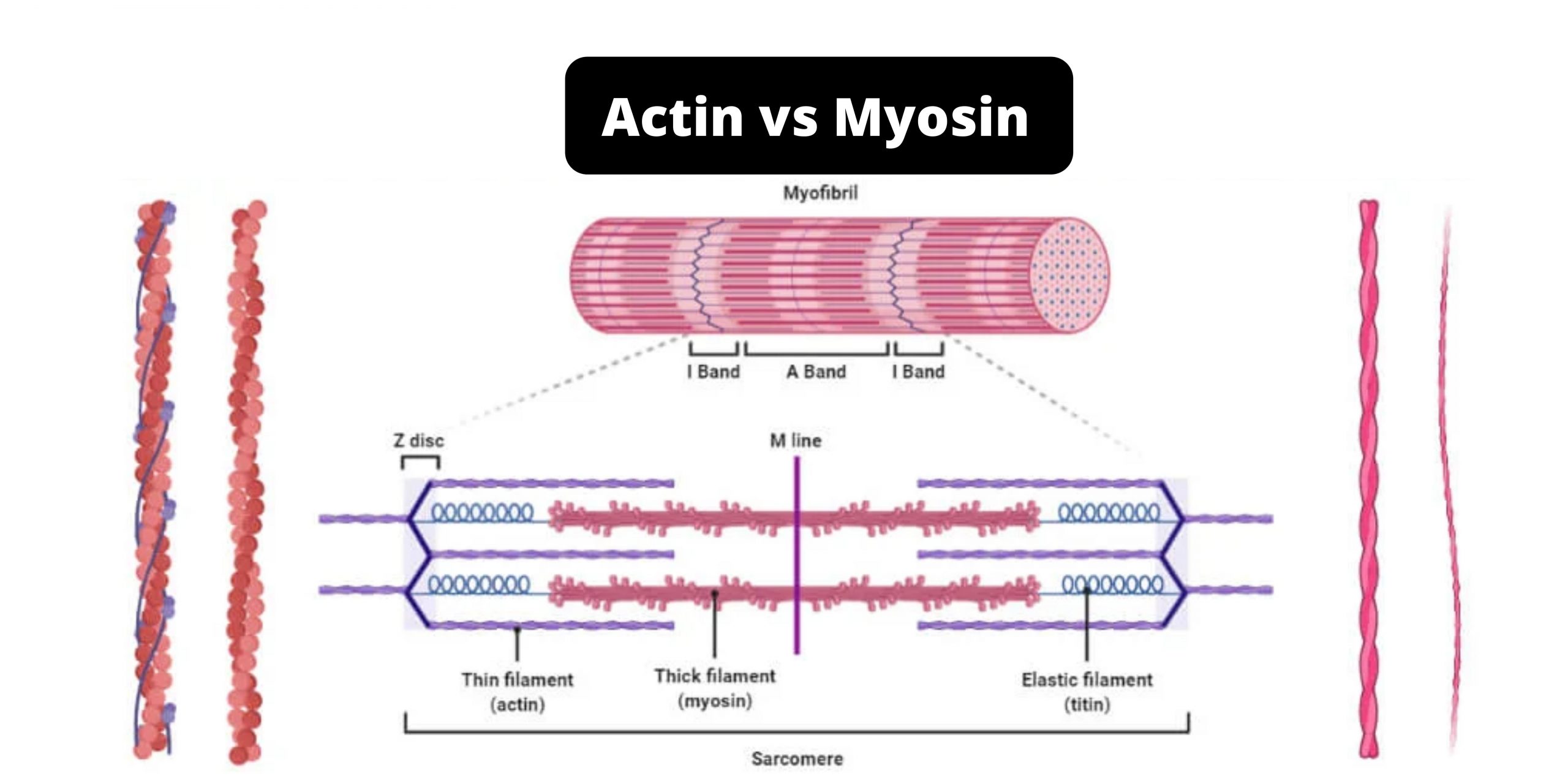
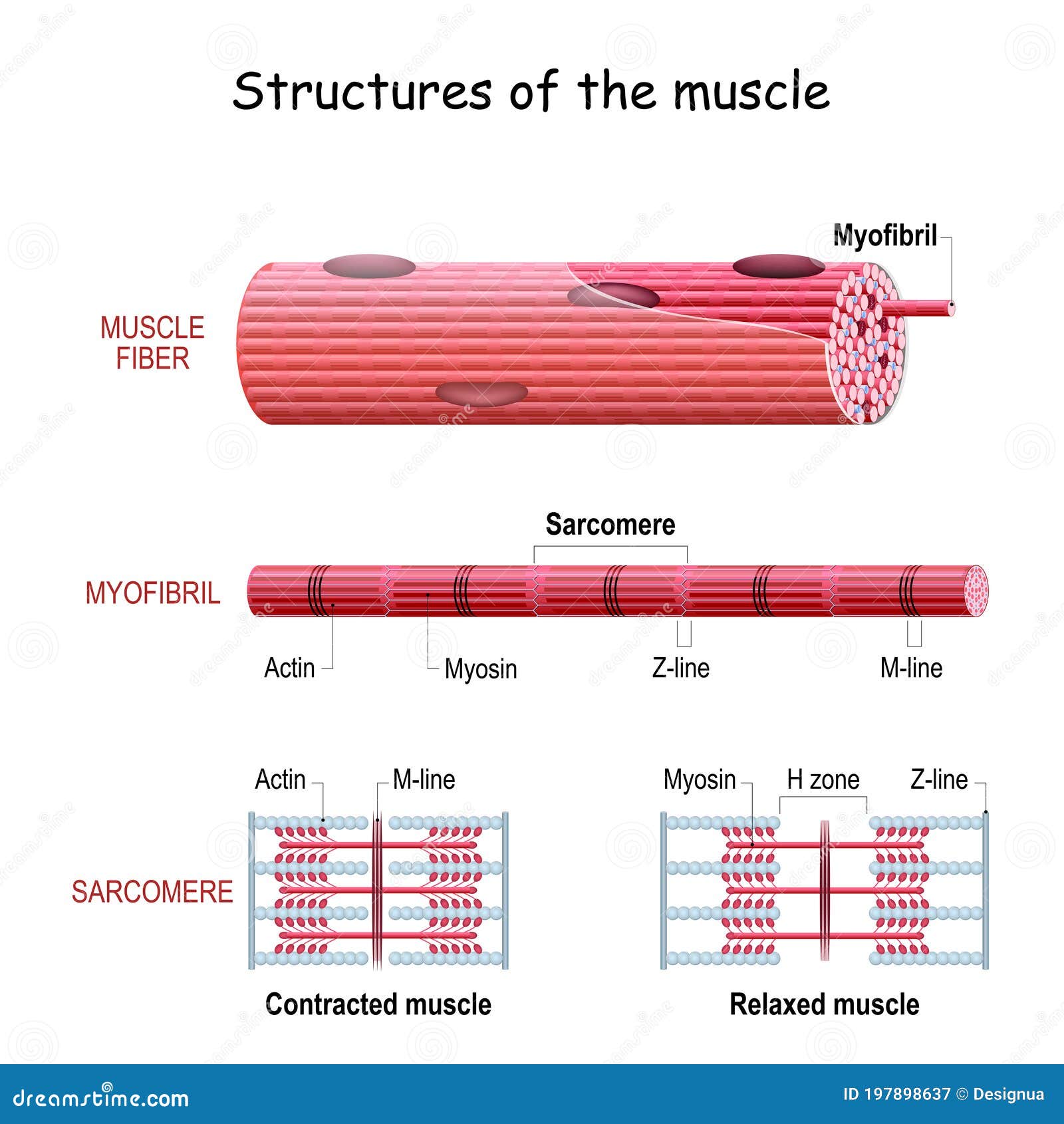
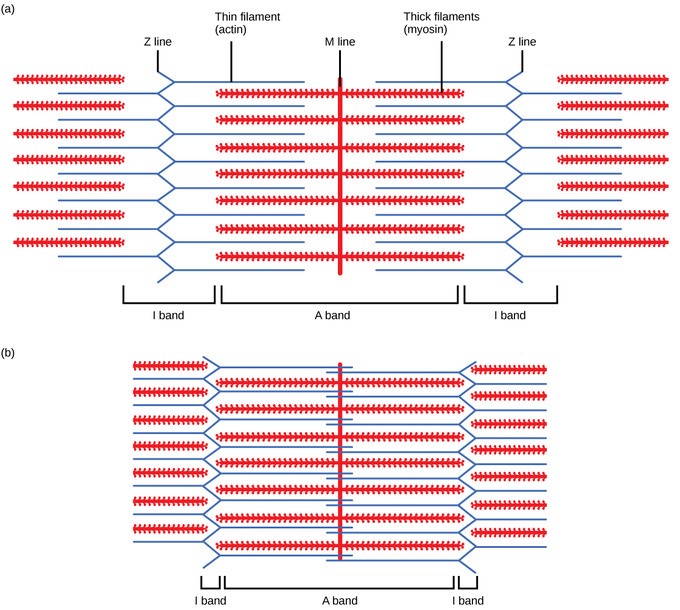
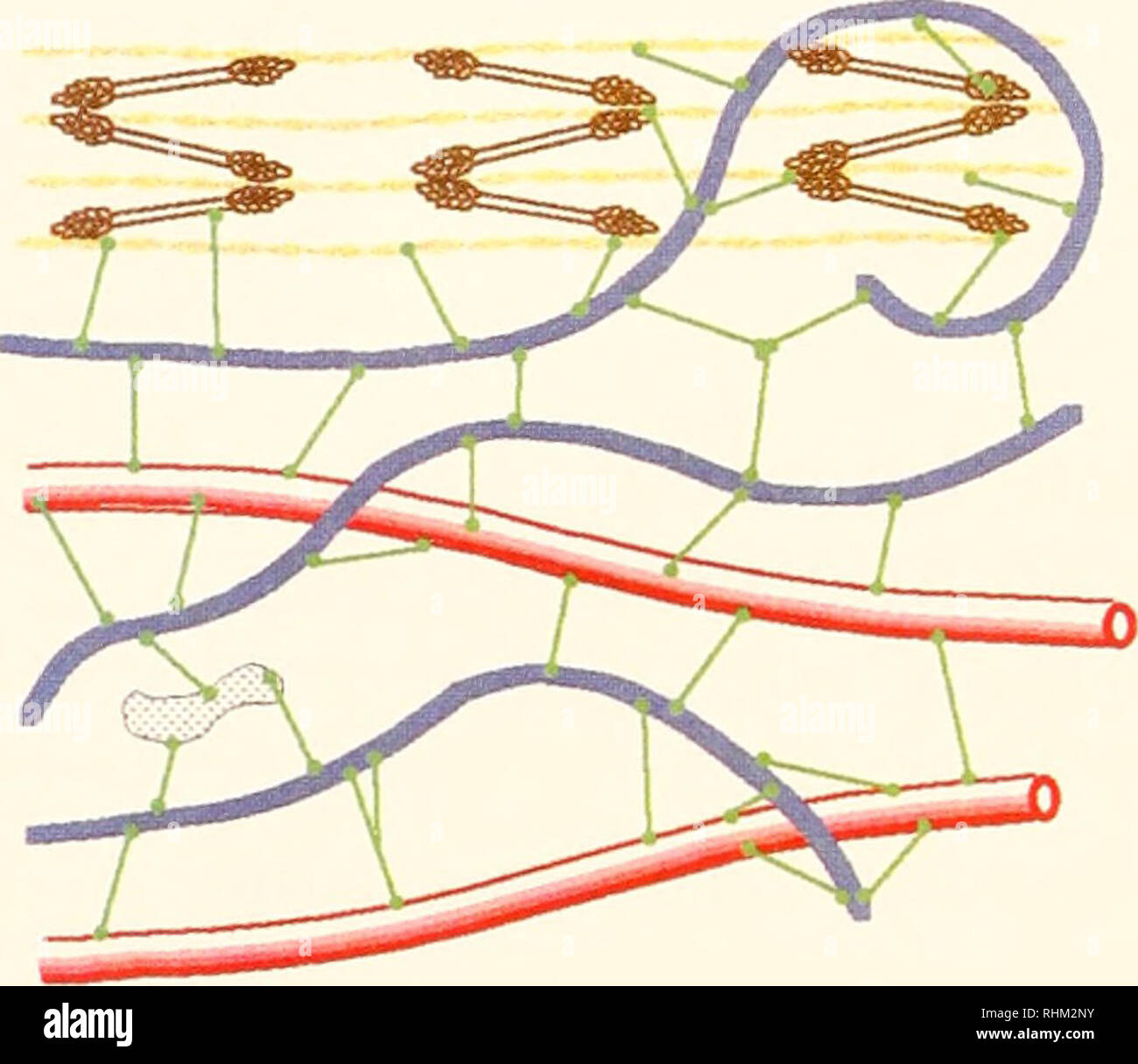
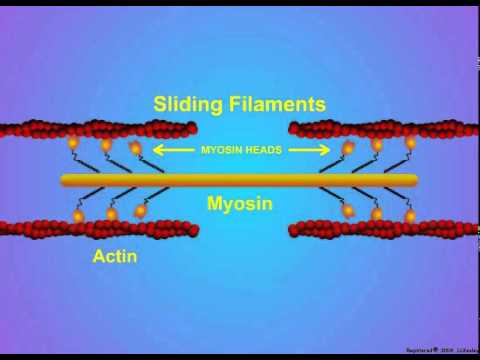
Myosin and actin diagram. Myosin | Summary, Structure, Synthesis, Classes & Role The actin filaments slide over the myosin filaments. This is why it is called the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. Myosin heads can only bind to actin filaments when their light chains are phosphorylated. This phosphorylation is carried out by myosin light chain kinase. › anatomy-physiology › slidingMuscle Contraction & Sliding Filament Theory - TeachPE.com The diagram above shows a fully contracted muscle with lots of overlap between the actin and myosin. Because the thin actin filaments have overlapped there is a reduced potential for cross bridges to form again. Therefore, there will be low force production from the muscle. Sarcomere Contraction Is Driven by Sliding of Myosin and Actin... These other myosins, the most widely studied of which is myosin I, have shorter tails and, at least in We obtain the active length-tension diagram by stimulating the muscle at each predefined length (i.e Smooth muscle uses actin and myosin filaments for contraction. The mechanism, illustrated in... Myosin Potentiates actin-myosin interaction at low Ca++ levels. Related enzymes: Myosin phosphatase target subunit 1 ; Guanosine triphosphatase Rho. Each actin can bind to 4 other actins. G-actin molecule contains a high-affinity myosin head binding site.
Myosin filament-based regulation of the dynamics of... | PNAS Myosin-based mechanisms are increasingly recognized as supplementing their better-known The fraction of myosin motors attached to actin (fA) at PF was estimated from the intensity of the , The low-angle X-ray diagram of vertebrate striated muscle and its behaviour during contraction and rigor. Myosin - Wikipedia Myosins (/ˈmaɪəsɪn, -oʊ-/) are a superfamily of motor proteins best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are ATP-dependent and responsible for actin-based motility. Differences Between Actin and Myosin... - Bio Differences Actin and Myosin are responsible for various types of cellular movements, and the most striking one is the muscle contraction, that provides the Therefore, it is said that myosin and actin together work at the time of the muscles contractions, where myosin is the precursor protein that plays its critical role... Actin and myosin crossbridge cycling: Actin and myosin are... Actin-myosin crossbridge cycling in skeletal muscle (and Hill's equation, and two demos...) -- Terminology: By "muscle" we mean whole muscle, such as the gastrocnemius or biceps or deltoid muscle. Whole muscle is made of many muscle fibers in parallel.
Integrating Actin and Myosin II in a Viscous Model for Cell Migration In the model, both myosin II contraction and actin polymerization were treated as active stresses. The adhesion sites could switch between the gripping mode and the slipping mode and their dynamics were integrated with actin flow. The polymerization stress only acts in the cell periphery. Actin and myosin - Big Chemical Encyclopedia Actin and myosin. Contraction of muscle follows an increase of Ca " in the muscle cell as a result of nerve stimulation. In addition to the major proteins of striated muscle (myosin, actin, tropomyosin, and the troponins), numerous other proteins play important roles in the maintenance of muscle... Difference Between Actin and Myosin | Definition, Structure, Function... Actin and myosin are two proteins in muscles, involved in the muscle contraction in animals. They control the voluntary muscular movements of the body in concert with the Actin refers to a protein that forms a thin contractile filament in muscle cells. It is the most abundant protein in eukaryotic cells . Cryo-EM structures reveal specialization at the myosin VI-actin... Comparison to the myosin IIC-F-actin rigor complex reveals an almost complete lack of conservation of residues at the actin-myosin interface despite preservation of the primary sequence regions composing it, suggesting an evolutionary path for motor specialization.
PDF 1. The diagram represents actin and myosin in a muscle cell. Myosin Actin. Myosin head. Off. On. Switch protein (tropomyosin). (a) With reference to the diagram: (i) describe the part played by calcium ions in This shortening is brought about when myosin and actin filaments in the cytoplasm of muscle cells slide over each other. Explain how ATP and calcium ions (Ca.
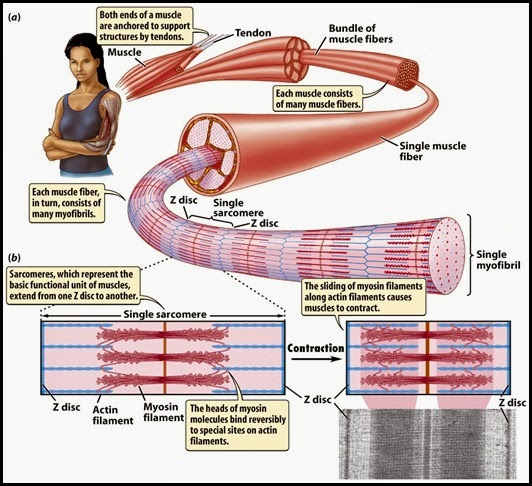
› books › NBK26888Molecular Motors - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Each myosin thick filament has about 300 heads (294 in frog muscle), and each head cycles about five times per second in the course of a rapid contraction—sliding the myosin and actin filaments past one another at rates of up to 15 μm/sec and enabling the sarcomere to shorten by 10% of its length in less than 1/50th of a second.
(PDF) Molecular mechanism of actin-myosin motor in muscle quantitation of actin-myosin interaction was not v ery. successful. Modeling the Diffraction Diagram of Relaxed Muscle. The first spatial muscle model, considering all actin-myosin lattice, and second, due to the presence of. unknown characteristics of myosin head arrangements. on the thin filament.
Myosin and actin (video) | Muscles | Khan Academy How myosin and actin interact to produce mechanical force. This right here is actin. What we're going to see in this video is how myosin essentially uses the ATP to essentially crawl along. You can almost view it as an actin rope and that's what creates mechanical energy.
Sliding Filament Theory - Definition, Diagram and Important FAQs The myosin and actin cross-bridges bind and contract using ATP. Recharging: ATP is resynthesized which allows actin and myosin to maintain Myosin and actin return to their unbound state causing the muscle to relax. Alternatively, relaxation (failure) also occurs when ATP is no longer available.
vanat.cvm.umn.edu › vanatpdf › GrossAnatLectNotesCVM 6100 Veterinary Gross Anatomy - University of Minnesota contractile proteins (actin and myosin) pulling on the tendon and contributing to muscle force. • pennation design increases the number of muscle fibers (cross sectional area) attached to the tendon • since force is a function of cross sectional area - a pennated muscle can generate more force than a comparable muscle with parallel fibers.
› cms › lib0103 b) myosin heads attach to the actin filaments 5 c) ATP is ... energy needed to attach the Myosin head to the Actin, forming a cross-bridge. Ca2+ binds to Troponin, changing its shape, which moves the Tropomyosin from the active site of the Actin. This is repeated all along the myofibril. The Myosin detaches from the Actin and the cross-bridge is broken when another ATP molecule binds to the Myosin head.
Muscle Contraction and Locomotion | Boundless Biology The molecular mechanism whereby myosin and acting myofilaments slide over each other is Tropomyosin and troponin prevent myosin from binding to actin while the muscle is in a resting Excitation-contraction coupling: This diagram shows excitation-contraction coupling in a skeletal...
[PDF] The actin-myosin interface | Semantic Scholar The actin-myosin model suggests extensive contacts between actin and the myosin head (S1), and suggests how the loop carrying the critical Arg 405 Glu mutation in S1 binds to two actin monomers. The contact surface between actin and S1 has increased dramatically compared with previous models.
PDF Myosin Structure, Allostery, and Mechano-Chemistry Myosin S1 is depicted as blue ribbon diagram. The two myosin light chains are colored green and cyan, respectively. Filamentous actin (F-actin) has a dual function in its interaction with the myosin mo-tor: it provides support as a track and acts as a release factor for the hydrolysis products.
Muscle Contraction | BioNinja Sliding mechanism of actin and myosin filaments. Sarcomere shortening (muscle contraction). The myosin heads bind to the new actin sites and return to their original conformation. This reorientation drags the actin along the myosin in a sliding mechanism.
Can you explain the link between actin, myosin, and ATP as it... - Quora Actin is a long globular protein, and it is covered by long strands of another protein known as tropomyosin. Essentially, what happens during muscle contraction is the thick and thin filaments seen in the bottom diagram are composed of myosin (thick filament) and actin (thin filament).
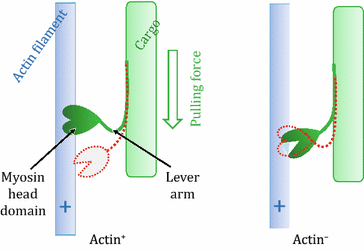
Difference Between Actin and Myosin | Compare the Difference... Actin-myosin contractile system is the main contractile system of all muscular tissues, and it works based on the interactions between the two proteins Actin-myosin complexes generate the cellular forces used in cell contractility and migration. The majority of myosins are (+) end motors, i.e., they...
The Role of Actin and Myosin The Role of Calcium and Myosin in Muscle Contraction. Figure 7.5 shows the placement of two other proteins associated with an actin filament, which you will recall is composed of a double row of twisted actin molecules.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Glomerulus_(kidney)Glomerulus (kidney) - Wikipedia The glomerulus is a tuft of capillaries located within Bowman's capsule within the kidney. Glomerular mesangial cells structurally support the tufts. Blood enters the capillaries of the glomerulus by a single arteriole called an afferent arteriole and leaves by an efferent arteriole.
Actin vs Myosin- Definition, 14 Major Differences, Examples Actin is a group of globular proteins that are the most abundant proteins in most eukaryotic cells and help in providing shape, structure, and mobility to the body. Myosin is a family of motor proteins that, together with actin proteins, form the basis for the contraction of muscle fibers.
PDF Polarity sorting drives remodeling of actin-myosin networks Since actin-myosin remodeling is rather fast, we develop an 95 open chamber assay that allows us to capture the initial steps of myosin-mediated 446 In the phase diagrams (Figs. 7d,e and 8a,b), the boundary between the Polarity Sorting (PS) and Filament 447 Buckling (FB) mechanisms was...
Actin and Myosin | Biology Dictionary Actin and myosin are both proteins that are found in all types of muscle tissue. Myosin forms thick filaments (15 nm in diameter) Actin and myosin work together to produce muscle contractions and, therefore, movement. First, a motor neuron delivers an electrical signal to the muscle cell from the brain.
› en › librarySmooth muscle: Structure, function, location | Kenhub Oct 28, 2021 · The actin filaments are stretched between dense bodies in the cytoplasm and attachment plaques at the cell membrane. The myosin filaments lie between the actin filaments. Furthermore intermediate filaments such as desmin and vimentin support the cell structure.



























0 Response to "39 myosin and actin diagram"
Post a Comment