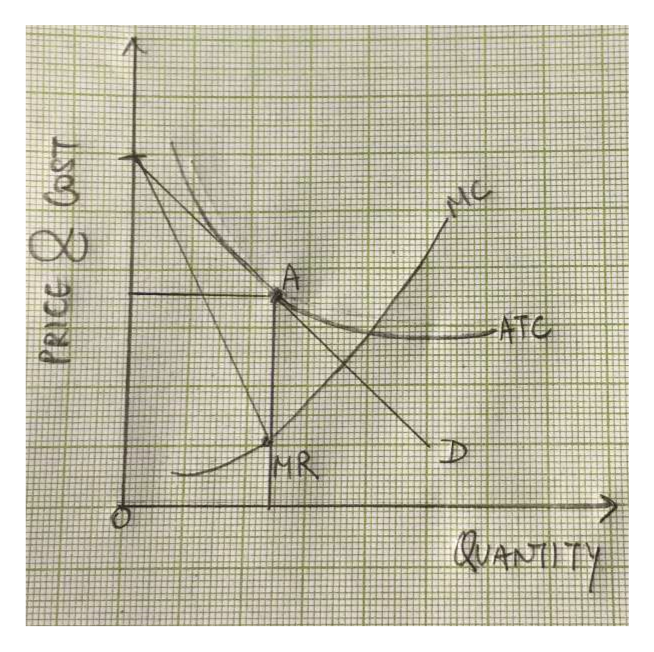
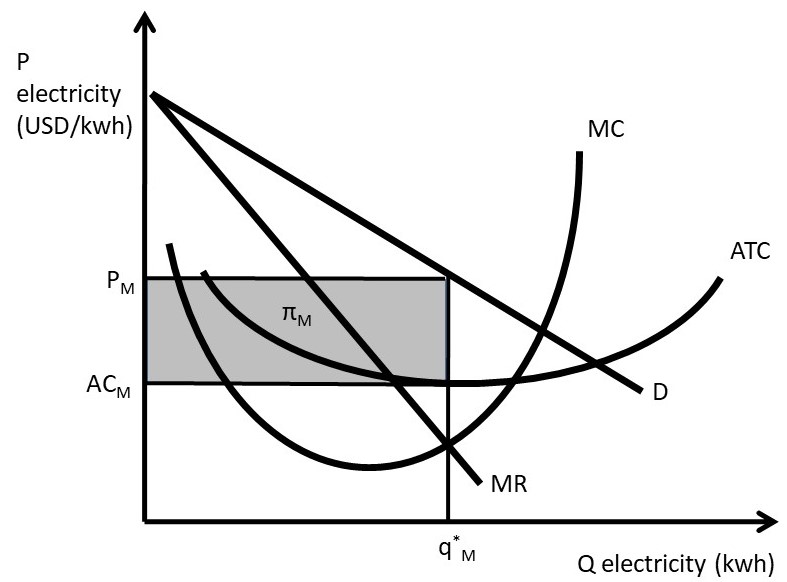
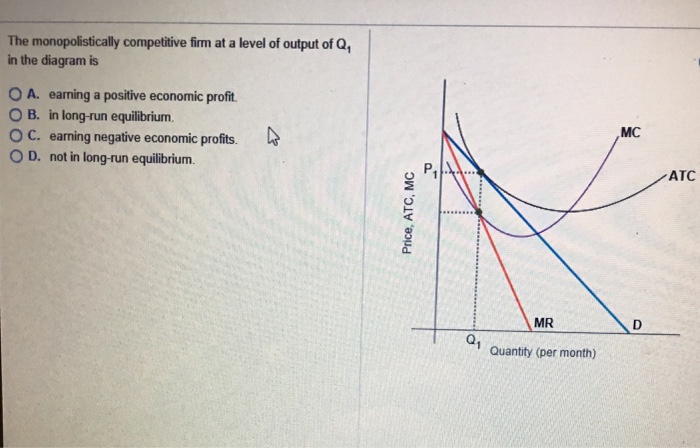
41 the monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is
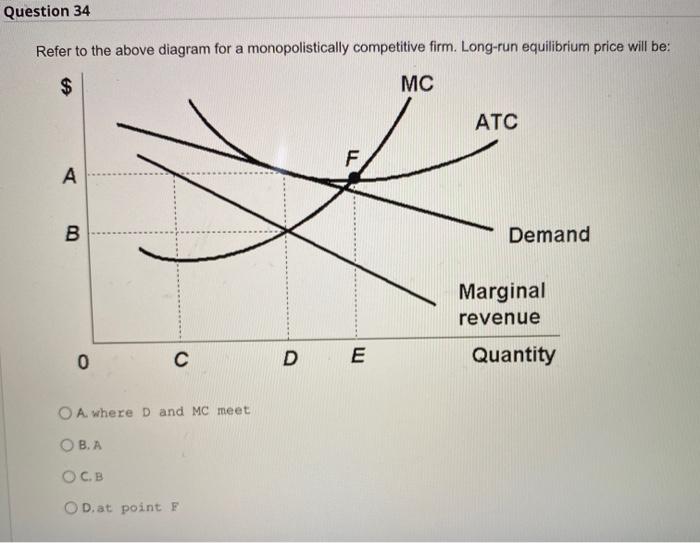
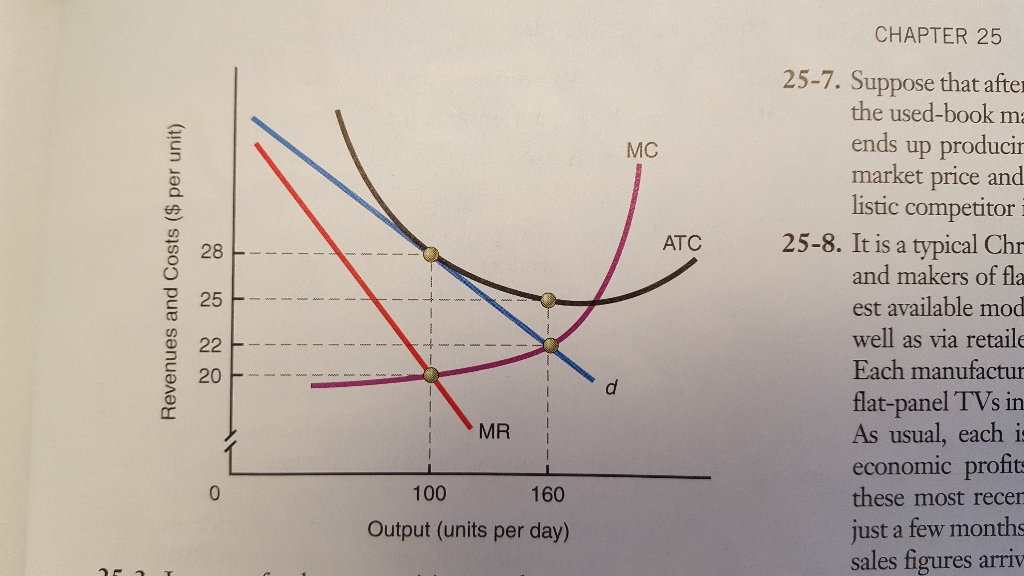
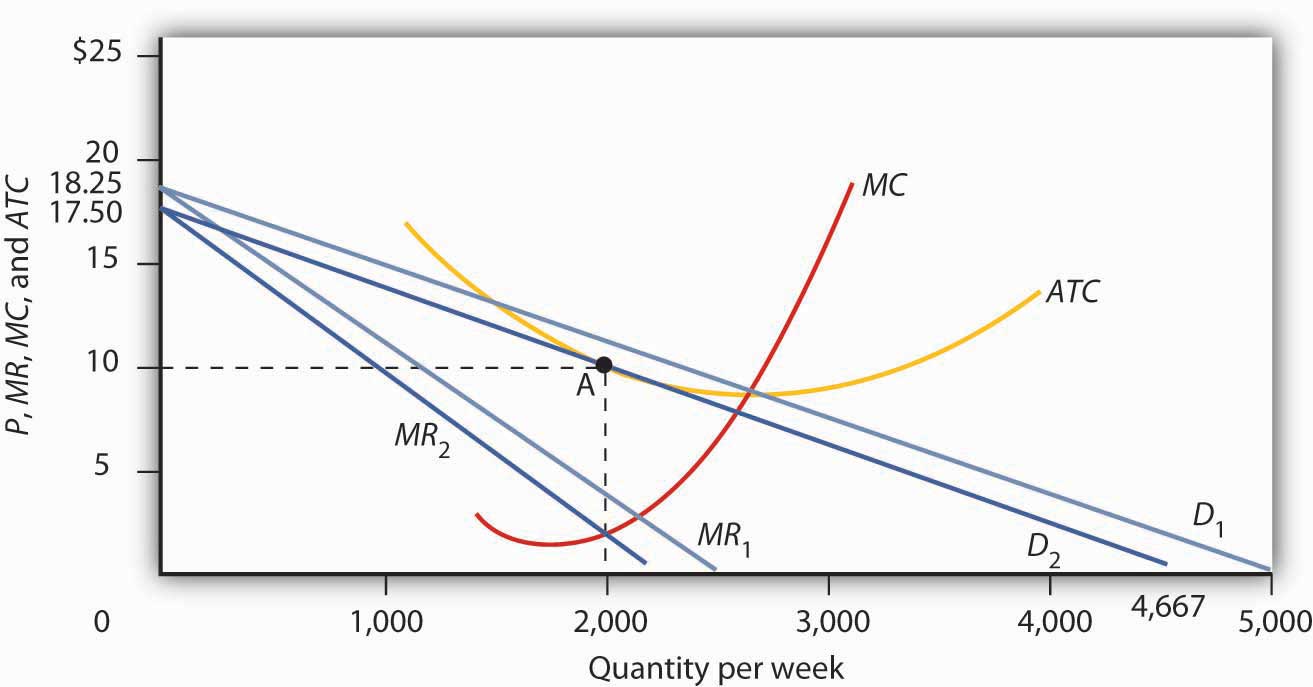
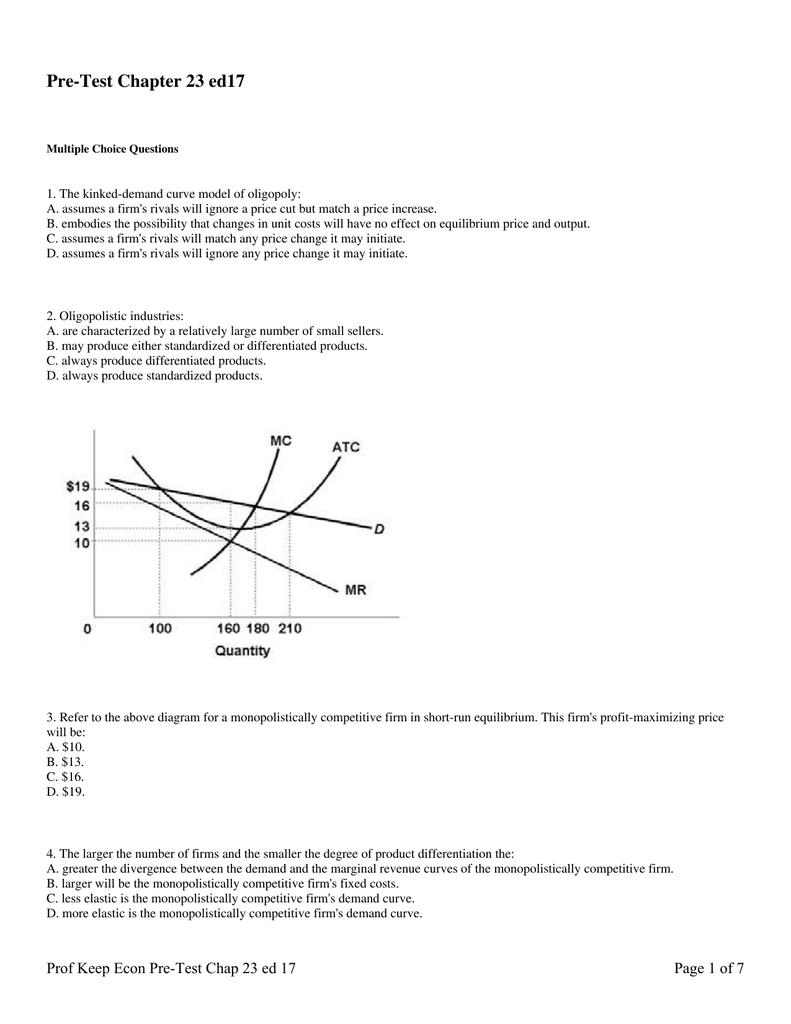
Monopolistic Competition Equilibrium| Long-run| Short-run ... Demand Curve for the Monopolistically Competitive Firm. Monopolistic competition is a type of competition that exists in between two extremes. Perfect competition and the monopoly.. A perfectly competitive firm's demand curve is a horizontal line with infinite price elasticity.The demand curve of a monopoly firm is the demand curve for the industry, and it is downward sloping, indicating ... Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... 26. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be: A. 100. B. 160. C. 180. D. 210. 27. When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium: A. production takes place where ATC is minimized. B. marginal revenue equals marginal cost and ...
Refer to the diagram The monopolistically competitive firm ... 62. Refer to the diagram. The monopolistically competitive firm shown A. will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output. B. cannot operate at a loss. C. is in long-run equilibrium. D . is realizing an economic profit.

The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically ... Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry. In the long run firms will: A.leave this industry, causing both demand and the ATC curve to shift upward. B.enter this industry, causing demand to rise and the ATC curve to shift downward. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... Refer to the information provided in Figure 15.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Figure 15.4 Refer to Figure 15.4. Assume The Hand Made Shirt Shop has fixed costs of $150 and is a monopolistically competitive firm. microeconomics chapter 25 Flashcards - Quizlet Monopolistic competition is similar to monopoly because in both industry structures, the firm's demand curve is downward sloping. Consider the diagram at the right depicting the revenue and cost conditions faced by a monopolistically competitive firm.
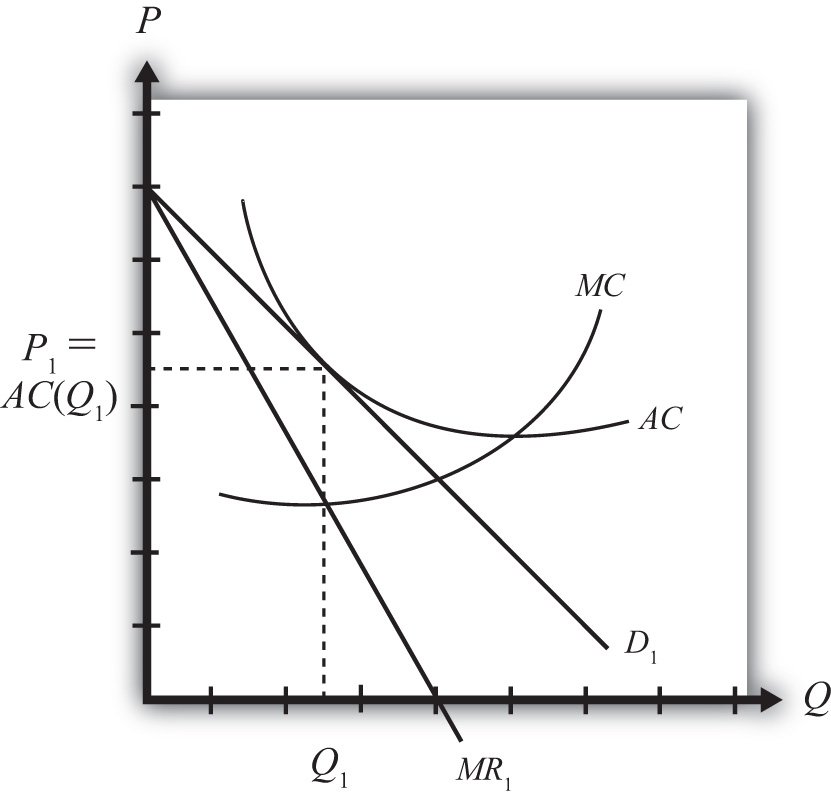
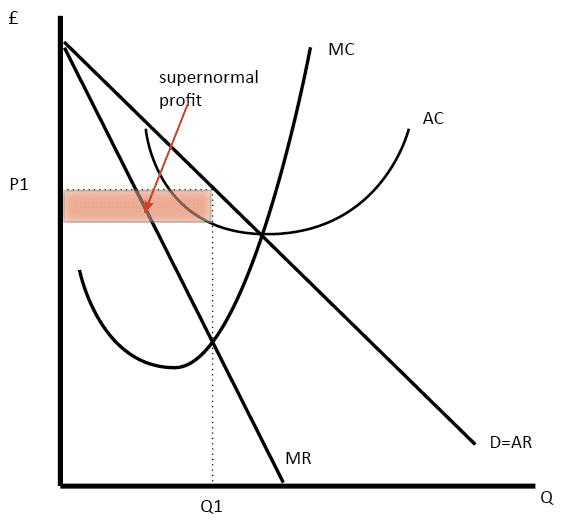
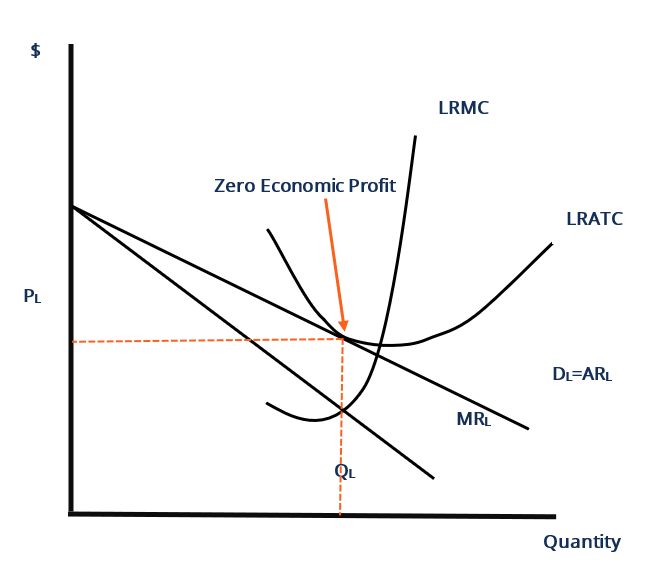
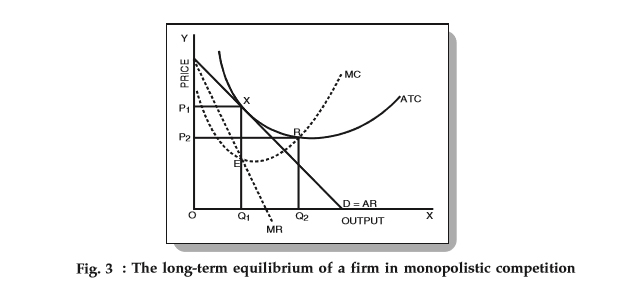
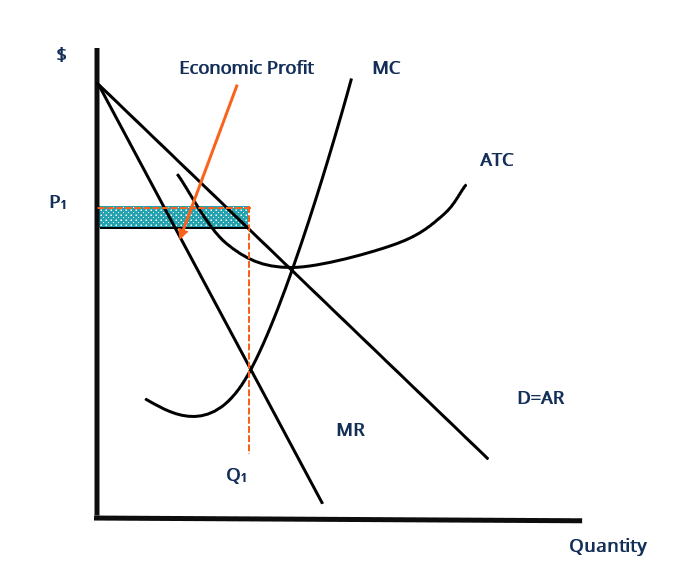
The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is. Chapter 25 Homework Flashcards - Quizlet In the diagram the demand curve (which shows prices that consumers will pay for various quantities) is tangent to the average total cost curve. Therefore (P minus− ATC) = 0, and economic profits are zero. The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is A.earning negative economic profits. Monopoly diagram short run and long run - Economics Help In a competitive market, firms may produce quantity Q2 and have average costs of AC2. A monopoly can produce more and have lower average costs. This enables efficiency of scale. Related. Monopolistic competition - where the short-run equilibrium is different from the long-run equilibrium; Monopoly - advantages and disadvantages. Solved The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for ... The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. Dollars per unit LRAC MC E1 P2- Demand MR 01 Output FIGURE 11-3 Refer to Figure 11-3. This monopolistically competitive firm is allocatively inefficient because in long-run equilibrium, OA) MC is greater than price. Chapter 13 (Monopolistic Competition) Homework Flashcards ... The long-run equilibrium position of the monopolistically competitive firm occurs at a point where average costs are - constant. - increasing. - decreasing. - at their minimum point. decreasing Refer to the diagram. The monopolistically competitive firm shown - will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output.
The Effects of Trade in a Monopolistically Competitive ... Use a monopoly diagram for a representative monopolistically competitive firm to depict a long-run equilibrium. Understand how the market equilibrium changes upon opening to free trade. Assume that there are two countries, each with a monopolistically competitive industry producing a differentiated product. Monopolistic competition - LegitWriting Welcome to Legit Writing. Draw the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm, label the level of output it will choose to produce in the short-run, and label the profit of the firm. Draw the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in the long-run and label its long-run level of output. Pricing in Theory (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Monopolistic competition is similar to pure competition in that there are a large number of firms selling a product that has been differentiated from that sold by other firms in the industry. That is, although the products sold by monopolistically competitive firms are good substitutes, they are not perfect substitutes. Monopolistic Competition in the Long-run The monopolistically competitive firm's long‐run equilibrium situation is illustrated in Figure . The entry of new firms leads to an increase in the supply of differentiated products, which causes the firm's market demand curve to shift to the left.
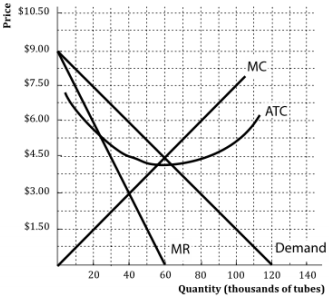
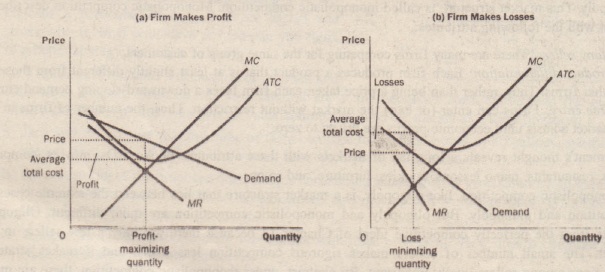
8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price similar to the way that a monopolist does. Since they face a downward sloping demand curve, the same considerations about how elasticity affects revenue are relevant, and the firm will maximize profits where MR = MC when P > MR. Step 1. Monopolistic competition - Economics Online Monopolistic competition The model of monopolistic competition describes a common market structure in which firms have many competitors, but each one sells a slightly different product. Monopolistic competition as a market structure was first identified in the 1930s by American economist Edward Chamberlin, and English economist Joan Robinson. Ch13 Flashcards - Quizlet Consider the diagram below depicting the revenue and cost conditions faced by a monopolistically competitive firm, and then answer the following questions. Suppose the firm produces where there is a break-even price. a. The resulting price and quantity combination is illustrated in graph above by point . 13 Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically ... 13. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: a. loss of $320. B loss of $480. c. profit of $280. d. profit of $600.
PDF Characteristics of Monopolistic competition Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition Diagram at right shows long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm. economic profits? price mark-up (P vs ... a firm in monopolistic competition must be in a state of continuous product development. New product development allows a firm to gain a competitive edge, if only temporarily ...
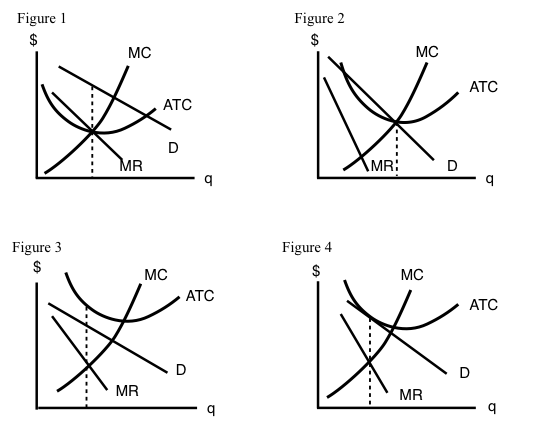
Solved > 31) Refer to Figure 11-2. Diagram C depicts ... C) monopolistically competitive industry. D) oligopolistic industry. E) an imperfectly competitive industry 32) Refer to Figure 11-2. Diagram D depicts the only possible long -run equilibrium for a typical firm in A) a perfectly competitive industry. B) a monopolistic industry. C) a monopolistically competitive industry. D) an oligopolistic ...
10.1 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Economics The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price in much the same way as a monopolist. A monopolistic competitor, like a monopolist, faces a downward-sloping demand curve, and so it will choose some combination of price and quantity along its perceived demand curve.
Monopoly Vs Monopolistic Competition (With Diagram) It means small fall in price, will lead to big increase in demand. Fig. 14 represents AR and MR under monopolistic competition. 6. Decision-Making: Under monopoly and monopolistic competition, a firm cannot determine both price and output at the same time. Under monopolistic competition, the firm has to spend more on selling costs.
Microeconomics Chapter 13 Flashcards - Quizlet When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium, MR = MC and minimum ATC > P. Refer to the above graphs. A short-run equilibrium that would produce profits for a monopolistically competitive firm would be represented by graph A. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. This firm is experiencing
PDF Chap 13 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly MULTIPLE ... 29)In the above figure, the monopolistically competitive firm earns an economic profit of A)between $50.01 and $100 per day. B)greater than $100.01 per day. C)$0. D)between $0 and $50 per day. 29) 30)The above figure is for a firm in monopolistic competition. The diagram represents the short run rather than the long run because
PDF ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically ... Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically. This preview shows page 5 - 7 out of 40 pages. 34. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: A. loss of $320. B. profit of $480. C. profit of $280. D. profit of $600. 35.
microeconomics chapter 25 Flashcards - Quizlet Monopolistic competition is similar to monopoly because in both industry structures, the firm's demand curve is downward sloping. Consider the diagram at the right depicting the revenue and cost conditions faced by a monopolistically competitive firm.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... Refer to the information provided in Figure 15.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Figure 15.4 Refer to Figure 15.4. Assume The Hand Made Shirt Shop has fixed costs of $150 and is a monopolistically competitive firm.
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically ... Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry. In the long run firms will: A.leave this industry, causing both demand and the ATC curve to shift upward. B.enter this industry, causing demand to rise and the ATC curve to shift downward.


















0 Response to "41 the monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is"
Post a Comment