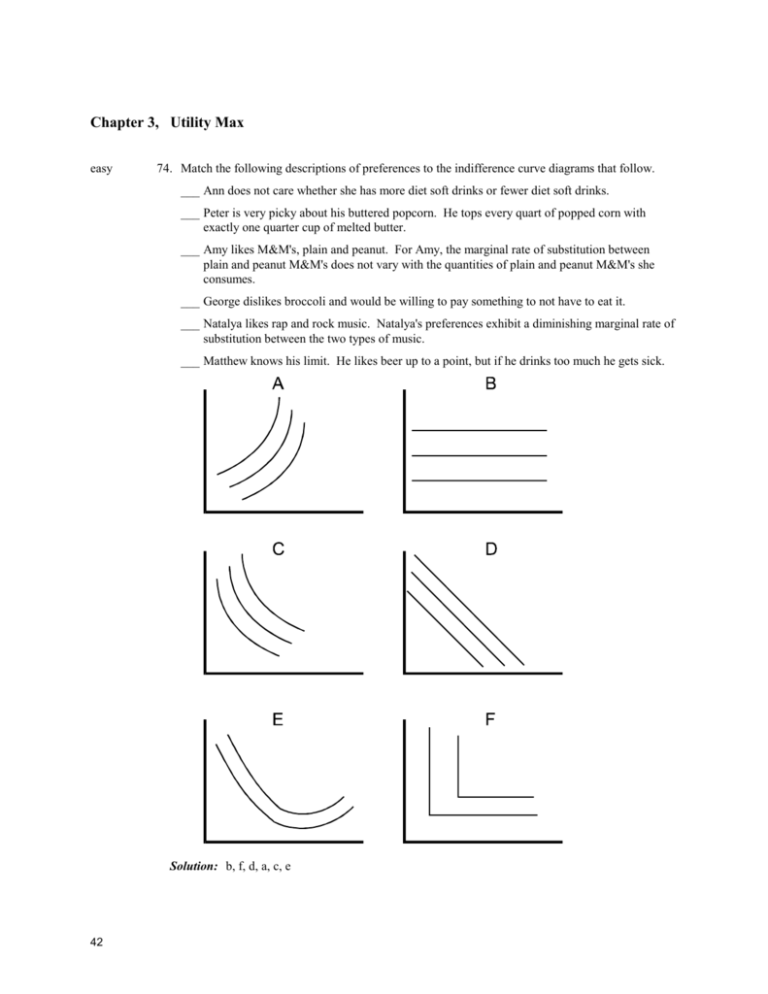
42 when the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution,
Sample FinalA - UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO ... - Course Hero View Test Prep - Sample FinalA from ECONOMICS MGEB02 at Al-Sirat Degree College. UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT MGEB02: Price Theory: A Mathematical Approach Instructor: (PDF) Indifference Curve Analysis: The Correct and the ... The thesis of this paper is that when the indifference curve is concave to the origin, the optimal point on the budget line is not the corner solution on the highest (most north eastern)...
Optimal point on budget line (video) - Khan Academy Well, there is no other point on the budget line that is to the top right. In fact, every other point on our budget line is to the bottom left of this indifference curve. So every other point on our budget line is not preferable. So remember, everything below an indifference curve-- so all of this shaded area.

When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution,
EBOOK: Microeconomics and Behaviour: Second South African ... A P (Pierre) de Villiers, Robert Frank · 2014 · Business & EconomicsLine Bin Fig. 4.45 is the original budget constraint. ... But in each case note that the slope of the indifference curve at the optimal point is the same. When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget ... 11 Dec 2019 When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution: A. the marginal rate of substitution usually does not equal the ratio of prices for the two goods. B. the budget line must have a kink in it. C. the consumer does not spend her entire budget on the two goods. D. All of the above. Indifference Curve Questions and Answers | Study.com Consider the indifference curve budget line model of labor supply, and assume consumption and leisure are both normal goods. A higher wage rate would result in: a. more consumption and less leisure...
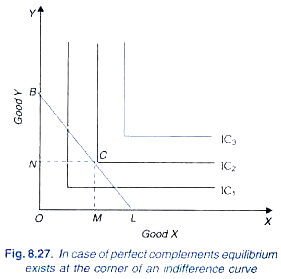
When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution,. ECON HW 3 Flashcards | Quizlet Consumer's Equilibrium: Meaning, Conditions and Corner ... The consumer will thus be in equilibrium at the corner point P of the indifference curve and the budget line PQ and consume only OP quantity of good Y and none of good X. If the consumer wishes to consume only good X, the corner solution will be at point Q on the indifference curve I 3. 3. Notes on Convex Indifference Curves and Corner Equilibrium The indifference curve analysis enables us to explain even this phenomenon. Consider Figure 8.22 where indifference map between two goods X and Y and budget line BL are such that the interior solution is not possible and consumer in its equilibrium position at point B will not consume any quantity of commodity X. dokumen.pub › microeconomic-theory-basicMicroeconomic Theory: Basic Principles and Extensions [12th ... Such a solution will have two properties: (1) The x’s will obey the constraint because the last line in Equation 2.47 imposes that condition and (2) among all those values of x’s that satisfy the constraint, those that also solve Equation 2.47 will make + (and hence f) as large as possible (assuming second-order conditions are met).
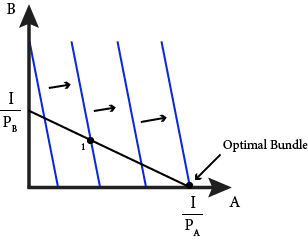
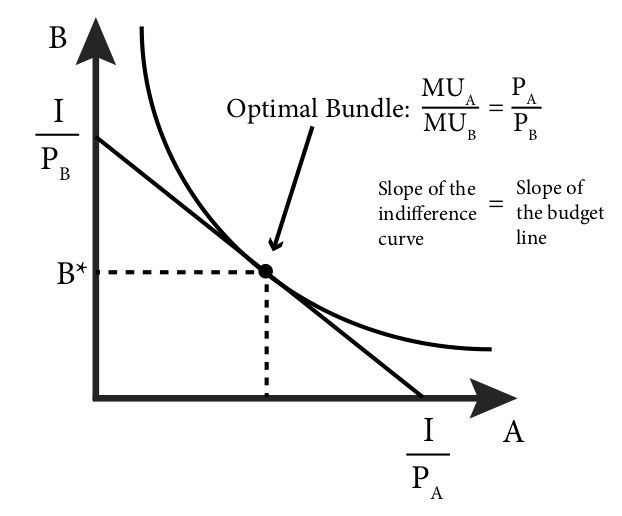
Module 4: Consumer Choice - Intermediate Microeconomics 1. The consumer's optimal choice is on the budget line itself, not inside the budget constraint. This is why we can focus on the line rather than the whole set of affordable bundles. 2. At the optimal choice, the indifference curve just touches the budget line and so at this one point they have exactly the same slope. PDF Econ 201: Introduction to Economic Analysis - Reed Interior solution •Most commonly drawn situation •Highest attainable indifference curve is at tangency with budget constraint •Slopes are equal, so MRS AB= P A /P B •Marginal benefit of one more ounce of asparagus (MRS) = marginal cost (relative price) •In terms of marginal utilities: •Marginal utility per dollar is equal 5 AB B AB U P PP Corner solution - Wikipedia This diagram shows an example corner solution where the optimal bundle lays on the x-intercept at point (M,0). IC 1 is not a solution as it does not fully utilise the entire budget, IC 3 is unachievable as it exceeds the total amount of the budget. The optimal solution in this example is M units of good X and 0 units of good Y. Indifference Curve Analysis | Microeconomics Shape of an Indifference Curve. The indifference curve Um has four points labeled on it: A, B, C, and D (see Figure 1). Since an indifference curve represents a set of choices that have the same level of utility, Lilly must receive an equal amount of utility, judged according to her personal preferences, from two books and 120 doughnuts (point A), from three books and 84 doughnuts (point B ...
Consumer Theory Introduction Outline Preferences Sometimes, the highest indifference curve attainable does not occur when the budget line and indifference curve are tangent. We have a corner solution in this ...18 pages ECON306 Chapter 3 & 4 MyLab Flashcards - Quizlet At the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram (assuming an interior solution) All of the above: (1) the marginal rate of substitution between the two goods equals the ratio of their prices. (2) the optimal indifference curve is tangent to the budget line. (3) the consumer spends his or her entire budget on the two goods. (PDF) Indifference Curve Analysis The Correct and the ... The thesis of this paper is that when the indifference curve is concave to the origin, the optimal point on the budget line is not the corner solution on the highest (most north eastern) indifference curve, the analysis all too often of fered in the literature, but, rather , somewhat paradoxically , the lowest Solved When the optimal point on an indifference curve and ... When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner? solution, A. the marginal rate of substitution usually does not equal the ratio of prices for the two goods. B. the budget line must have a kink in it. C. the consumer does not spend her entire budget on the two goods. D. All of the above.
PDF Solving for Optimal Bundle - ticoneva Solving for Optimal Bundle . The whole point of having indifference curve (IC) and budget constraint (BC) is to determine the optimal allocation—the feasible bundle that gives the highest utility to the ... Corner solution—individual buys only some of the goods .
Does convexity imply monotonicity? When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution, the marginal rate of substitution usually does not equal the ratio of prices for the two goods. Suppose we didn't have a budget constraint. When two goods are perfect complements the income effect is always?
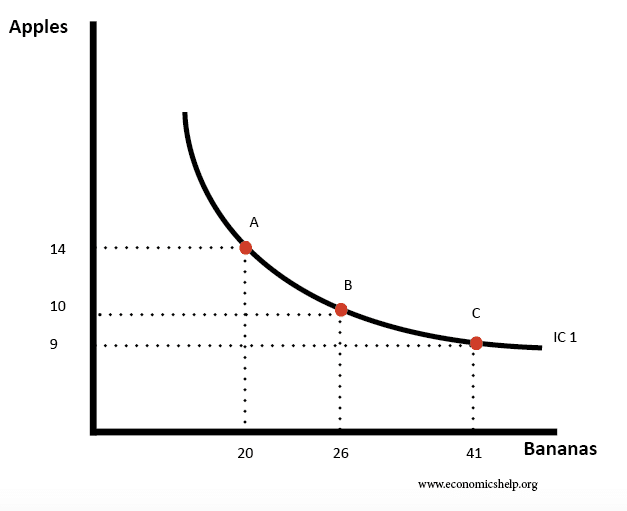
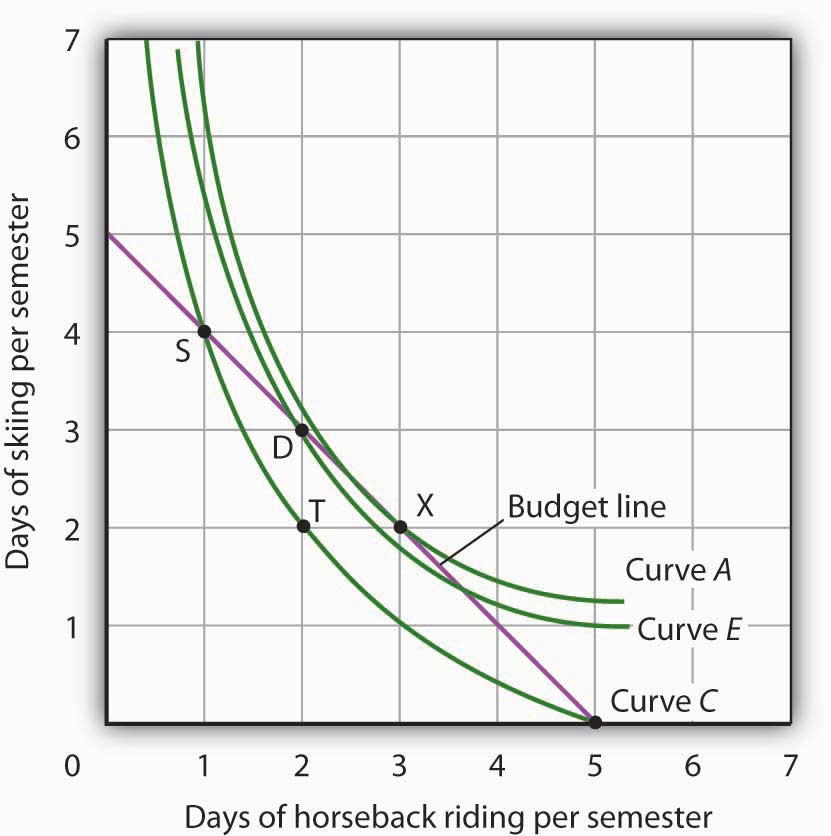
7.3 Indifference Curve Analysis: An Alternative Approach ... In general, any combination that lies above and to the right of an indifference curve is preferred to any point on the indifference curve. We can draw an indifference curve through any combination of two goods. Figure 7.11 "Indifference Curves" shows indifference curves drawn through each of the points we have discussed.
38 when the optimal point on an indifference curve and ... When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution: A. the marginal rate of substitution usually does not equal the ratio of prices for the two goods. B. the budget line must have a kink in it. C. the consumer does not spend her entire budget on the two goods. D. All of the above.
Micro Final HW 3 Flashcards | Quizlet When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution, the marginal rate of substitution usually does not equal the ratio of prices for the two goods. The diagram on the right shows a consumer's budget line and three indifference curves for goods X and Y.
PDF 4.Consumer Problem 4 - Columbia University What are the properties of this optimal point? 1. All the money is spent i.e. the budget line holds at equality L 5 T 5+ L 6 T 6 L U 2. The slopes of the indifference curve and the budget line are the same i.e. the Marginal Rate of Substitution equals the ratio of prices This is the tangency condition 15 Rational Constrained Choice x1 x2 x1* x2*
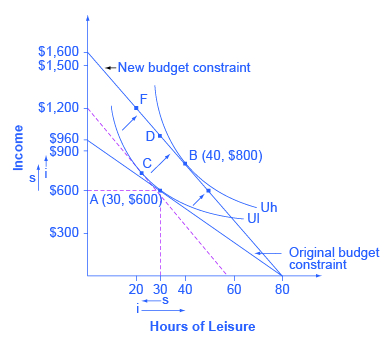
quizlet.com › 74234408 › microeconomic-theory-ch-4Microeconomic Theory, Ch. 4 Flashcards | Quizlet If the consumer's income increases while the prices of both goods remain unchanged, what will happen to the budget line? A) The budget line rotates inward from the intercept on the horizontal axis. B) The budget line rotates outward from the intercept on the vertical axis. C) The budget line shifts inward without a change in slope.
Solved At the optimal point on an indifference curve and ... At the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram? (assuming an interior? solution) A. the marginal rate of substitution between the two goods equals the ratio of their prices. B. the consumer spends his or her entire budget on the two goods. C. the optimal indifference curve is tangent to the budget line. D. All of the above.
Econ351 Chapter05 Pre-Quiz - Econ351Chapter5PreQuiz 1 ... 2. When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution, a. The marginal rate of substitution usually does not equal the ratio of prices for the two goods. b. The consumer does not spend her entire budget on the two goods. c. The budget line must have a kink in it. d. All of these above. Answer: A
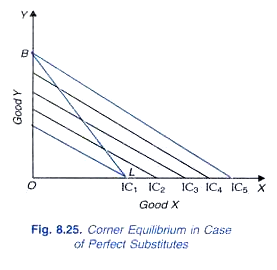
Why are corner solutions especially likely in the case of ... A corner solution is a special solution to an agent's maximization problem in which the quantity of one of the arguments in the maximized function is zero. In non-technical terms, a corner solution is when the chooser is either unwilling or unable to make a tradeoff. Also Know, what is the MRS of perfect substitutes?
OneClass: When is a corner point solution always the ... When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution: A. the marginal rate of substitution usually does not equal the ratio of prices for the two goods. B. the budget line must have a kink in it. C. the consumer does not spend her entire budget on the two goods. D. All of the above.
When is an indifference curve tangent to the budget line ... Answer (1 of 3): * An indifference curve is a curve That shows all combination of a good that provide the same level of utility * Budget line Represents all The combination of good and services That a consumer may purchase Given current price Within his given income To maximize utility one can...
PDF Quarterly Journal OeconomiA - ResearchGate the origin, the optimal point on the budget line is not the corner solution on the highest (most north eastern) indifference curve, the analysis all too often offered in
Chapter 3 - Consumer Behavior Jon's budget line is now flatter than his indifference curves, and his optimal bundle is the corner solution with 4 Sprites and no Cokes.20 pages
Indifference Curve Questions and Answers | Study.com Consider the indifference curve budget line model of labor supply, and assume consumption and leisure are both normal goods. A higher wage rate would result in: a. more consumption and less leisure...
When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget ... 11 Dec 2019 When the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution: A. the marginal rate of substitution usually does not equal the ratio of prices for the two goods. B. the budget line must have a kink in it. C. the consumer does not spend her entire budget on the two goods. D. All of the above.
EBOOK: Microeconomics and Behaviour: Second South African ... A P (Pierre) de Villiers, Robert Frank · 2014 · Business & EconomicsLine Bin Fig. 4.45 is the original budget constraint. ... But in each case note that the slope of the indifference curve at the optimal point is the same.











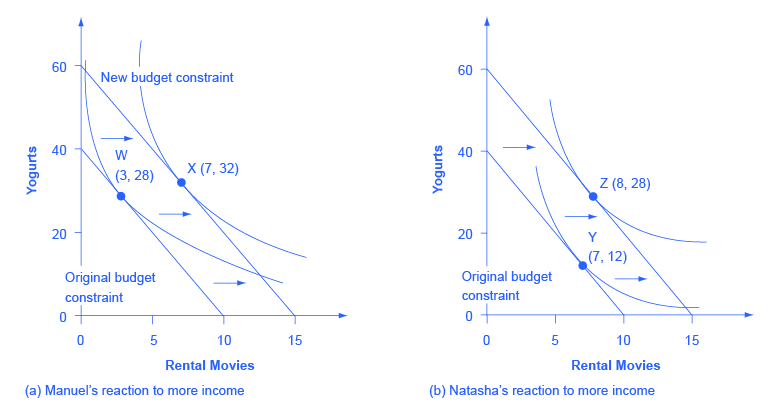
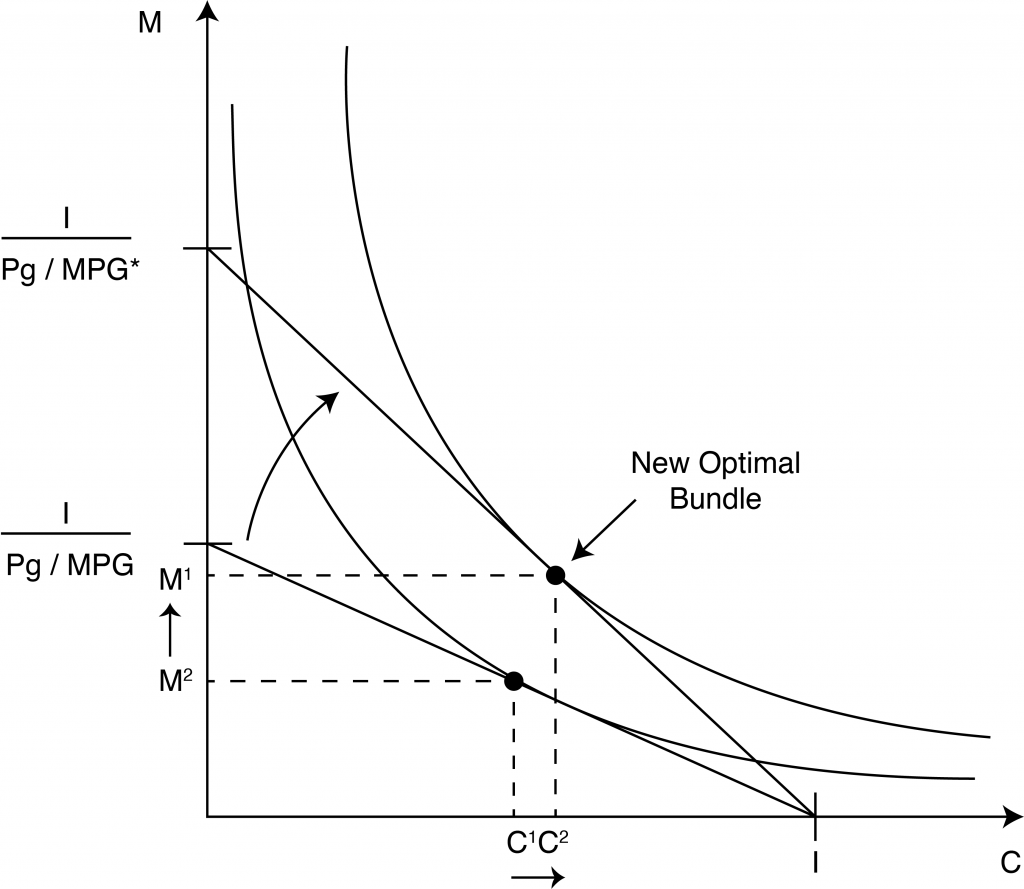

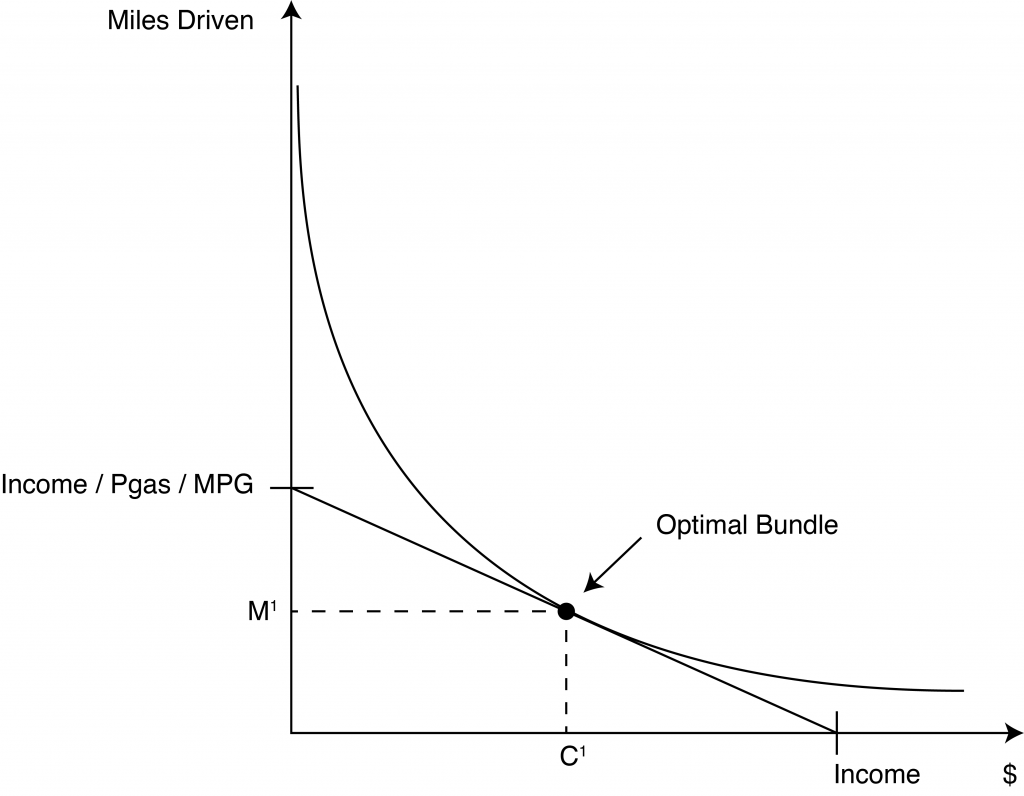



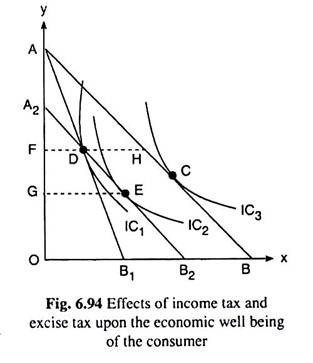


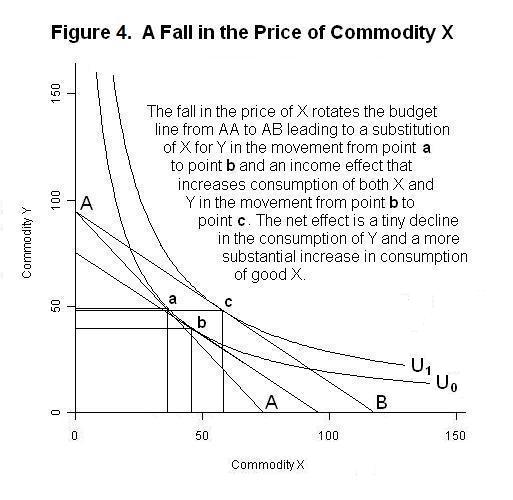
0 Response to "42 when the optimal point on an indifference curve and budget line diagram is a corner solution,"
Post a Comment