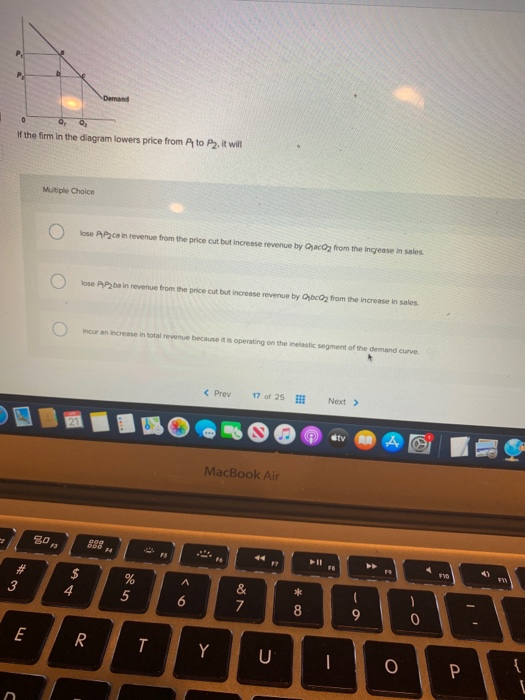
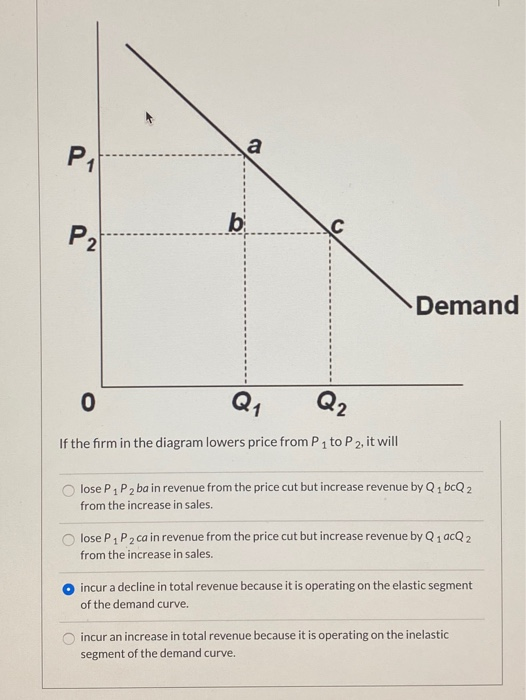
38 if the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will
CHAP 12 Flashcards - Quizlet If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. ... (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by. producing where marginal revenue equals zero and charging a price equal to demand ... ECON CH 12 Flashcards | Quizlet In the accompanying diagram, if price is reduced from P1 to P2, total revenue will: Increase by C − A. ... When a monopolist lowers price to sell more output, the lower price applies to all units sold. ... Refer to the long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q2 at an average cost of ATC3, then the firm is: ...
PDF before your name, TA name, and section number staple Part ... What is the level of output the firm will produce of the firm acts as a perfect price discriminating monopolist? Show your work. b. ... P1 is that price on the demand curve when quantity is equal to 18 + 10 = 28: thus, P1 ... P2 is that price on the demand curve when quantity is equal to 28 + 4 = 32: thus, P2 = 20 - (1/2)(32) = $4 per unit of ...
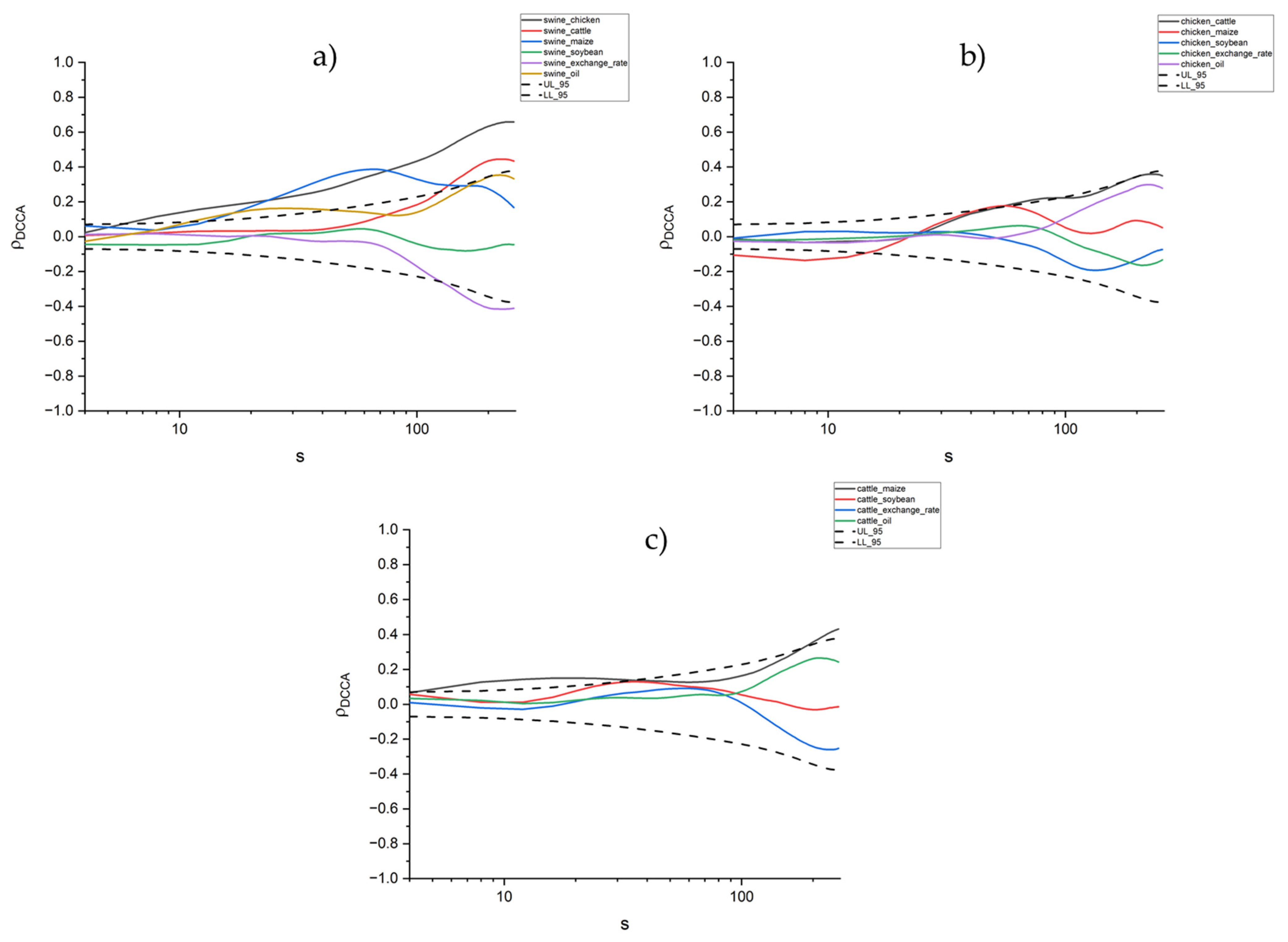
If the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will
Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips 41. If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B. lose P1P2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales. Ch 6 Elasticity - Subjecto.com Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A. B+D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: D. increase total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: D. that demand is elastic with respect to price. Chapter 10 | Business Quiz - Quizizz 120 seconds. Q. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm should produce. answer choices. 4 units at a loss of $109. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 8 units at a loss of $48.80.
If the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will. Answered: 17. At price P1, the firm would… | bartleby At price P1, the firm would produce: Q1 units 6. Q3 units. C Q5 units. d Zero units. ... Price and ATC AVC MC cost P. P3 P2 Pr Q,… A: The firm shuts down when P< ... In the long run, firms are producing output at lowers point of average cost curve. This point can be… Microeconomics Flashcards - Quizlet 17. If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B. lose P1P2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales. Section 2: The Monopolist's Revenue ... - Inflate Your Mind Therefore, the marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve. At any output, except for the first output value, marginal revenue is less than price and the average revenue. The following example illustrates this. The monopolist sells 100 newspapers at a price of $.50. It sells 120 newspapers at $.45, and 140 newspapers at $.40 per paper. Price Discrimination - A-level Economics Notes In this case to maximise profits, the firm produces quantity q2 and price p2. This price is below the original price p1 when there is no price discrimination. So the elastic group is better off under price discrimination - they face a lower price and higher consumer surplus. The right diagram shows the group with the more inelastic price ...
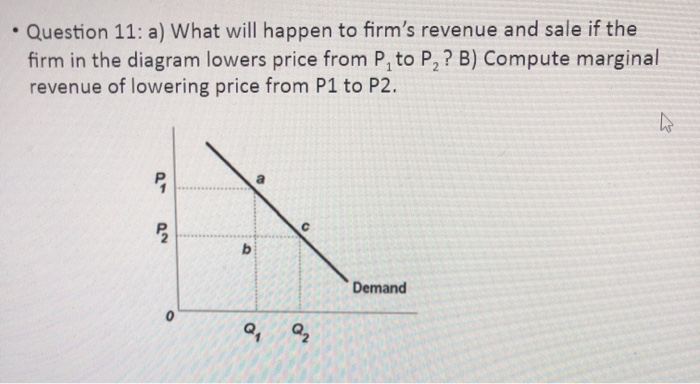
PDF Econ 101A — Final exam Th 16 December. price and quantity of cars produced. (6 points) 4. Compare the quantities and prices produced to the monopoly case. Provide intuition on the result. (4 points) 5. Compare total profits in Cournot and in monopoly (3 points). 6. Draw a graph with price on the yaxis and quantity on the xaxis. Locate the Cournot and monopoly outcomes. Chapter 6: Price Elasticity of Demand Calculate the price elasticity of supply for the following price ranges: P1 = $2.20 Q1 = 13 . P1 = $2.00 Q1 = 11. P1 = $1.80 Q1 = ... raise price by more than $1. 3. raise price by $1. 4. lower price by $1. Elasticity - Quick Quiz. PRICE ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY ... 1. the profit-maximizing level of production. 2. why the firm's long-run average ... ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com This firm will earn only a normal profit if product price is: a. P1 b. P2 c. P3 d. P4. c. P3. In answering the question, assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axis. ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: Maximizing Revenue instead of Price - Tomoyo's IB Blog According to Figure 1, the point at whcih MR intersects AC sets the quantity Q1, as well as price P1. In comparison to the maximizing price, maximizing revenue has a lower price, but with a higher quantity. Therefore, price of each unit of quantity sold will decrease but the number of units sold will increase. Thus the firm will lose profit ...
Refer to the above diagram The decline in price from P1 to ... 7. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2will: A. increase total revenue by D. B. increase total revenue by B + D. C. decrease total revenue by A. D. increase total revenue by D - A. 8. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: A. that consumer purchases are relatively insensitive to price changes. 19 The efficient scale of the firm is the quantity of ... The efficient scale of the firm is the quantity of output that a. maximizes marginal product. b. maximizes profit. c. minimizes average total cost. d. minimizes average variable cost. ____ 20. When marginal cost is less than average total cost, a. marginal cost must be falling. b. average variable cost must be falling. Chapter 12 Flashcards | Quizlet A single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes. ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will. Lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. 15 The more elastic the demand facing a firm A the higher ... See Page 1. 15) The more elastic the demand facing a firm, A) the higher the value of the Lerner index. B) the lower the value of the Lerner index. C) the less monopoly power it has. D) the higher its profit. b . the lower the value of the Lerner index .
Econ Final Flashcards | Quizlet P2. If a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm is selling its 100th unit of output for $35, its marginal revenue: will be less than $35. If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales.
Refer to the graph above if labor supply ... - Course Hero 131. Refer to the graphs above. If product demand increases from D1 to D2, causing the product price to increase, firm A (a supplier of this product) will: A. pay a higher wage rate and reduce employment from q2 to q1. B. pay a lower wage rate and increase employment from q3 to q4. C. increase employment because its MRP curve will shift rightward.
PDF ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 2 because if demand is price inelastic and the price increases, then the total revenues will increase. (If demand in elastic and the price increases the total revenue will go down). So you have to calculate the coefficient of price elasticity of demand. P1 = $ 70; Q1 = 40 and P2 = $ 80; Q2 = 30 -10 / 35 Ed = ----- = .286 / .133 = 2.2
Answered: Two firms compete by choosing price.… | bartleby suppose there are two firms that compete in prices, say firms 1 and 2, but that the firms produce differentiated products. Suppose that the demand for firm 1 is q1(p1,p2)=10-2p1+p2 and the demand for firm 2 is q2(p2,p1)=10-2p2+p1. Also, assume that firm 1 has a constant marginal cost of c1 = 2 and firm 2 has a constant marginal cost of c2 = 3. i.
Reading: Illustrating Monopoly Profits | Microeconomics Thus,the monopoly will charge a price (P1). In Step 3, the monopoly identifies its profit. Total revenue will be Q1 multiplied by P1. Total cost will be Q1 multiplied by the average cost of producing Q1, which is shown by point S on the average cost curve to be P2.
Solved Demand If the firm in the diagram lowers price from ... Economics questions and answers. Demand If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will lose P1 P2 ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ 2 from the increase in sales. lose P1 P2 ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q 1 acQ2 from the increase in sales. o incur a decline in total revenue ...
182 Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms Figure ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: ANSWER: lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. 195. Refer to the diagram. The quantitative difference between areas Q1bcQ2 and P1P2ba in the diagram measures: ANSWER: marginal revenue. 196.
Chapter 10 | Business Quiz - Quizizz 120 seconds. Q. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm should produce. answer choices. 4 units at a loss of $109. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 8 units at a loss of $48.80.
Ch 6 Elasticity - Subjecto.com Refer to the above diagram. If price falls from P1 to P2, total revenue will become area(s): A. B+D. Refer to the above diagram. The decline in price from P1 to P2 will: D. increase total revenue by D-A. Refer to the above diagram. In the P1 to P2 price range, we can say: D. that demand is elastic with respect to price.
Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips 41. If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B. lose P1P2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales.






![Output combinations P1,P2\documentclass[12pt]{minimal ...](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288933213/figure/fig2/AS:960357875085313@1605978568214/Output-combinations-P1-P2documentclass12ptminimal-usepackageamsmath_Q320.jpg)



/dotdash_Final_Which_Vertical_Option_Spread_Should_You_Use_Sep_2020-01-def4a17c8b054eba9f90189fc30bf002.jpg)


0 Response to "38 if the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will"
Post a Comment