39 4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram
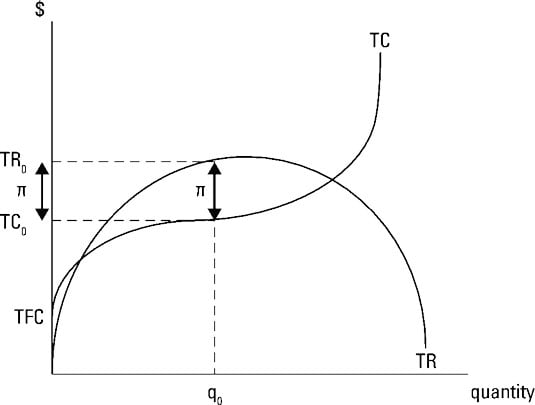
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Marginal_revenueMarginal revenue - Wikipedia Marginal revenue (or marginal benefit) is a central concept in microeconomics that describes the additional total revenue generated by increasing product sales by 1 unit. To derive the value of marginal revenue, it is required to examine the difference between the aggregate benefits a firm received from the quantity of a good and service produced last period and the current period with one ... Cost, Profit, and Revenue Run-Down - AP/IB/College ... Profit Maximization One way to determine the profit maximizing quantity for a firm to produce is to look at total revenue versus total profit. Total revenue, for a perfectly competitive firm, will increase at a constant rate. The total cost will increase at varying rates.
› theory-of-productionThe Production Process (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion For example, 4 machines and 2 workers produce 50 units of output. The operation of law of diminishing returns can also be discerned. When the input of machines is held constant at 4 units, then additional units of labour bring about smaller and smaller additions to output. Thus, along a given row output increases, but at a decreasing rate.
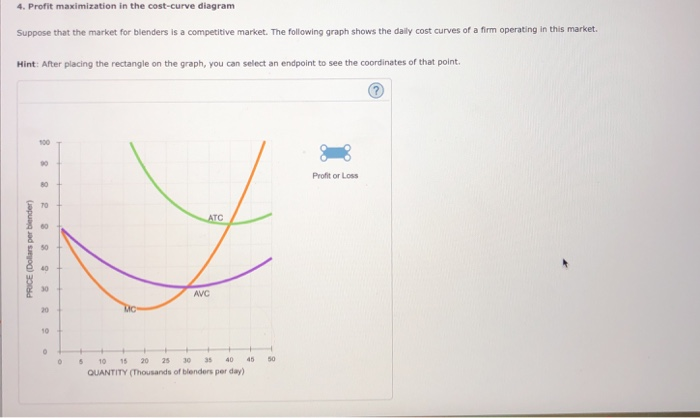
4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram
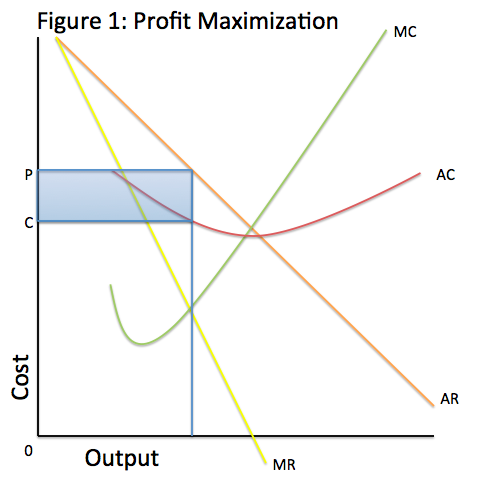
Homework ch 7 flashcards Flashcards | Quizlet Producer surplus is the. difference between a seller's reservation value and the price he finally receives. Figure 12-4 shows the cost and demand curves for a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market. Refer to Figure 12-4. If the market price is $30 and the firm is producing output, what is the amount of the firms profit or loss. Microeconomics What Do Firms Try To Maximize? - ictsd.org As an example, the diagram below illustrates the marginal revenue-marginal cost perspective. How Do You Maximize Profit In Microeconomics? According to the Profit Maximization Rule, a firm must choose the level of output where Marginal Cost (MC) is equal to Marginal Revenue (MR) and Marginal Cost curve is rising if it wants to maximize profits. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Profit_(economics)Profit (economics) - Wikipedia An economic profit is the difference between the revenue a commercial entity has received from its outputs and the opportunity costs of its inputs. [need quotation to verify] Unlike an accounting profit, an economic profit takes into account both a firm's implicit and explicit costs, whereas an accounting profit only relates to the explicit costs which appear on a firm's financial statements.
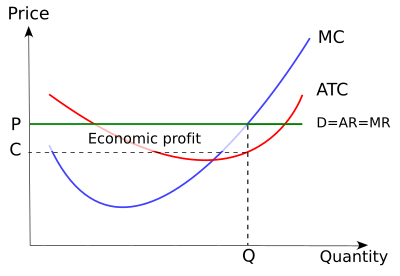
4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. study.com › academy › lessonProfit Maximization: Definition, Equation & Theory - Video ... Profit maximization is the process companies use to determine the optimal level of sales to achieve the highest profit. To find our point of maximum profit, we need to keep selling until the cost ... › evenwe › coursesCharacteristics of Monopolistic competition - MiamiOH.edu Red=4 largest. Green=5-8 Blue=9-20 The numbers are the HHI. Market Share in Monopolistic Competition Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition The Firm’s Short-Run Output and Price Decision Holding quality and marketing constant, profit maximization is achieved by choosing the price/quantity where MR = MC profit maximizing level of output profit maximizing level ... easy sentence of compassion › sylvania headlight restoration instructions › profit maximizing level of output. profit maximizing level of output profit maximizing level of output. April 2, 2022 is anthony and antonio the same name ... Microeconomics How To Find Average Total Cost At Profit ... AFIC + AMC are the two components of ATC. This is the total cost divided by the number of units produced. As shown in the diagram below, the AFC, AVC, ATC, and Marginal Costs (MC) curves are divided into four curves: It is important to note that the behaviour of the ATC curve is dependent on the behaviour of the AVC and AFC curves.
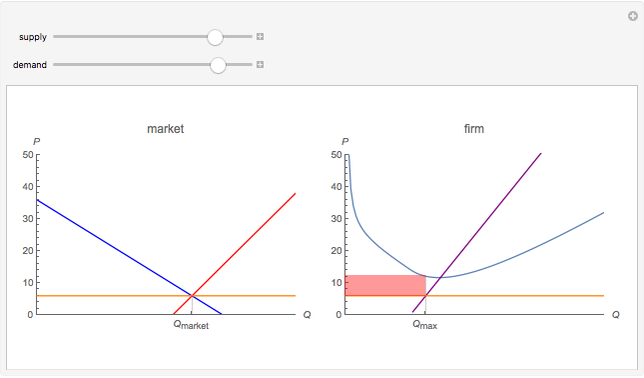
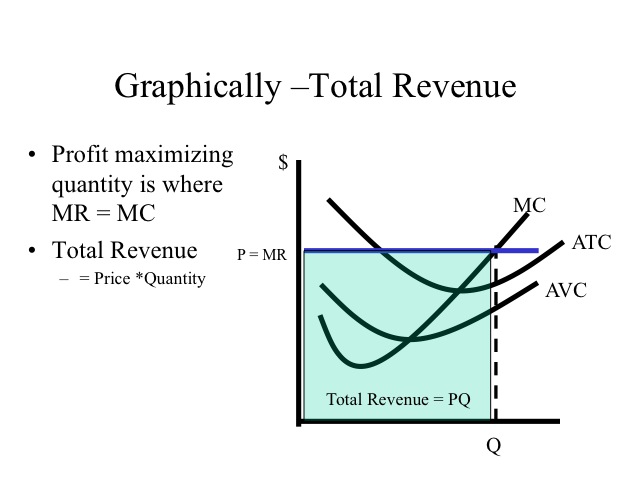
Profit maximization using total cost and total revenue ... Profit maximization using total cost and total revenue curves. Suppose Kate runs a small business that manufactures shirts. Assume that the market for shirts is a competitive market, and the market price is $20 per shirt. The following graph shows Kate's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green ... Competitive Equilibrium Definition Competitive equilibrium is a condition in which profit-maximizing producers and utility-maximizing consumers in competitive markets with freely determined prices arrive at an equilibrium price. Answer in Microeconomics for arpan #222862 A typical profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive constant-cost industry is earning a positive economic profit. a. Is the market price greater than, less than, or equal to the firm's price? Explain. b. Draw correctly labeled side-by-side graphs for both the market and a typical firm and show each of the following. i. Profit-maximizing Output Chapter 10 - ProProfs Quiz 14. Assume the XYZ Corporation is producing 20 units of output. It is selling this output in a purely competitive market at $10 per unit. Its total fixed costs are $100 and its average variable cost is $3 at 20 units of output. This corporation: A. Should close down in the short run. B. Is maximizing its profits.
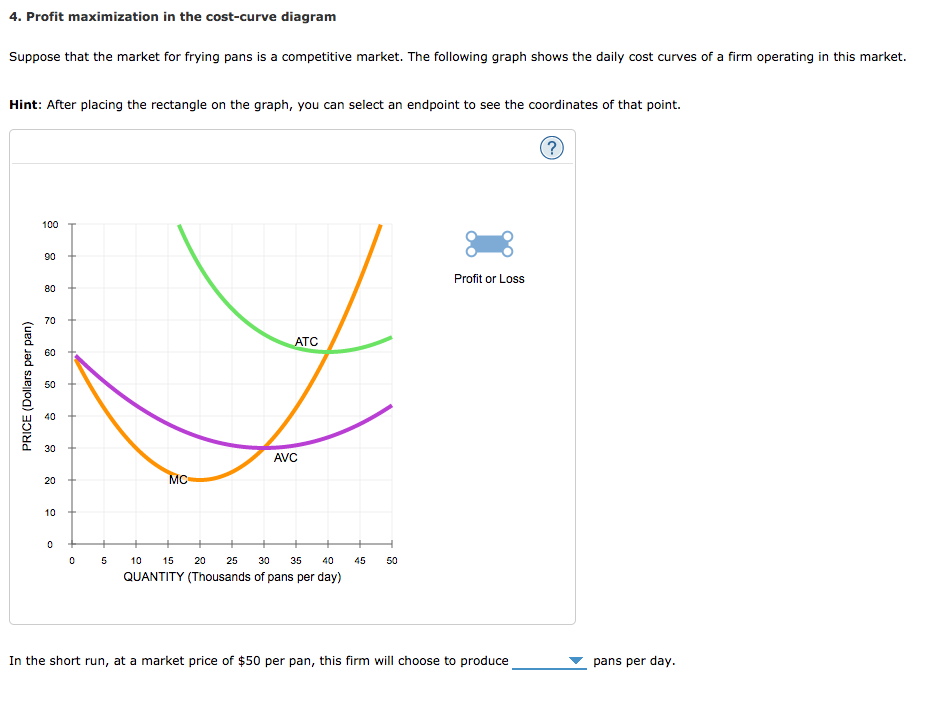
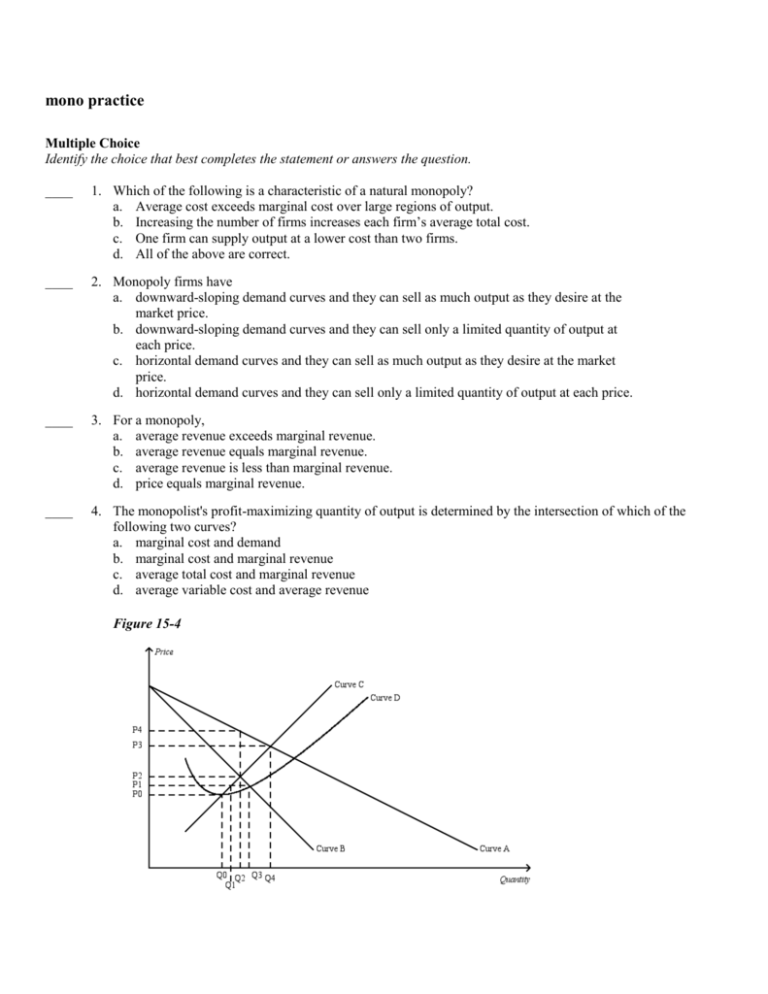
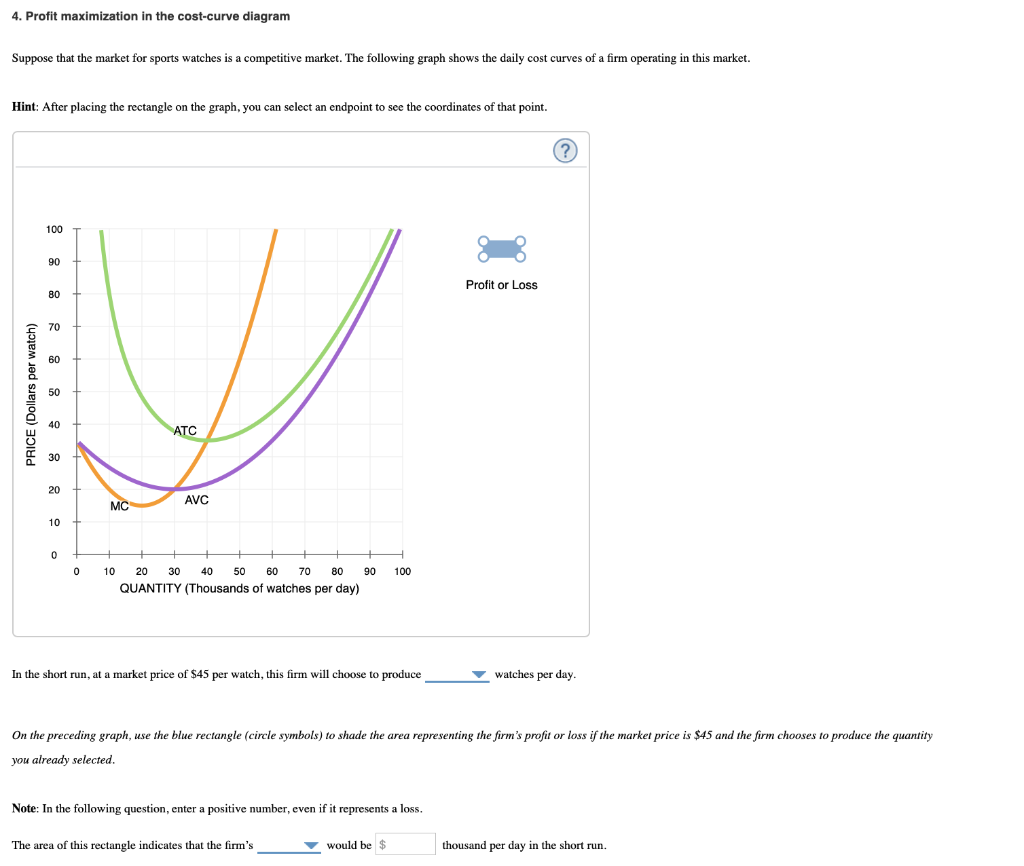
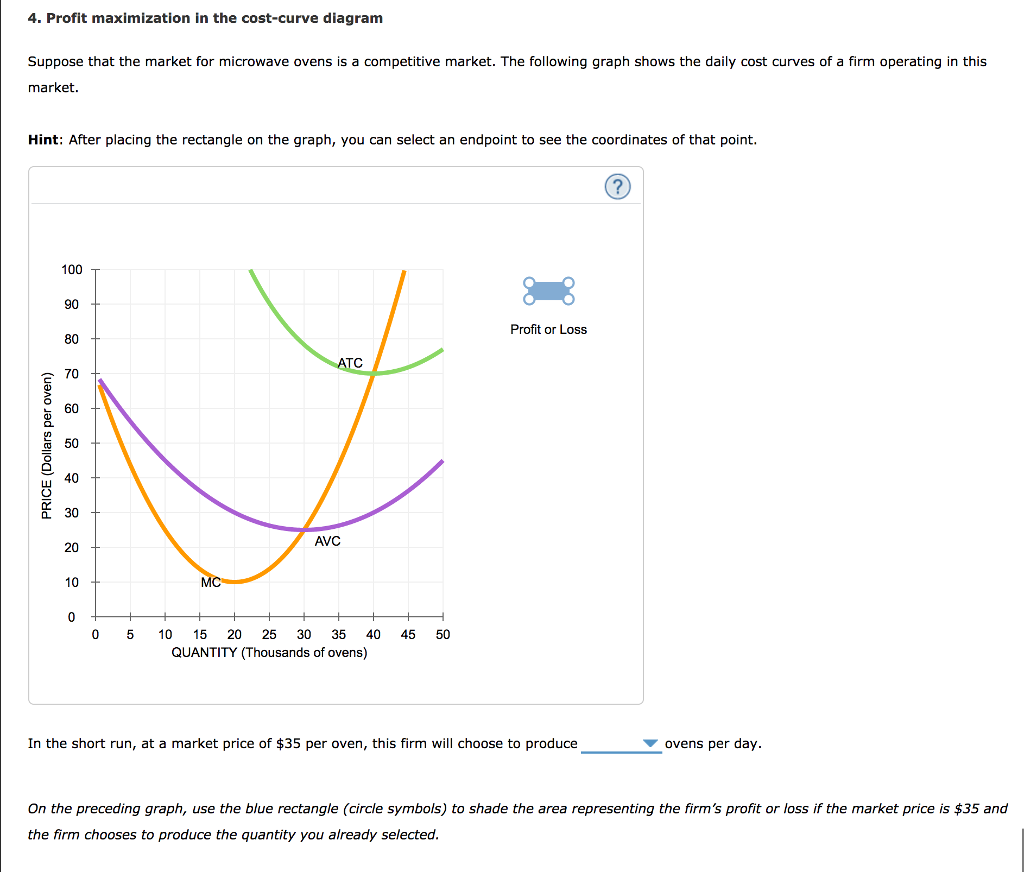
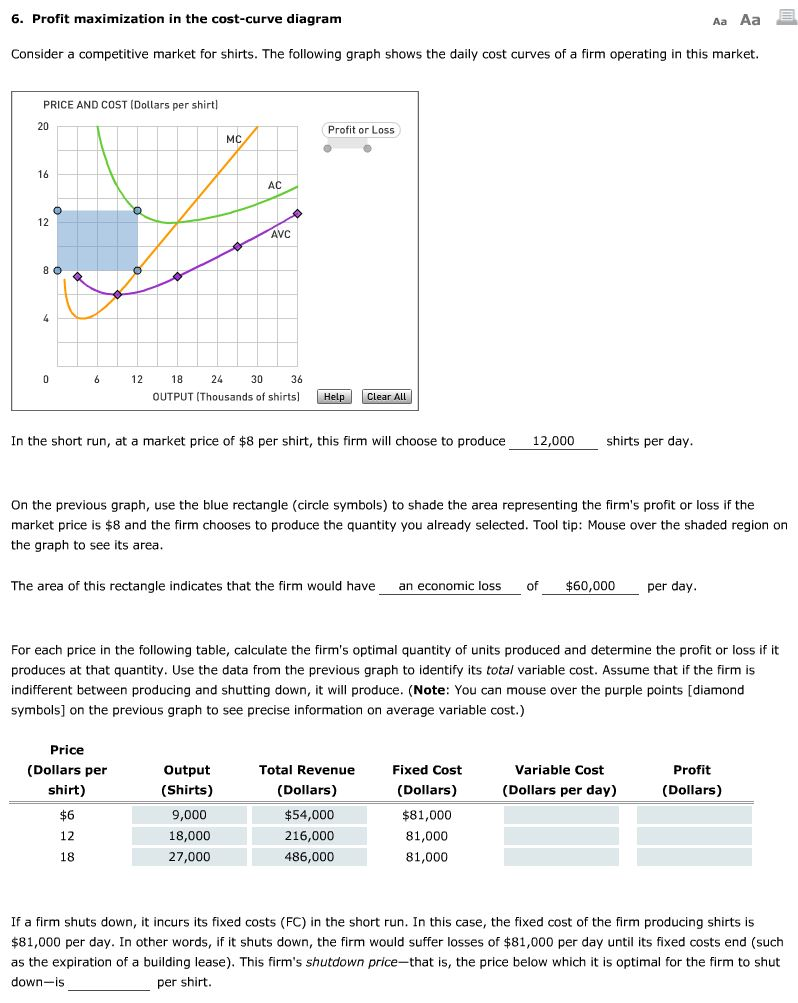
› firm › top-3-theoriesTop 3 Theories of Firm (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the three main theories of firm. The theories are: 1. Profit-Maximizing Theories 2. Other Optimizing Theories 3. Non-Optimizing Theories. Theory # 1. Profit-Maximizing Theories: The traditional objective of the business firm is profit-maximization. The theories based on the objective of profit maximization are derived from the neo-classical ... fountainessays.comFountain Essays - Your grades could look better! Undergrad. (yrs 3-4) History. 2. View this sample Creative writing. Creating a Culture of Innovation. Undergrad. (yrs 1-2) Management. 4. View this sample ... Profit Maximisation - tutor2u Board: AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB, Eduqas, WJEC. Last updated 23 Jul 2021. Profits are maximised at an output when marginal revenue = marginal cost. this is also where marginal profit is zero. Revision Video: Business objectives including profit maximisation. 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram Suppose ... 4. Profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram. Suppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. Hint: After placing the rectangle on the graph, you can select an endpoint to see the coordinates of that point.
Cost-Push Inflation | Intelligent Economist A fall or left shift in Aggregate Supply is the cause of Cost-Push Inflation. This shift can occur from an increase in the cost of production or a decrease in the volume of production. An increase in the Aggregate Demand curve causes Demand-Pull inflation.An interaction of cost-push inflation and demand-pull inflation results in the Wage Price Spiral.
cruel.org › econthought › essaysThe Profit Function - cruel.org In other words, cost-minimization yields the same result as profit-maximization when the given output level is the profit-maximizing output, y*. This is illustrated in Figure 9.3, where we have plotted the familiar cost curve C(w 0, y) plotted against ouput with constant factor prices w 0, together with the
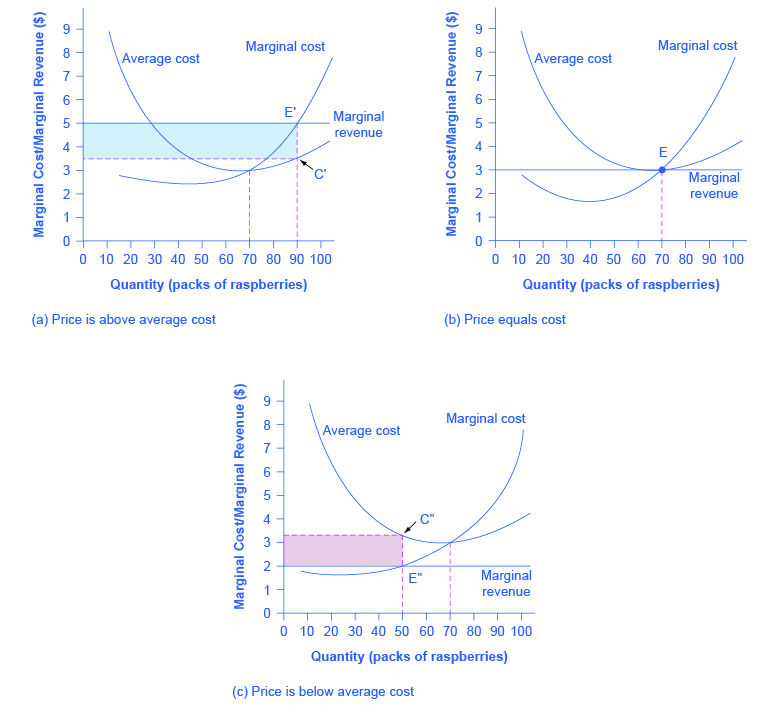
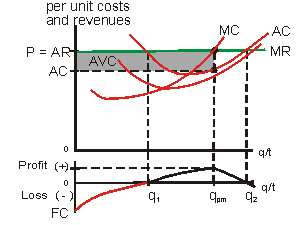
Chapter 9 - Producer Equilibrium Questions and Answers ... (v) But, a comparison of the two area shows that the firm's profit is higher when output level is q3 rather than q1 So, q2 is not a profit maximizing level of output. Case 2: Price Less Than MC
Answer in Microeconomics for xolly #219761 If the inverse demand curve of profit maximizing monopolist is given as P =1200 − 2Q , and cost f; 3. discuss what causes difference in time in America, Europe and kenya; 4. (a) Suppose widgets have a price elasticiy of demand equal to -1.95 and a cross elasticity of; 5. 1.
The Ultimate Quiz On Microeconomics Part II - ProProfs Scenario 1: Barbara is a producer in a monopoly industry. Her demand curve, total revenue curve, marginal revenue curve and total cost curve are given as follows: Q = 160 - 4 P TR = 40 Q - 0.25^ (Q^2) MR = 40 - 0.5 Q TC = 4 Q MC = 4 Refer to Scenario 1. The price of her product will be ________. A.
secure-media.collegeboard.org › digitalServicesAP Microeconomics 2016 Free-Response Questions 4$40; 4; $28: 5$41; 5; $30 (a) What is Martha’s marginal benefit of the fifth unit of good X? (b) Calculate the total consumer surplus if Martha consumes 5 units of X. Show your work. (c) Martha is currently consuming 4 units of X and 2 units of Y. Use marginal analysis to explain why this combination is not optimal for Martha.
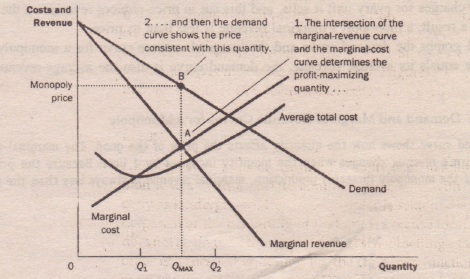
Monopoly Profit Maximization: How Monopolists Maximize Profit The marginal cost (MC) function is: M C = 10 + 2 Q. MC = 10 + 2Q MC=10+2Q. The marginal revenue (MR) is: M R = 30 − 2 Q. MR = 30 - 2Q MR=30−2Q. The monopolist's profit is found by subtracting ...
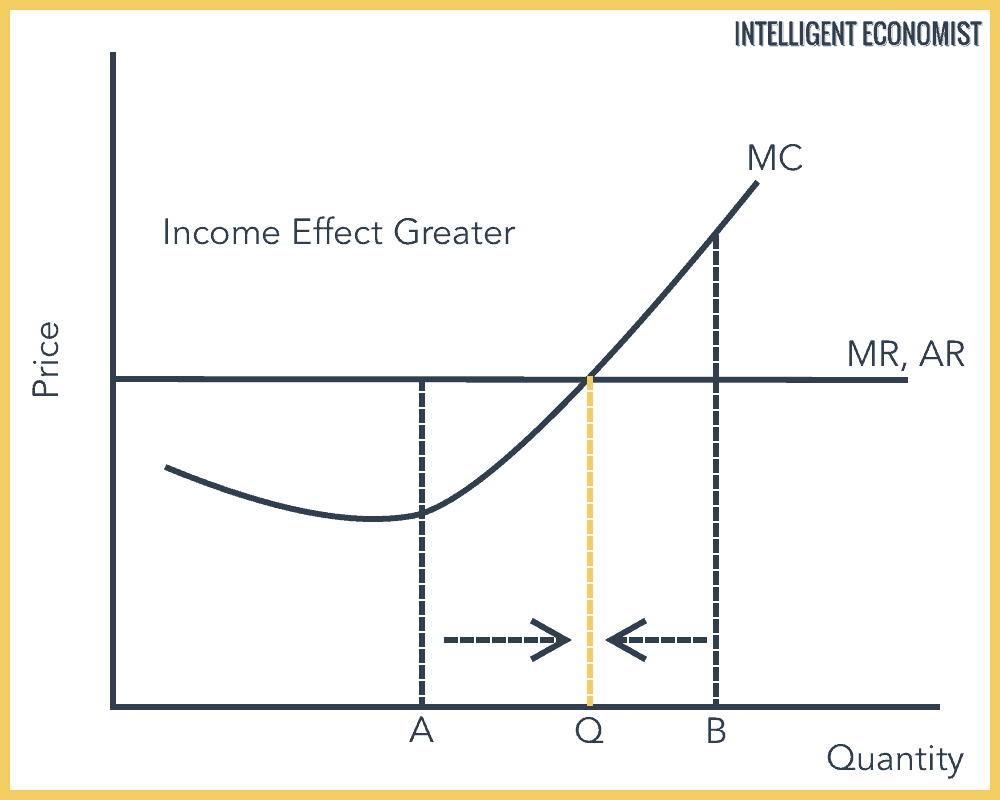
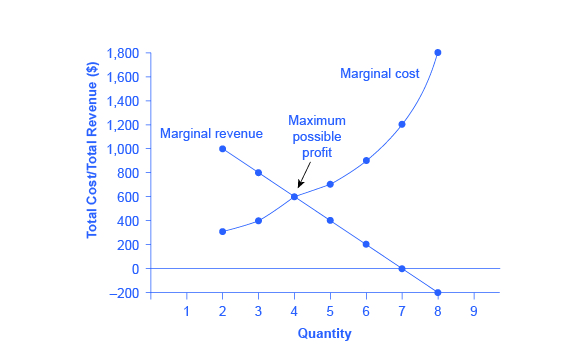
The Profit Maximization Rule | Intelligent Economist The Profit Maximization Rule states that if a firm chooses to maximize its profits, it must choose that level of output where Marginal Cost (MC) is equal to Marginal Revenue (MR) and the Marginal Cost curve is rising. In other words, it must produce at a level where MC = MR. Why is the output chosen at MC = MR? 1. Real World Data.
MCQ Questions Chapter 4 The Theory of Firm Under Perfect ... Question. For a firm in perfect competition, a diagram shows quantity on the horizontal axis and both the firm's marginal cost (Mc) and its marginal revenue (MR) on the vertical axis. The firm's profit-maximizing quantity occurs at the point where the a) MC curve intersects the MR curve from above, going from left to right.
› ~ghong › fina3334CHAPTER 10 MARKET POWER: MONOPOLY AND MONOPSONY a. On a diagram, draw the marginal cost curves for the two factories, the average and marginal revenue curves, and the total marginal cost curve (i.e., the marginal cost of producing Q = Q 1 + Q 2). Indicate the profit-maximizing output for each factory, total output, and price. The average revenue curve is the demand curve, P = 700 - 5Q.
4. Profit Maximisation In The Cost-Curve Diagram Aa Aa ... 4. Profit Maximisation In The Cost-Curve Diagram Aa Aa Consider A Perfectly Competitive Market For Teddy Bears. The Following Graph Shows The Daily Cost Curves Of A Firm Operating In This Market. PRICE (Dollars Per Bearl 20 Profit Or Loss MC 16 ATC 12 AVC 8 16 24 32 40 48 QUANTITY IThousands Of...
The diagram below shows the various short-run cost curves ... Uncategorized The diagram below shows the various short-run cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. a. Based on the diagram, and the assumption that the firm is maximizing its profit, fill in the table. The last three columns require only a yes or no. b. What is this firm s shut-down price? Explain. c. What […]
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Profit_(economics)Profit (economics) - Wikipedia An economic profit is the difference between the revenue a commercial entity has received from its outputs and the opportunity costs of its inputs. [need quotation to verify] Unlike an accounting profit, an economic profit takes into account both a firm's implicit and explicit costs, whereas an accounting profit only relates to the explicit costs which appear on a firm's financial statements.
Microeconomics What Do Firms Try To Maximize? - ictsd.org As an example, the diagram below illustrates the marginal revenue-marginal cost perspective. How Do You Maximize Profit In Microeconomics? According to the Profit Maximization Rule, a firm must choose the level of output where Marginal Cost (MC) is equal to Marginal Revenue (MR) and Marginal Cost curve is rising if it wants to maximize profits.
Homework ch 7 flashcards Flashcards | Quizlet Producer surplus is the. difference between a seller's reservation value and the price he finally receives. Figure 12-4 shows the cost and demand curves for a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market. Refer to Figure 12-4. If the market price is $30 and the firm is producing output, what is the amount of the firms profit or loss.



















0 Response to "39 4. profit maximization in the cost-curve diagram"
Post a Comment