37 full orbital diagram for n
Full Orbital Diagram: The full orbital diagram shows all electrons of an atom. The electrons are shown by using a box and arrows. Different orbitals are presented by different boxes. Figure 8.10 or Table 8.3), give the full and condensed electron configurations, partial orbital diagrams showing valence electrons only, and number of inner electrons for the following elements: (a) potassium (K; Z = 19) (b) technetium (Tc; Z = 43) (c) lead (Pb; Z = 82) PLAN: The atomic number gives the number of electrons, and the
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal –each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for “build up” •Electrons are notated with an arrow –Up arrow goes first then, down arrow –Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
Full orbital diagram for n
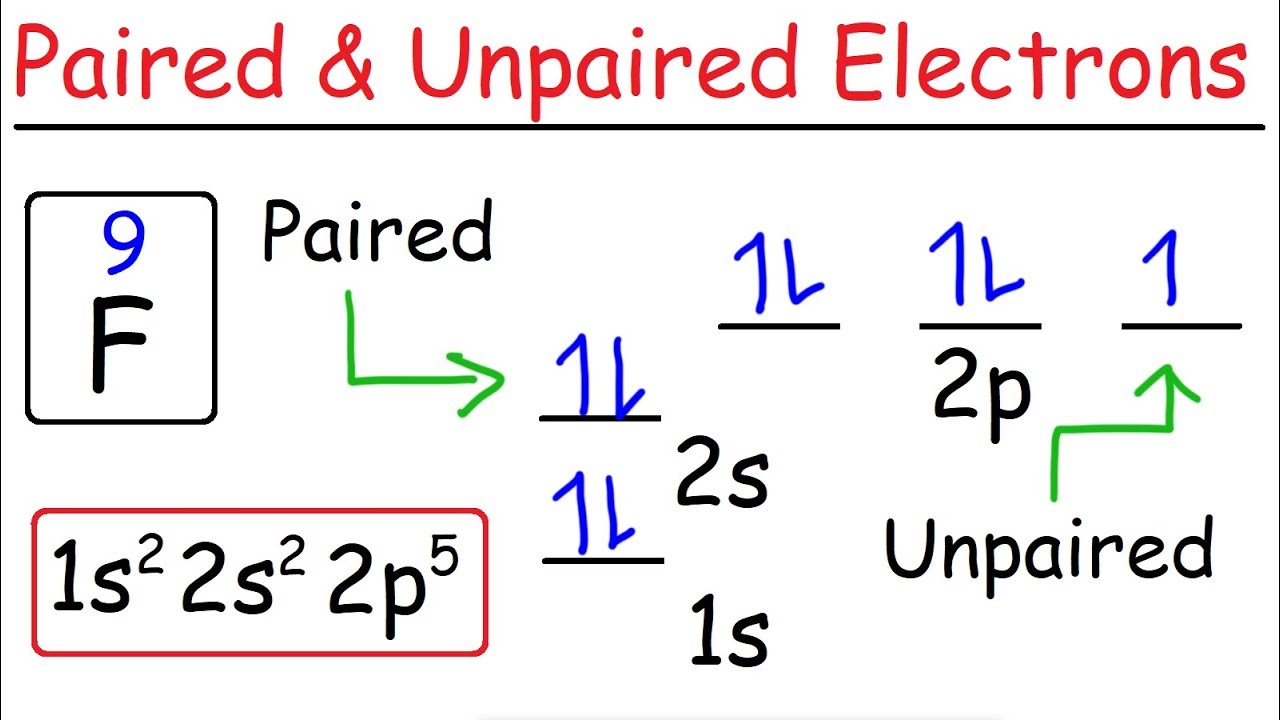
The atomic number of carbon is 6, which is also the number of positively charged protons its atomic nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of negatively charged electrons. Its electron configuration is "1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^2". The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is 2, each with ... Question: 41. Write the full electron configuration for each element. (a) Si (b) 0 (c) K (d) Ne 43. Write the full orbital diagram for each element. (a) N (b)F (c) Mg (d) Al 45. Use the periodic table to write an electron configuration for each element. Represent core electrons with the symbol of the previous noble gas in brackets. The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +1 2 m s = + 1 2 ).
Full orbital diagram for n. Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ... Answer and Explanation: 1. For neon, the atomic number is 10. The electronic configuration for neon is 1s22s22p6 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 . The full orbital diagram for neon is shown below. Orbital diagram. Nov 01, 2021 · Orbital Diagram of All Elements Diagrams; 1: Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine ... (n)s n)p (n-1)d (n-2)f In electron configurations, write in the orbitals that are occupied by electrons, followed by a superscript to indicate how many electrons are in the set of orbitals (e.g., H 1s1) Another way to indicate the placement of electrons is an orbital diagram, in which each orbital is
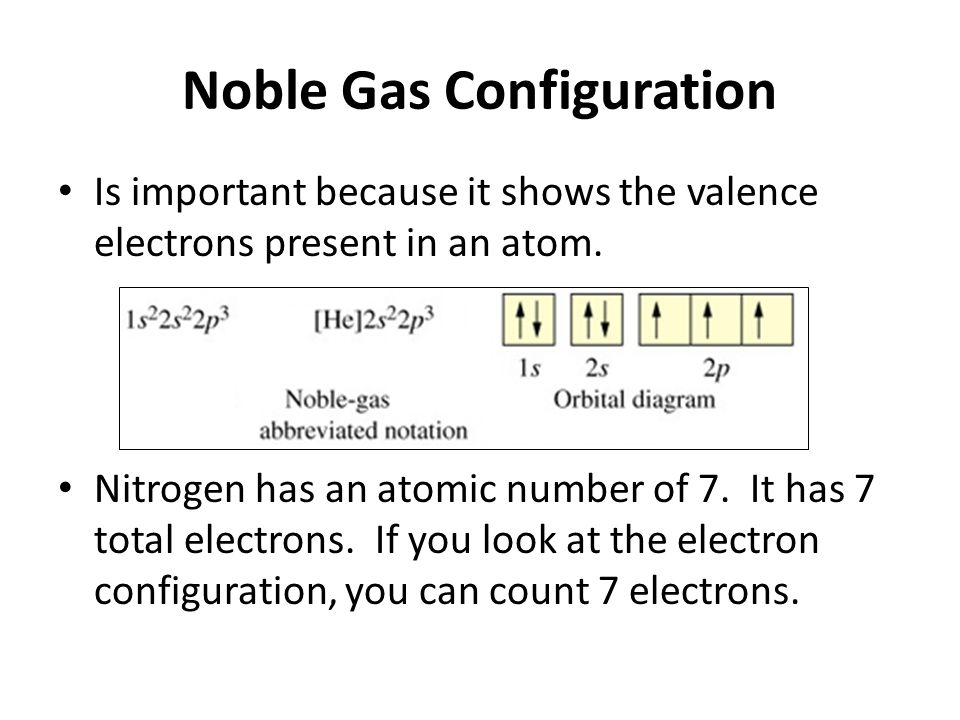
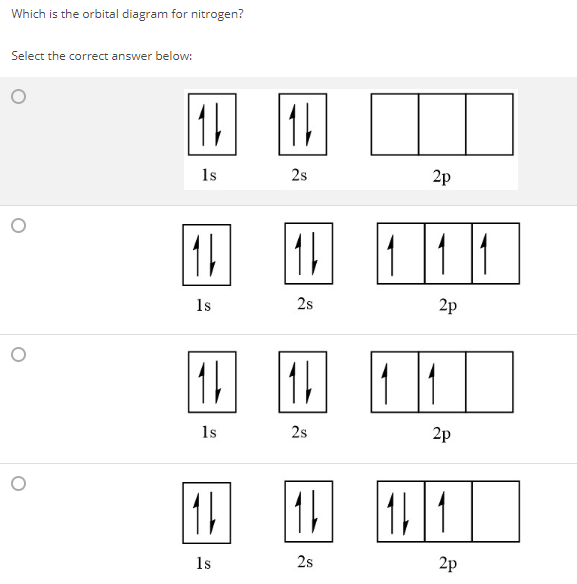
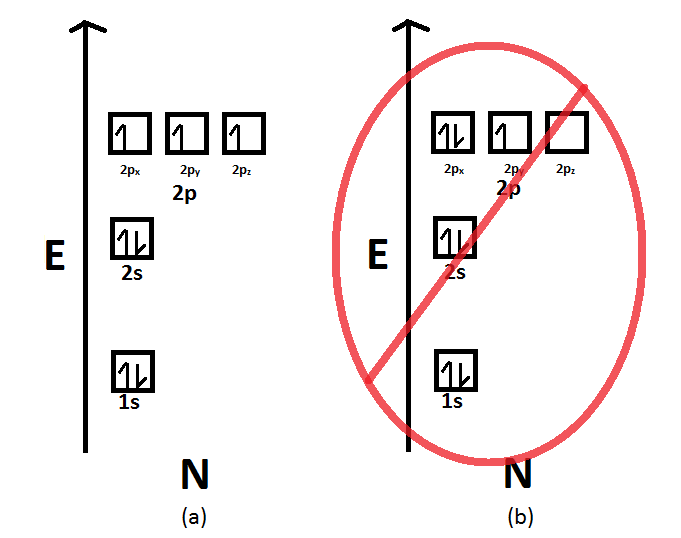
Write a full orbital diagram for each element. a. N b. F c. Mg d. Al. a. 1s^2 2s^2 2p^3 (p boxes only half filled) b. [He] 2s^2 2p^5 (p boxes missing only 1) c. [Ne] 3s^2 (3s boxes full) d. [Ne] 3s^2 3p^1 (3p box missing 5) 46. Use the periodic table to determine the element corresponding to each electron configuration. a. [Ar] 4s^2 3d^10 4p^6 Transcribed image text: Prompt 1) For the following, determine (i) the Electron Configuration (full or condensed), (ii) # of Valence Electrons, (iii) the Orbital Diagram, and (iv) the full set of Quantum Numbers (n, l, m, and ms) for t final electron: a. Potassium (19 e-) b. Nickel (28 e-) C. Polonium (84 e) 2) Explain, using complete sentences, all of the steps and considerations followed to ... How to Write the Electron Configuration for Nitrogen (N) Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for N goes in the 2s orbital. The first number is the principal quantum number (n) and the letter represents the value of l (angular momentum quantum number; 1 = s, 2 = p, 3 = d and 4 = f) for the orbital, and the superscript number tells you how many electrons are in that orbital. Orbital diagrams use the same basic format, but instead of numbers for the electrons, they ...
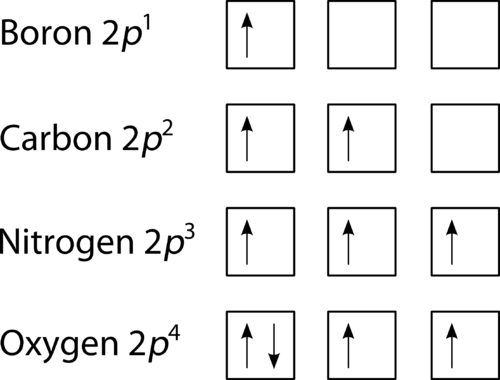
The third electron goes into the next orbital in the energy diagram, the 2s orbital. Li (Z = 3): 1s 2 2s 1. The fourth electron fills this orbital. Be (Z = 4): 1s 2 2s 2. After the 1s and 2s orbitals have been filled, the next lowest energy orbitals are the three 2p orbitals. The fifth electron therefore goes into one of these orbitals. B (Z ... Orbital Diagram For Carbon - Materials Free Full. electron configuration for fluorine f terpconnect electron configuration notation the remaining five electrons will go in the 2p orbital therefore the f electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5. What Is An Orbital Diagram - Functional Block Diagram Examples Originalstylophone. Electron configurations are a shorthand form of an orbital diagram, describing which orbitals are occupied for a given element. For example, 1s^2 2s^2 2p^1 is the electron configuration of boron. Use this tool to generate the electron configuration of arsenic (As). To write electron configurations and orbital notations successfully, you must formulate a plan of attack—learn the following relationships: ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS 1. Each main energy level has n sublevels, where n equals the number of the energy level. That means the first energy level has one sublevel, the second has two, the third has ...
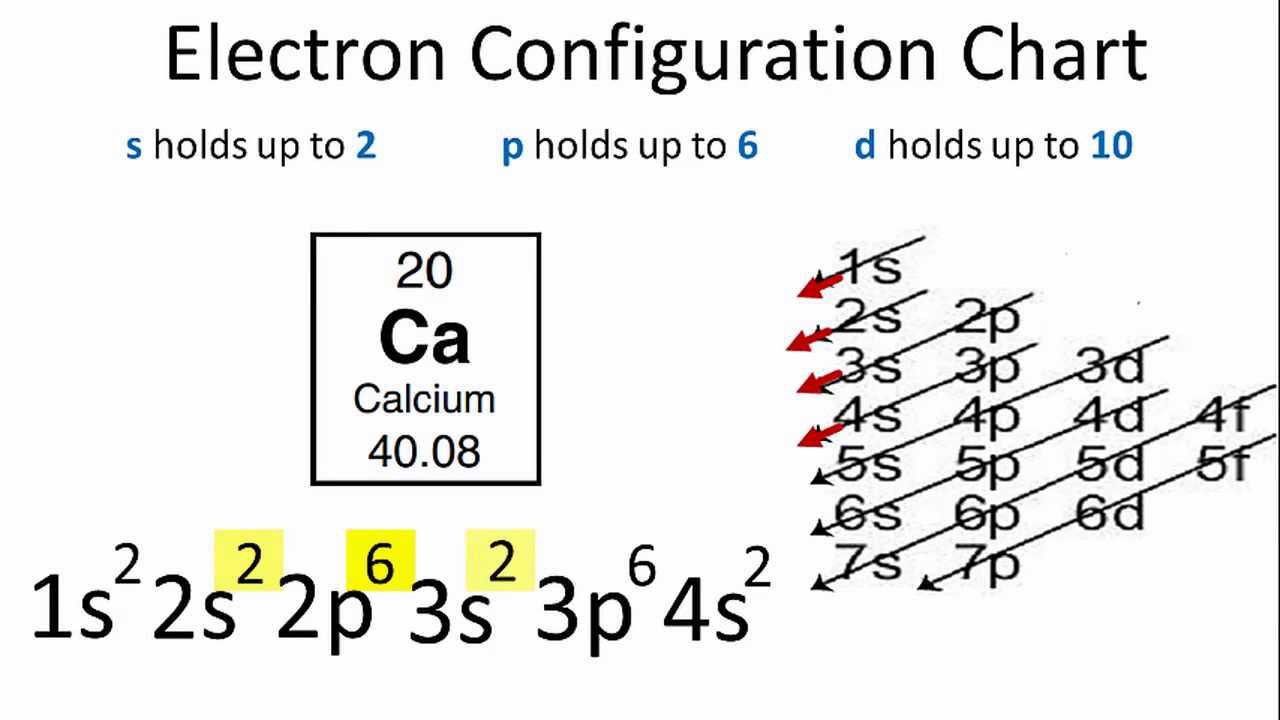
For example, the 5s orbital is of lower energy than the 4d orbital (see Figure 3 for a complete pattern of orbital levels). Ca electron occupancy The orbital notation of calcium (Ca) is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 Or short-hand: [Ar] 4s2. The orbital filling diagram of lithium. The electron configuration of lithium is 1s²2s¹.
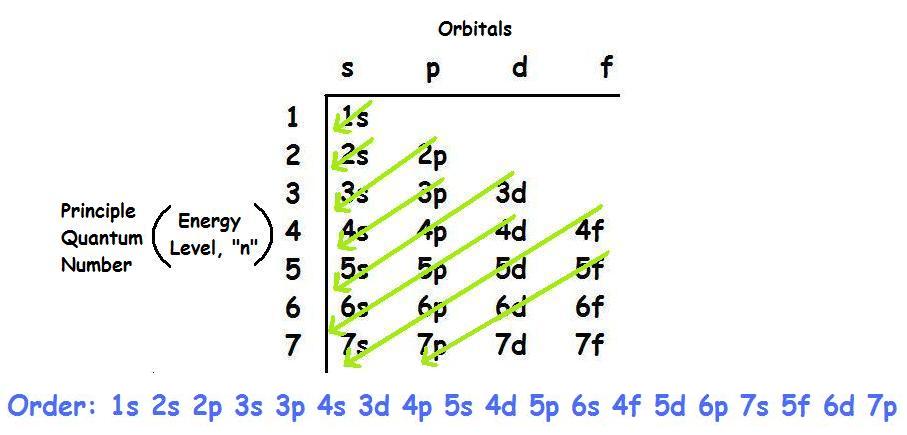
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. →. 2s.
The period of nitrogen is 2 and nitrogen is a p-block element. The electron configuration of nitrogen(N) and the orbital diagram is the main topic of this article. Also, period and group determination, valency and valence electrons of nitrogen, various reactions and compound formation, bond formation of nitrogen have been discussed.

Solved For The Following Determine The Electron Configuration Full Or Condensed Of Valence Electrons Orbital Diagram And Full Set Of Quantum Numbers N L Ml And Ms For The Final Electron A
Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau...
Feb 15, 2021 · If you are still not getting the Nitrogen Electron Configuration of the element nitrogen then, the full electronic configuration of nitrogen is written as the following; 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. If we gave you brief information then, the first two electrons lie in the 1s orbital, following the next 2 electrons, it comes under the 2s orbital.
Orbital Diagrams. Another way to represent the order of fill for an atom is by using an orbital diagram often referred to as "the little boxes": ... "Half fill before you Full fill" and again this rule was established based on energy calculations that indicated that this was the way atoms actually distributed their electrons into the orbitals.
Write full orbital diagrams and indicate the number of unpaired electrons for: N Write electron configuration and use the symbol of the previous noble gas in brackets to represent core electrons:
Neon electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6.The symbol for neon is 'Ne' and it is an inert element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of neon(Ne) and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of neon, application of different principles. The tenth element in the periodic table is neon.
The electron configuration for oxygen is: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^4 This video will walk you through the step of writing orbital diagram. The video uses Kr as an example, but the process is exactly as the same as what you need to do for oxygen. Hope this helps!
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...
ANSWER: n= Exercise 9.52. Part A Write full orbital diagram for F Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals. Click within the orbital to add electrons.. ANSWER: Part B Indicate the number of unpaired electrons in it. Express your answer as an integer. ANSWER: n= Part C.
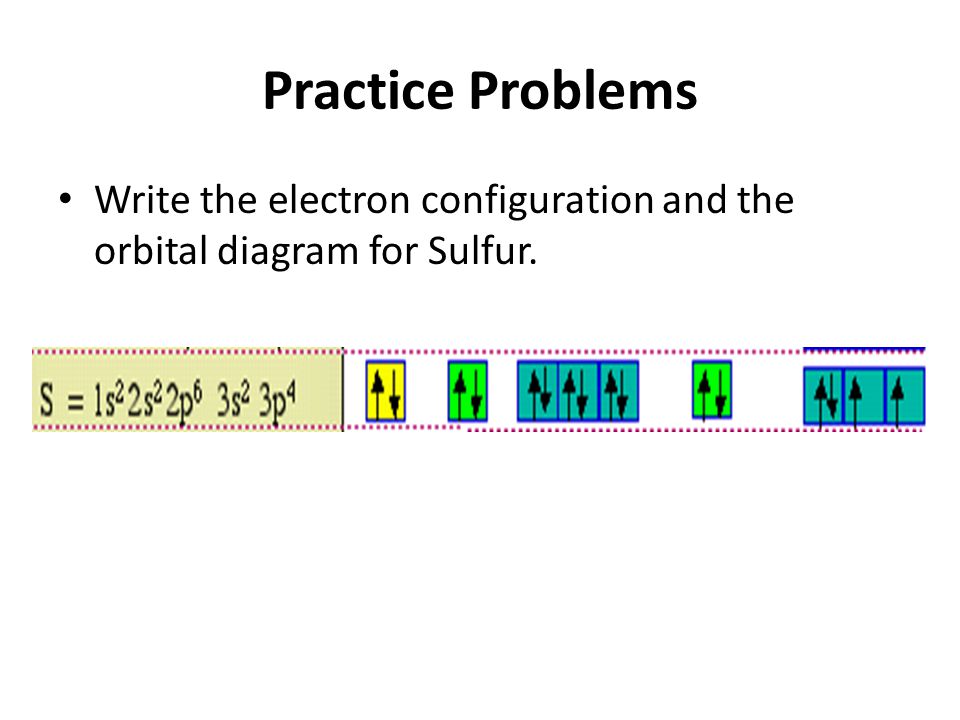
Answer to Draw the full orbital filling diagram for Sulfur, make sure you show the energy relationship between orbitals and label. The orbital diagram for sulfur has seven boxes with two arrows pointing in opposite directions and two boxes with one arrow pointing up in each.
Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium Where are the Electrons? Write the full electron configuration, short-hand electron configuration, and fill in the orbital diagrams, for the following elements. 1.
The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of:
The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +1 2 m s = + 1 2 ).
Question: 41. Write the full electron configuration for each element. (a) Si (b) 0 (c) K (d) Ne 43. Write the full orbital diagram for each element. (a) N (b)F (c) Mg (d) Al 45. Use the periodic table to write an electron configuration for each element. Represent core electrons with the symbol of the previous noble gas in brackets.
The atomic number of carbon is 6, which is also the number of positively charged protons its atomic nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of negatively charged electrons. Its electron configuration is "1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^2". The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is 2, each with ...

Give Orbital Diagram Of The Following A Magnesium Chloride B Nitrogen C Methane D Hydrogen Chloride Flash Education

Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes


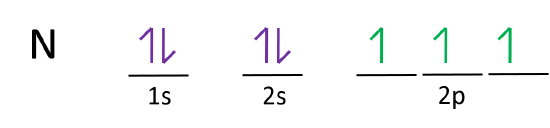















0 Response to "37 full orbital diagram for n"
Post a Comment