39 the diagram at right shows an arbitrary point
1. The diagram below represents magnetic lines of force within a region of space. The magnetic field is strongest at point (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D 2. The diagram below shows the magnetic field that results when a piece of iron is placed between unlike magnetic poles. At which point is the magnetic field strength greatest? (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D 3. 46. The diagram given shows a transverse wave moving to the right along a rope. As the wave passes point X, the motion of Xwill be A. up, then down B. down, then up C. left, then right D. in a circle 47. In the diagram shown, a water wave having a speed of 0.25 meter per second causes a cork to move up and down 4.0 times in 8.0 seconds.
This means that at the point of application of a bending moment, there is a step change in the bending moment diagram, equal to the magnitude of the moment applied. The 6 boxed equations in this section above can be used to infer a huge amount of information about the behaviour of a structure under load.
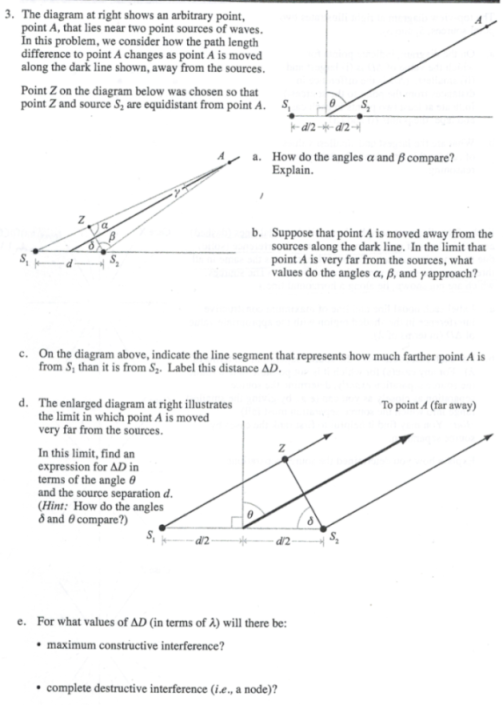
The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point
Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S, are equidistant from point A. 1-d2+d2 a. Question: 3. The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown ... 0 votes. Step 1: A, B, and C are the points lying on the line . Since the point A lies on the y - axis, Substitute in the line equation. Thus, the point A is . Step 2: The line from to B is perpendicular to AC . Which means that the line BD is perpendicular to AC . Find the slope of the line AC . 26. When the Bunsen burner is on, as shown in the diagram to the right, the paper string Will spin. Explain what causes the paper to spin. (S8P2d) 27. Identify the types of Energy transfer shown in the diagram to the right. (S8P2d) 16. The image to the right shows a train traveling from a starting point at the top of the hill. What type of energy
The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point. [JMO 2015 B2] The diagram shows triangle 𝐴𝐵𝐶, in which ∠𝐴𝐵𝐶=72° and ∠𝐶𝐴𝐵=84°. The point 𝐸 lies on 𝐴𝐵 so that 𝐸𝐶 bisects ∠𝐵𝐶𝐴. The point 𝐹 lies on 𝐶𝐴 extended. The point 𝐷 lies on 𝐶𝐵 extended so that 𝐷𝐴 bisects ∠𝐵𝐴𝐹. Prove that 𝐴𝐷=𝐶𝐸. 3 The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A, that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source R are equidistant from point A ... To set up the equilibrium conditions, we draw a free-body diagram and choose the pivot point at the upper hinge, as shown in panel (b) of (Figure). Finally, we solve the equations for the unknown force components and find the forces. Figure 12.17 (a) Geometry and (b) free-body diagram for the door. 3 The diagram shows some cells in the root of a plant that is absorbing water from the soil. 2 1 3 ... / arbitrary units 30 °C 20 °C 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 ... Which position on the graph corresponds to the point at which the ribs are beginning to be lowered? expiration inspiration
C) left of the page D) right of the page 9.The diagram below shows a transverse wave moving toward the left along a rope. At the instant shown, point P on the rope is moving toward the A) 10 Hz B) 20 Hz C) 50 Hz D) 100 Hz 10.The graph below shows displacement versus time for a At a point on the beam where the type of bending is changing from sagging to hogging, the bending moment must be zero, and this is called a point of inflection or contraflexure. By integrating equation (2) between the x = a and x = b then: (6) Which shows that the increase in bending moment between two sections is the area under the Kinematic Diagram. • The acceleration of point G is horizontal since it moves along a straight-line path. • Just before point A touches the ground, its velocity is directly downward along the y axis, just after contact, its velocity is directed upward. • Therefore, point A begins to accelerate upward when it leaves the ground at A. The lower portion of the figure shows the derivation of the Hicks and Slutsky compensated demand curves and the ordinary demand curve. First consider the lower diagram (B) where the price of good X is taken on the vertical axis. Point P is an arbitrary point on this axis which shows the price of X when the budget line is PQ in the upper diagram.
The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point point A, that lies near two point sources of waves In this problem, we consider how the path lengtlh difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source R are equidistant from point A ... arbitrary point in space. The result includes the case of the field on the axis of the rod beyond one of its ends, and the case of an infinitely long rod. The general answer is most conveniently expressed in terms of the linear charge density λ; for a finite rod of length L and total charge Q, that charge density is equal to Q/L. To begin with ... 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) support reactions, and, c) the weight of the body. Idealized model Free-body diagram (FBD) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape. point with reference to a coordinate axis. The origin of the coordinate axis may be arbitrary. Position to right of origin, position(x) is positive Position to left of origin, position(x) is negative ... • A motion diagram shows only the POSITION of the object on the position axis.
The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A, that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S2 are equidistant from point A.
The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A. that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S_2 are equidistant from point A.
The diagram at right shows a flat surface containing a line and a circle with no points in common. Can you visualize moving the line and/or circle so that they intersect at exactly one point? Two points? Three points? Explain each answer and illustrate each with an example when possible.
An 80.0-kg painter stands 1.0 m from the left end of the scaffold, and his painting equipment is 1.5 m from the right end. If the tension in the left cable is twice that in the right cable, find the tensions in the cables and the mass of the equipment. Show Answer. right cable, 444.3 N; left cable, 888.5 N; weight of equipment 156.8 N; 16.0 kg
The figure below shows a ball & stick figure of a water molecule viewed down the twofold rotation axis that passes through the central oxygen atom. As pointed out earlier, this molecule has the crystallographic point-group symmetry mm2. Superimposed on the molecule is the steroegraphic diagram for this particular point group.
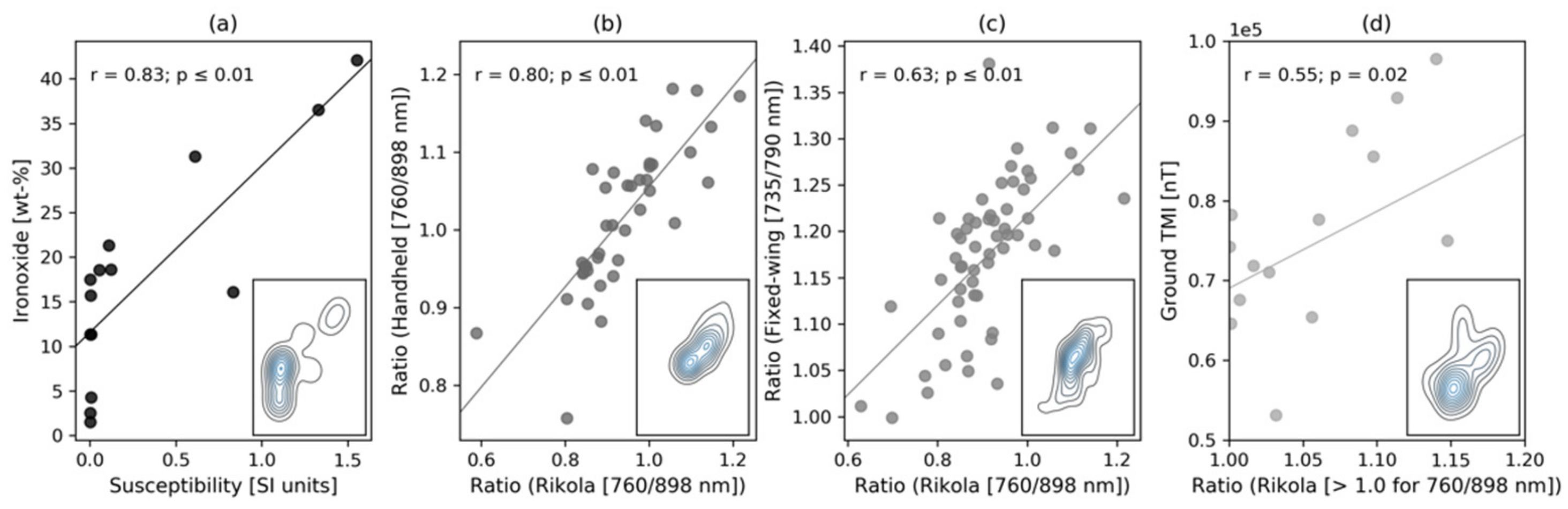
Remote Sensing Free Full Text Drone Borne Hyperspectral And Magnetic Data Integration Otanmaki Fe Ti V Deposit In Finland Html
Rotation About Arbitrary Point other ... Symbol‐instance table does not show relationships ... • Note: Diagram uses old glTranslate, glScale, etc commands • We want same behavior though Apply matrix at top of CTM to vertices of object created PopMatrix and ...
So that the lipase broke down the lipid quickly So that the lipase and the lipid reached the right temperature To give enough time for the lipase to break down the lipid ... factors that could be limiting the rate of photosynthesis at a light intensity of 250 arbitrary units. ... The diagram below shows four plants. The plants were grown in ...
We defined a tangent to a circle as a line with one point in common with the circle. This definition can be used in coordinate geometry using simultaneous equations. For example, the diagram to the right shows the line x + y = 2 and the circle x 2 + y 2 = 2. Substituting the equation of the line into the equation of the circle gives
The diagram shows a solid made from a hemisphere and a cone. Diagram NOT accurately drawn The radius of the hemisphere is 4 cm. The radius of the base of the cone is 4 cm. Calculate the volume of the solid. Give your answer correct to 3 significant figures. .....cm3 (Total for Question is 3 marks)
The four steps of the process for drawing a ray diagram are listed, described and illustrated below. 1. Draw the image of the object. Use the principle that the object distance is equal to the image distance to determine the exact location of the object. Pick one extreme on the object and carefully measure the distance from this extreme point ...
26. When the Bunsen burner is on, as shown in the diagram to the right, the paper string Will spin. Explain what causes the paper to spin. (S8P2d) 27. Identify the types of Energy transfer shown in the diagram to the right. (S8P2d) 16. The image to the right shows a train traveling from a starting point at the top of the hill. What type of energy
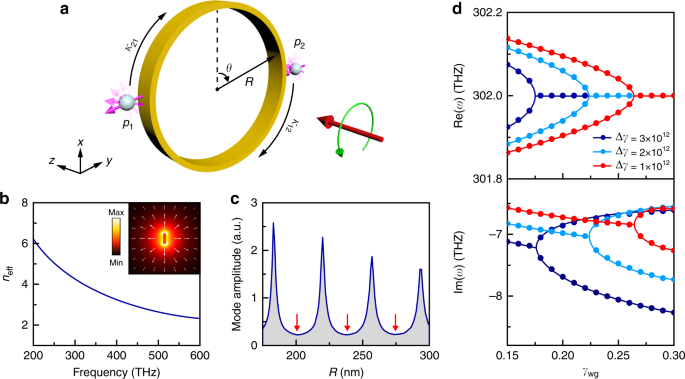
Arbitrary Order Exceptional Point Induced By Photonic Spin Orbit Interaction In Coupled Resonators Nature Communications
0 votes. Step 1: A, B, and C are the points lying on the line . Since the point A lies on the y - axis, Substitute in the line equation. Thus, the point A is . Step 2: The line from to B is perpendicular to AC . Which means that the line BD is perpendicular to AC . Find the slope of the line AC .
Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S, are equidistant from point A. 1-d2+d2 a. Question: 3. The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown ...
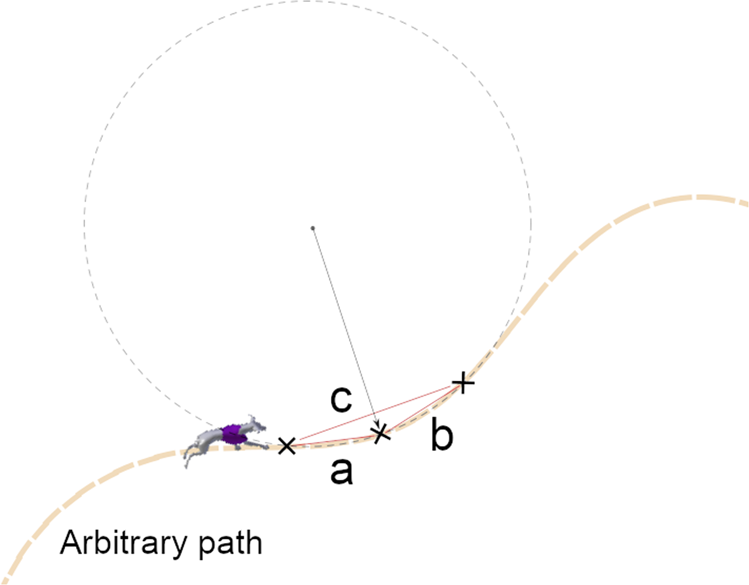
Greyhound Racing Ideal Trajectory Path Generation For Straight To Bend Based On Jerk Rate Minimization Scientific Reports

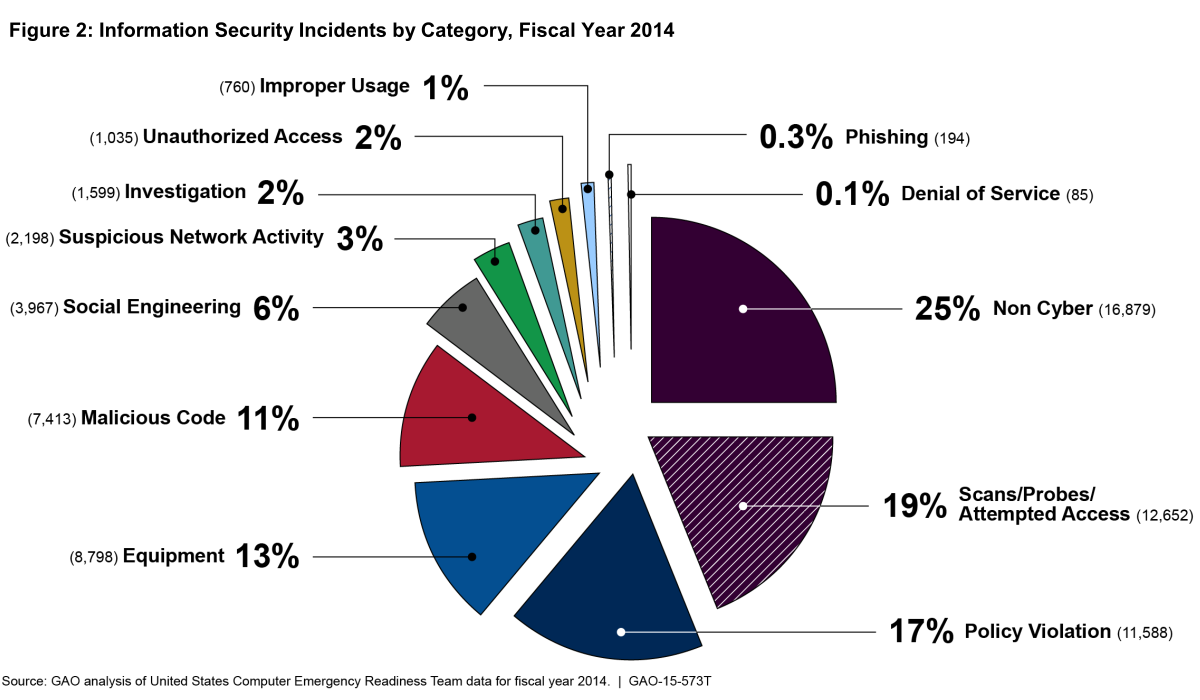






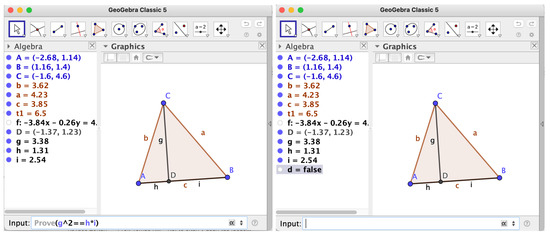


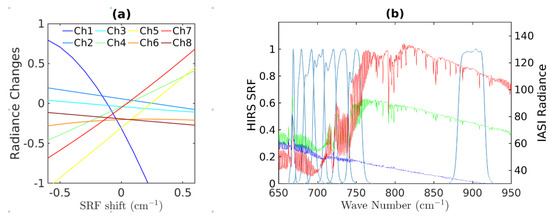













0 Response to "39 the diagram at right shows an arbitrary point"
Post a Comment