39 two blocks on top of each other free body diagram
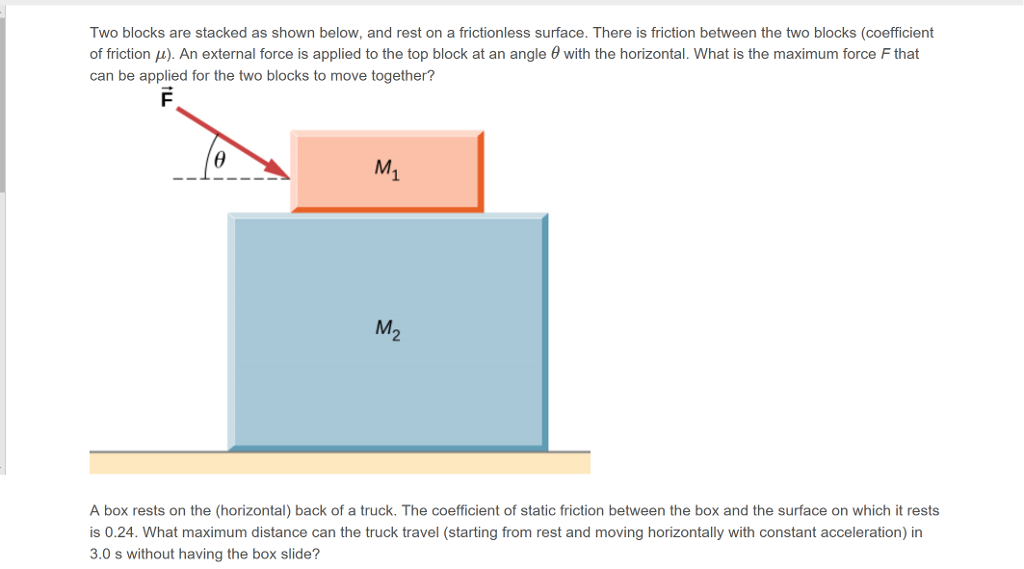
i think your free body diagram needs correction; if the system is moving to the right by say acceleration a , then the top block will experience a frictional force in the forward direction which will oppose the top block being left behind and if it can not counter it the top one will slip behind - so there is a limit to the acceleration of the system. 7 Aug 2016 — Then draw the free-body diagram and write down the force ... the value of F for which the blocks start gliding relative to each other by ...3 answers · Top answer: I'll provide a complete solution to the case where the friction force is fully developed. ...
8:13PS.2.2 Worked Example - Stacked Blocks - Free Body Diagrams and Applying Newtons 2nd Law. 62,659 ...2 Jun 2017 · Uploaded by MIT OpenCourseWare

Two blocks on top of each other free body diagram
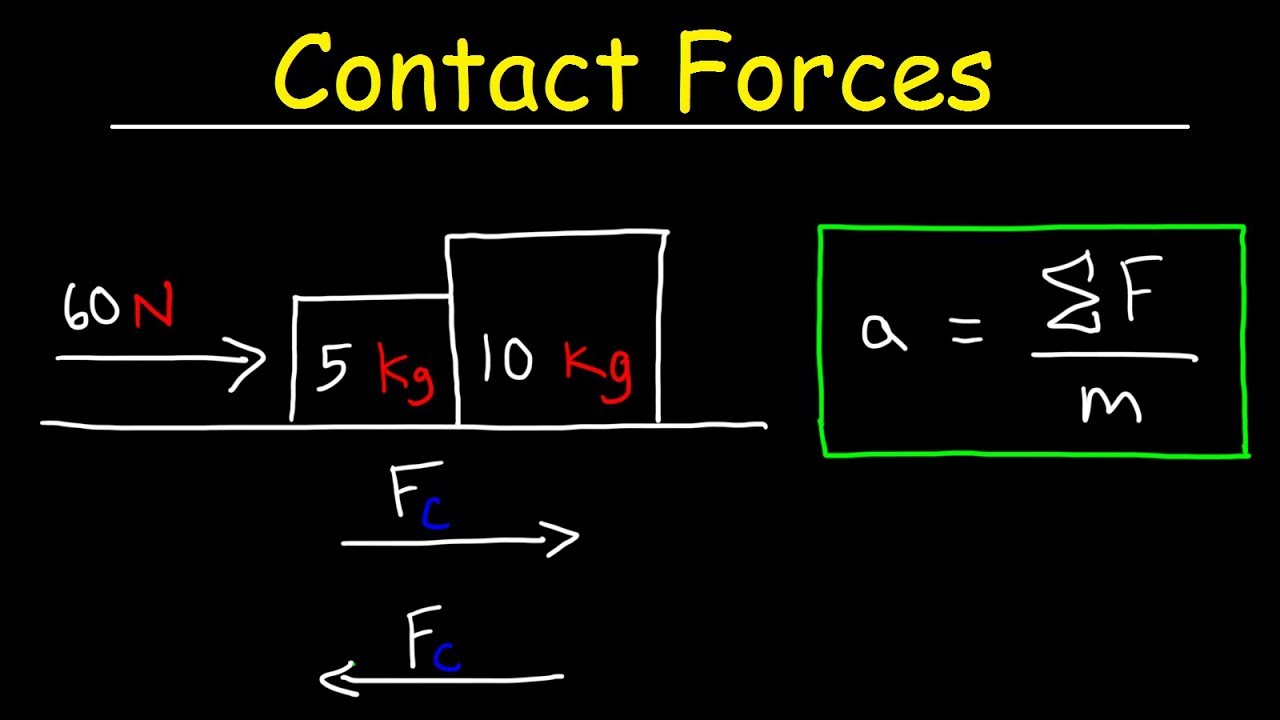
11:24This physics video tutorial explains how to calculate the contact force between blocks using free body diagrams ...3 Nov 2017 · Uploaded by The Organic Chemistry Tutor Two blocks on top of each other free body diagram. Which of the following represents best the free body diagram of the block in the middle ie. Between the bottom of the block and the floor there is normal force perpendicular to the floor. You will want to draw two free body diagrams one for each book then you can put in the forces that act from ... The top box is used in this analysis since it encounters one less force. The free-body diagram is shown at the right. The force of gravity on the top box is m•g where m = 6.0 kg. The force of gravity is 58.8 N. The upward force is not known but can be calculated if the F net = m•a equation is applied
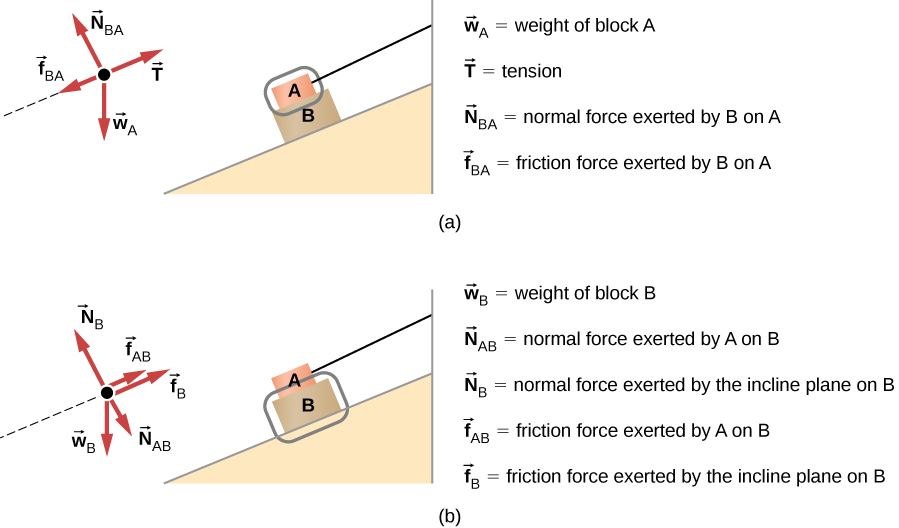
Two blocks on top of each other free body diagram. 11:09Free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website Key Words: Newton 1st first and 2nd second ...24 Jan 2016 · Uploaded by Physicshelp Canada Two blocks on top of each other free body diagram. Top 10 equations that changed. Gravity m 1 g points down normal force n 1 points up and friction f 1 points to the right. The force of gravity is calculated in the usual manner using 140 kg as the mass. I was wondering if anyone can provide feedback on my free body diagram of two objects acting ... Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... 5:51Hi reader,this video explains the complex situation of Frictional Forces when a Block is placed on top of ...27 Jul 2016 · Uploaded by physicsmodels by kaustubhan
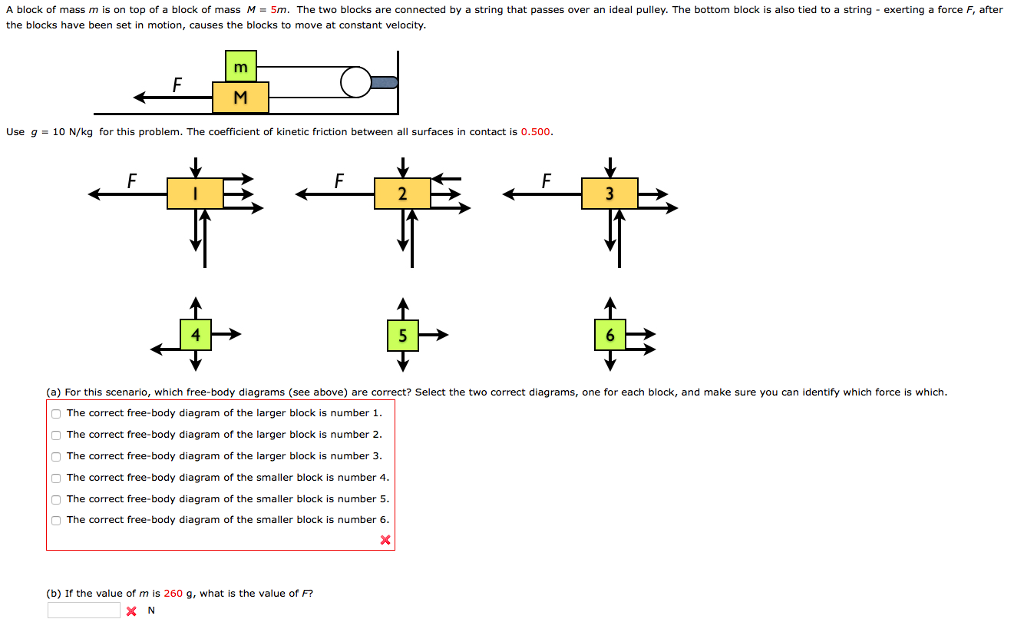
2:01This video screencast was created with Doceri on an iPad. Doceri is free in the iTunes app store. Learn more ...27 Oct 2018 · Uploaded by Mark Willis by W Moebs · 2016 — Draw a free-body diagram for each block. ... The other end of the rope is attached to a second block. ... Explain how the graphs relate to one another. Two blocks on top of each other free body diagram. In other words for this problem you will need to make two free body diagrams and set up two sets of equations. Three blocks are placed on a surface resting on top of each other as shown. So the short answer. The direction of friction might be up the slope or 180 degrees opposite down the slope ... Free Body Diagram-Two Blocks SystemLaws of Motionstudiesmadeeasy.com
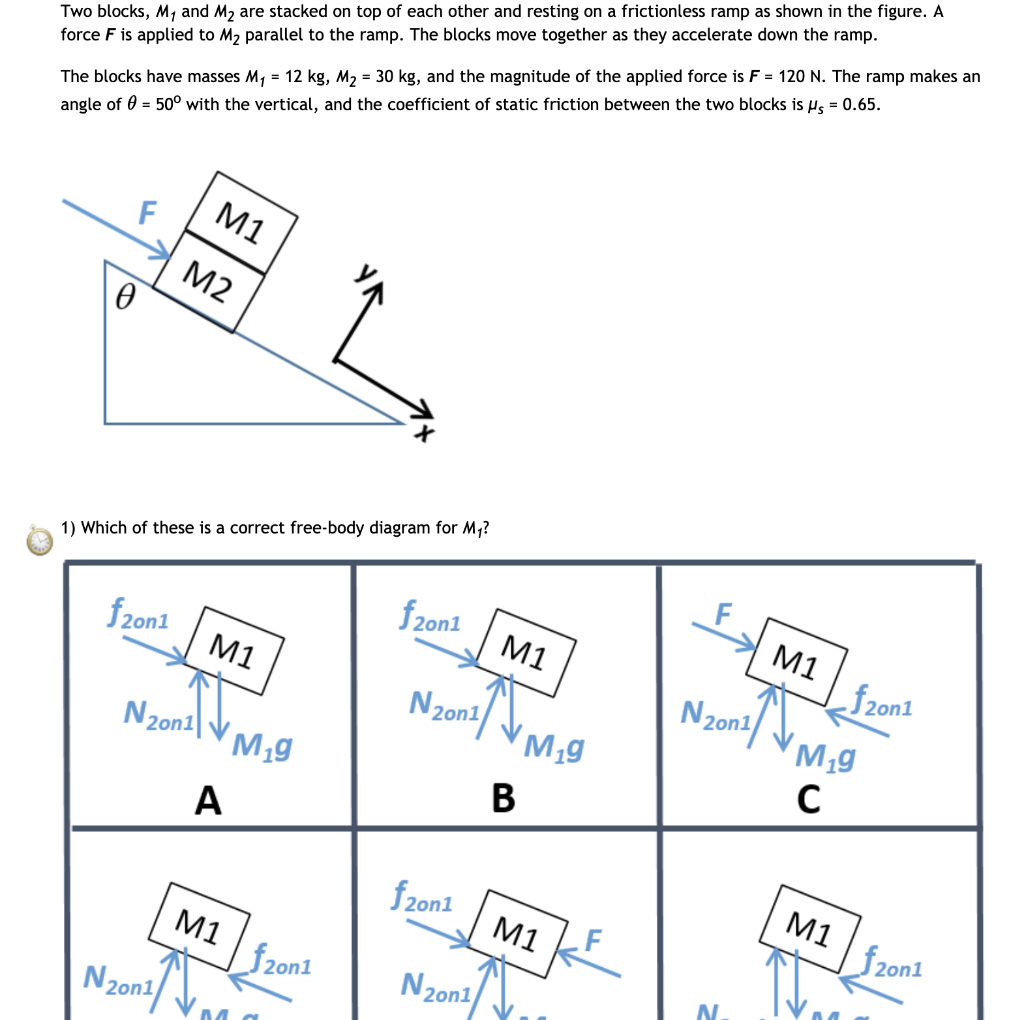
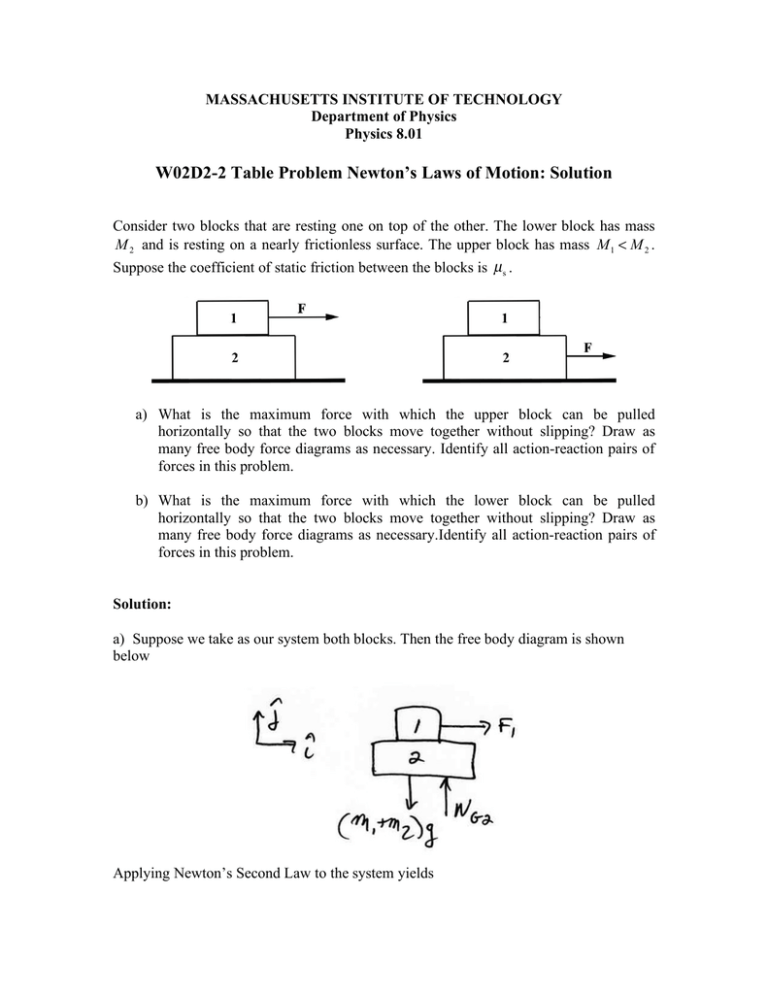
Consider two blocks that are resting one on top of the other. ... Worked Example - Stacked Blocks - Free Body Diagrams and Applying Newton's 2nd Law ...2 Jun 2017 · Uploaded by MIT OpenCourseWare Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... Example 8 : A system with two blocks, an inclined plane and a pulley. A) free body diagram for block m 1 (left of figure below) 1) The weight W1 exerted by the earth on the box. 2) The normal force N. 3) The force of friction Fk. 4) The tension force T exerted by the string on the block m1. B) free body diagram of block m 2 (right of figure below) Solved Two 10kg Boxes Are Stacked On Top Of Each Other On Finally the leftward friction force is the result of friction with the floor over which the 50 kg object moves. Two blocks on top of each other free body diagram. Between the two blocks normal force is perpendicular to the slope friction is parallel.

Ps 2 2 Worked Example Pushing Stacked Blocks Week 2 Newton S Laws Classical Mechanics Physics Mit Opencourseware
The top box is used in this analysis since it encounters one less force. The free-body diagram is shown at the right. The force of gravity on the top box is m•g where m = 6.0 kg. The force of gravity is 58.8 N. The upward force is not known but can be calculated if the F net = m•a equation is applied
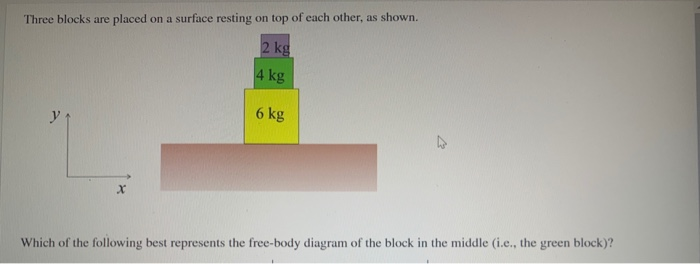
Two blocks on top of each other free body diagram. Which of the following represents best the free body diagram of the block in the middle ie. Between the bottom of the block and the floor there is normal force perpendicular to the floor. You will want to draw two free body diagrams one for each book then you can put in the forces that act from ...
11:24This physics video tutorial explains how to calculate the contact force between blocks using free body diagrams ...3 Nov 2017 · Uploaded by The Organic Chemistry Tutor

Physics 141 Chapter 61 Force Motion Outline Friction Static And Kinetic The Drag Force And Terminal Speed Uniform Circular Motion Chapter Ppt Download

Two Blocks With Rough Surfaces Are Stacked On Top Of A Slippery Horizontal Surface The Top Block Has Brainly Com
Solved Two Blocks Are Stacked On Top Of Each Other As Shown The Block Of Mass M Is Resting On A Friction Less Surface The Coefficient Of Static F Course Hero
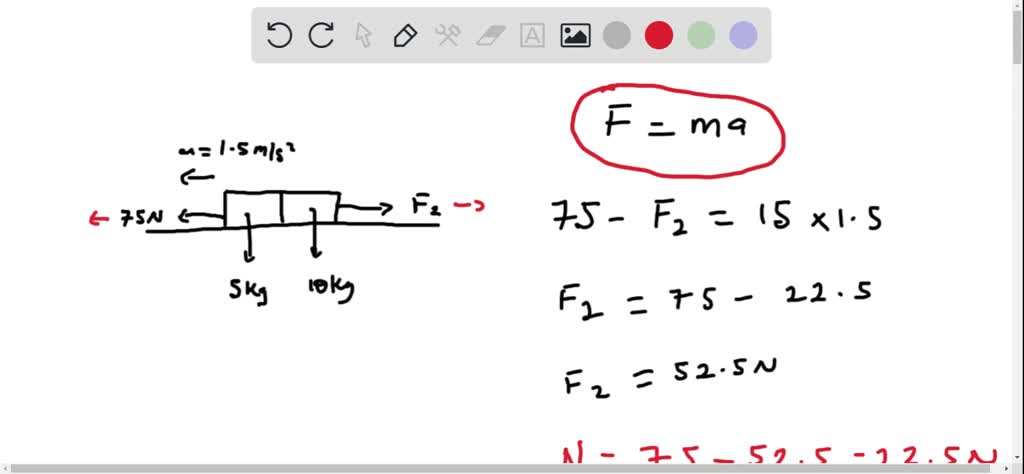
Solved Consider Two Blocks Of Mass 5 0 Kg Sitting On Top Each Other On Top Of A Table A Draw The Free Body Diagrams Of The Two Blocks B Calculate The Normal

Two Blocks A And B Of Mass M A And M B Are Stacked On Top Of Each Other On A Ramp Of Angle Theta The Two Object Are Stationary And Connected By A

Two Blocksa Andb Are Connected To Each Other By A String And A Spring The Spring Pases And A Frictionlesss Pulley As Down Over In The Figure Block B Sides

Block 1 M1 8kg And Block 2 M2 2 Kg Are Adjacent To Each Other On The Surface Of A Table Block 2 Is To The Left Of Block 1 A Hand Pushes
Ps 2 2 Worked Example Pushing Stacked Blocks Week 2 Newton S Laws Classical Mechanics Physics Mit Opencourseware

Solved Two Blocks And B Of Mass M And Mg Are Stacked On Top Of Each Olhcr On Ramp O Angle The Two Objeets Are Stationary And Connected By Massless Rope Via Pulley










0 Response to "39 two blocks on top of each other free body diagram"
Post a Comment