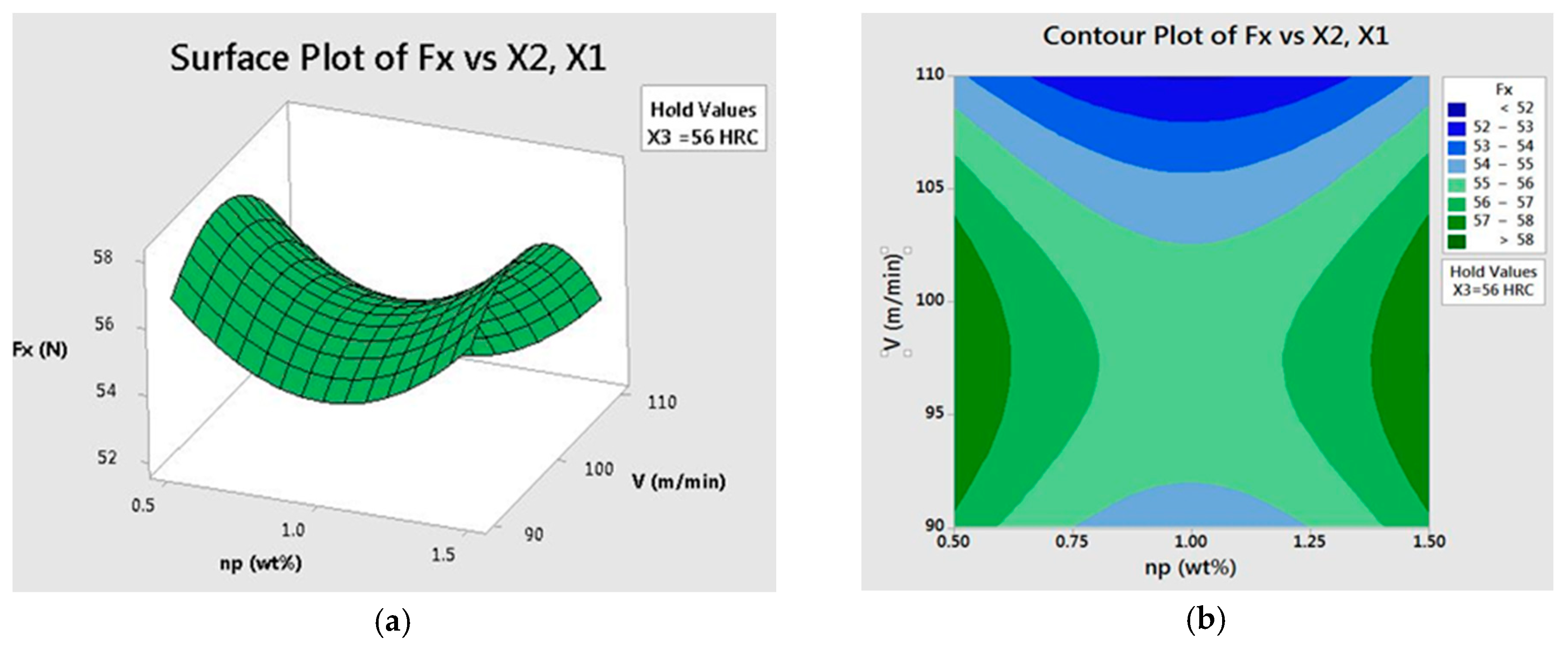
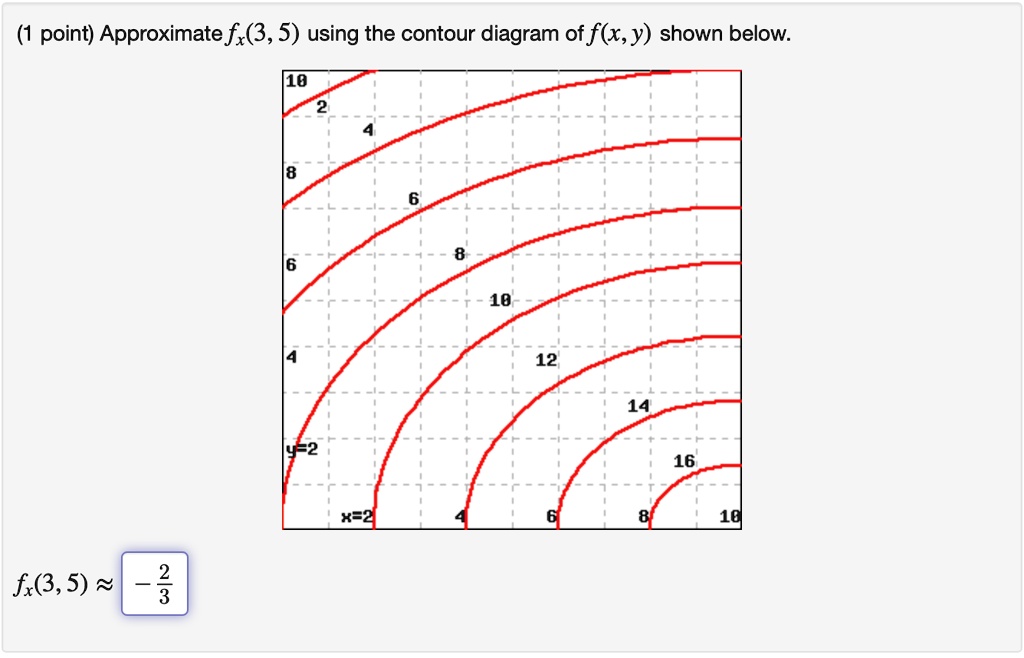
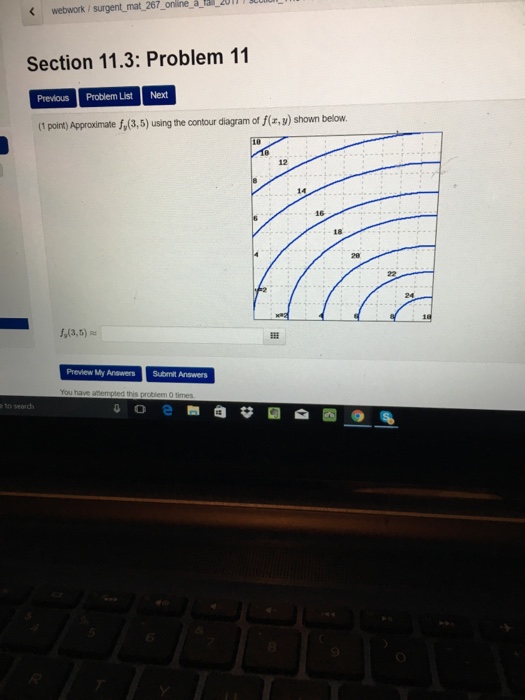
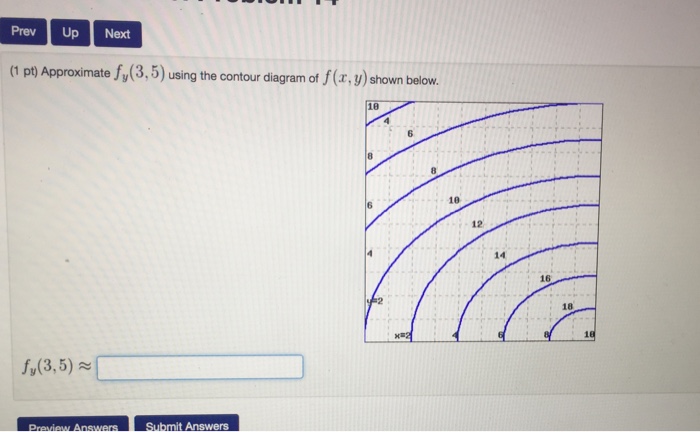
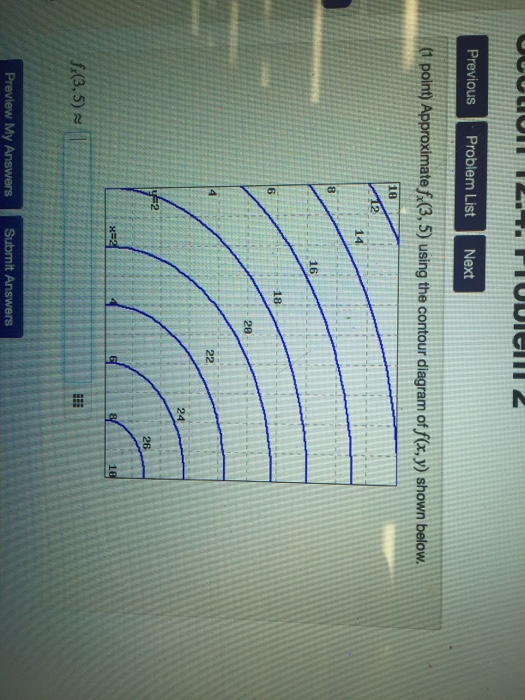
40 approximate fx(3,5)fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y)f(x,y) shown below.
Changing "c" only changes the vertical position of the graph, not it's shape. The parabola y = x 2 + 2 is raised two units above the graph y = x 2. Similarly, the graph of y = x 2 - 3 is 3 units below the graph of y = x 2. The constant term "c" has the same effect for any value of a and b. Parabolas in the vertex-form or the a-h-k form, y = a(x ... Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of fx(x,y). I am very confused full credit for right answer. Show transcribed image text (1 point) Approximate fx(3, 5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. Fx(3,5). Posted 8 months ago. HELP!! POINTS WILL BE REWARDED, ANSWERS WITH WORK SHOWN!! THANK YOU!!! Show transcribed image text Sketch the contour plot for the following functions ...
The diagram above shows a sketch of the curve with equation y = x 1n x, x 1. The finite region R, shown shaded in Figure 1, is bounded by the curve, the x-axis and the line x = 4. The table shows corresponding values of x and y for y = x 1n x. x 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 y 0 0.608 3.296 4.385 5.545 , (4 ) 4 1 x x2 4 y t

Approximate fx(3,5)fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y)f(x,y) shown below.
Level curves of G (x, y) are shown in the figure below. Find its approximate x- and y-derivatives at (3, 3). Ans: {10/1.3, 10/1.4} 3. Let the figure below be the contour diagram of f (x,y ). Find an approximate x derivative at (2, 2) by using the centered difference quotient. Ans:1/2 4. Figure 11 shows the graph of the function P(x, 2) of x that is obtained from P(x, y) b y setting y = 2, and ... Solutions to Graphing Using the First and Second Derivatives. SOLUTION 1 : The domain of f is all x -values. Now determine a sign chart for the first derivative, f ' : f ' ( x) = 3 x2 - 6 x. = 3 x ( x - 2) = 0. for x =0 and x =2 . See the adjoining sign chart for the first derivative, f ' . Now determine a sign chart for the second derivative ... 4 Gradients and directional derivatives in the plane Remark 4.1. The partial derivatives f x and f y tell us the rate of change of f parallel to the coordinate axes. In this section, we consider partial derivatives
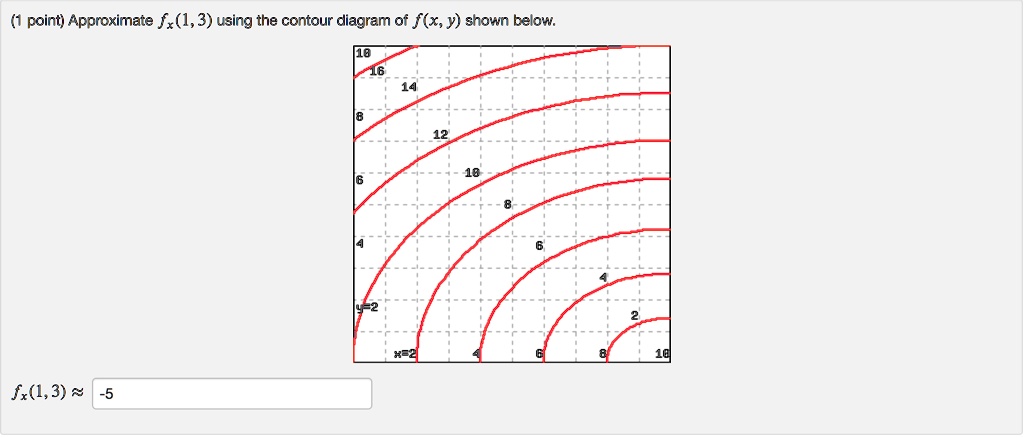
Approximate fx(3,5)fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y)f(x,y) shown below.. Using right triangle trigonometry, Fx is adjacent to angle A, Fy is opposite to angle A, and F is the hypotenuse, as: Unusual diagram The above diagram shows how the trigonometry is usually presented - the cosine function is associated with the x-component and the sine function is associated with the y-component . Answer to 16. (1 point) Approximate fr(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. 10 14 12 10 2 *=2 of 10 fx (3, 5) ~ Pt approximate f x 3 5 using the contour diagram of f. This preview shows page 4 - 5 out of 5 pages. Suppose that f(x,y)is a smooth function and that its partial derivatives have the values, fx(- 1,- 8) =4 andfy(- 1,- 8) = 3. Given thatf(- 1,- 8) = - 9, use this information to estimate the following values: Estimate of (integer value) f(- 1,- 7 ... See the answer See the answer done loading. Approximate f x (1,3) using the contour diagram of f (x,y) shown below. Solve for f x (1,3) = ????? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (21 ratings)
subject to the constraint 2x2 +(y 1)2 18: Solution: We check for the critical points in the interior f x = 2x;f y = 2(y+1) =)(0; 1) is a critical point : The second derivative test f xx = 2;f yy = 2;f xy = 0 shows this a local minimum with Once again, the derivative gives the slope of the tangent line shown on the right in Figure 10.2.3.Thinking of the derivative as an instantaneous rate of change, we expect that the range of the projectile increases by 509.5 feet for every radian we increase the launch angle \(y\) if we keep the initial speed of the projectile constant at 150 feet per second. fx x gx xx −≤ ≤− = +−<≤ Is g continuous at x =−3? Use the definition of continuity to explain your answer. (d) Find the value of 5 2 0 x 25 .− xdx (a) () ()() 2 12 2 1 25 2 , 5 5 2 25 x xx x fx x − − =− −= −<< − ′ 2 : f′()x (b) () 33 294 3 5 f == − ′ − f ()−= − =39425 An equation for the tangent line is ... See the answer See the answer done loading. Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. fx(3,5)? Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
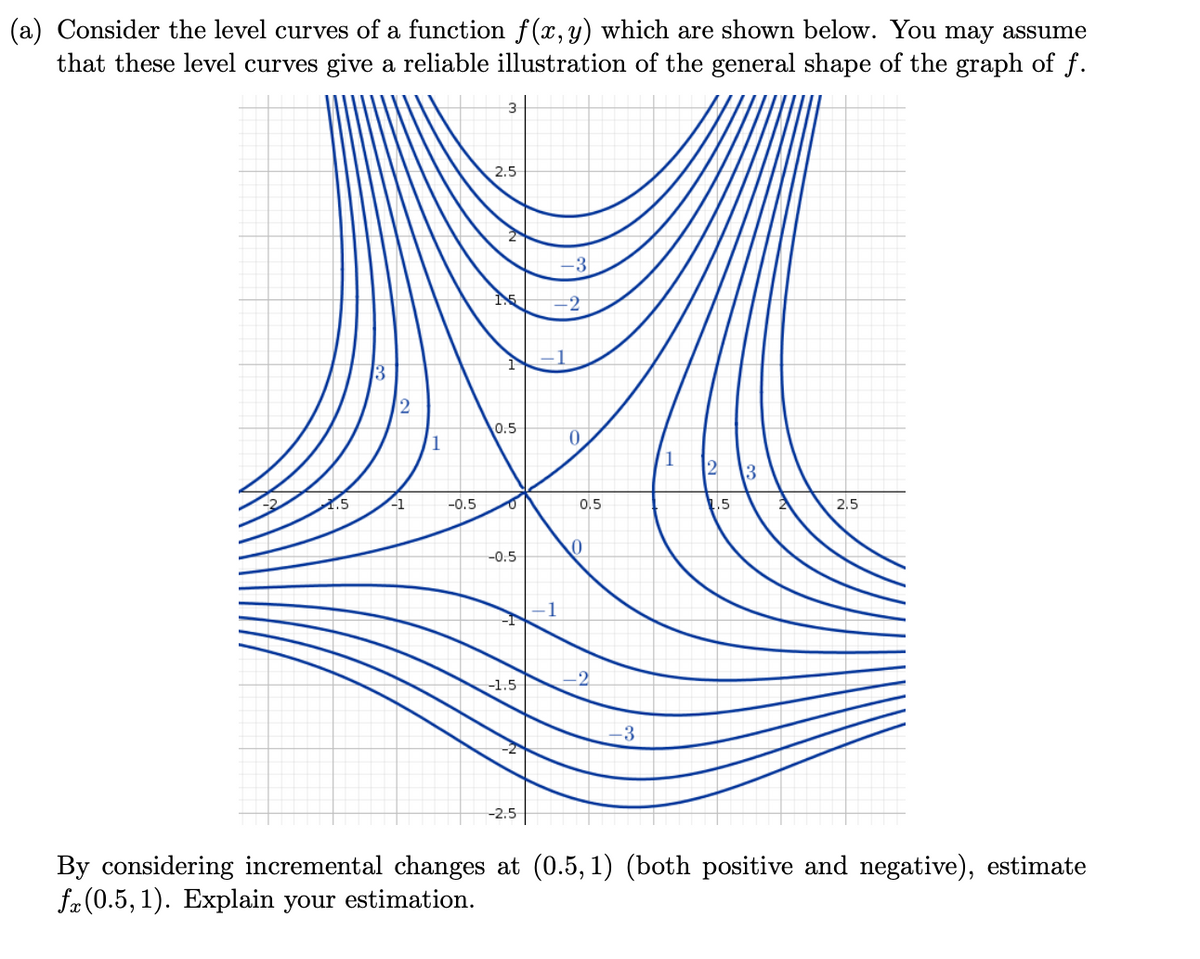
24 Jan 2021 — I am very confused full credit for right answer. Show transcribed image text (1 point) Approximate fx(3, 5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) ... Okay, so we want to ask to meet ah the partial derivative of F with respect to X at the 0.3 comma five. And so at this point right here is Has coordinates 3:05. Now, if we want to estimate the partial derivative with respect to X, then from this point we want to move in the direction of the X axis until we arrive at the next contour line. And and so the partial derivative F with respect to X ... Contour maps give a way to represent the function while only drawing on the two-dimensional input space. Step 1: Start with the graph of the function. Example function graph. Step 2: Slice the graph with a few evenly-spaced level planes, each of which should be parallel to the -plane. We provide solutions to students. Please Use Our Service If You’re: Wishing for a unique insight into a subject matter for your subsequent individual research;

1 Point Determine The Sign Of Fe And Fy At Each Indicated Point Using The Contour Diagram Of Shown Below The Point P Is That In The First Quadrant At A Positive
Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of fx(x,y). I am very confused full credit for right a Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of fx(x,y). I am very confused full credit for right answer. Show transcribed image text (1 point) Approximate fx(3, 5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. Fx(3,5). Sep …
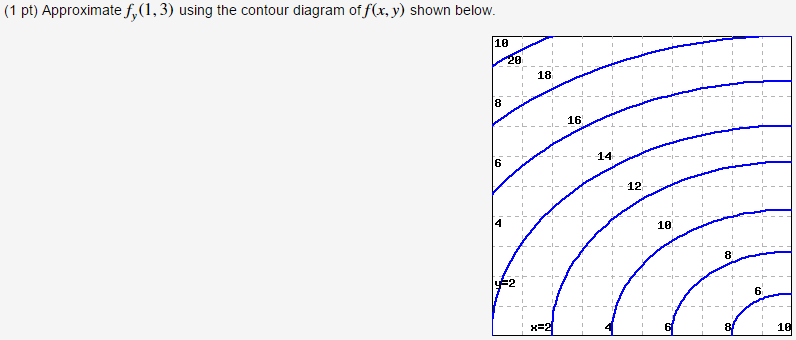
1. (1 point) Approximate f y(1;3) using the contour diagram of f(x;y) shown below. f y(1;3)ˇ Answer(s) submitted: -0.8 (correct) 2. (1 point) Find the partial derivatives indicated. Assume the variables are restricted to a domain on which the function is defined. z= x5 +x y 6: ¶z ¶x = ¶z ¶y = Answer(s) submitted: 6((xˆ5+x-y)ˆ5)*(5*xˆ4 ...
Graphs of Surfaces and Contour Diagrams - 5 In principle, the contour diagram and the graph can each be reconstructed from the other. Here is a picture illustrating this: As shown above, the contour f(x;y) = k is obtained by intersecting the graph of f with the horizontal plane, z = k, and then dropping (or raising) the resulting curve

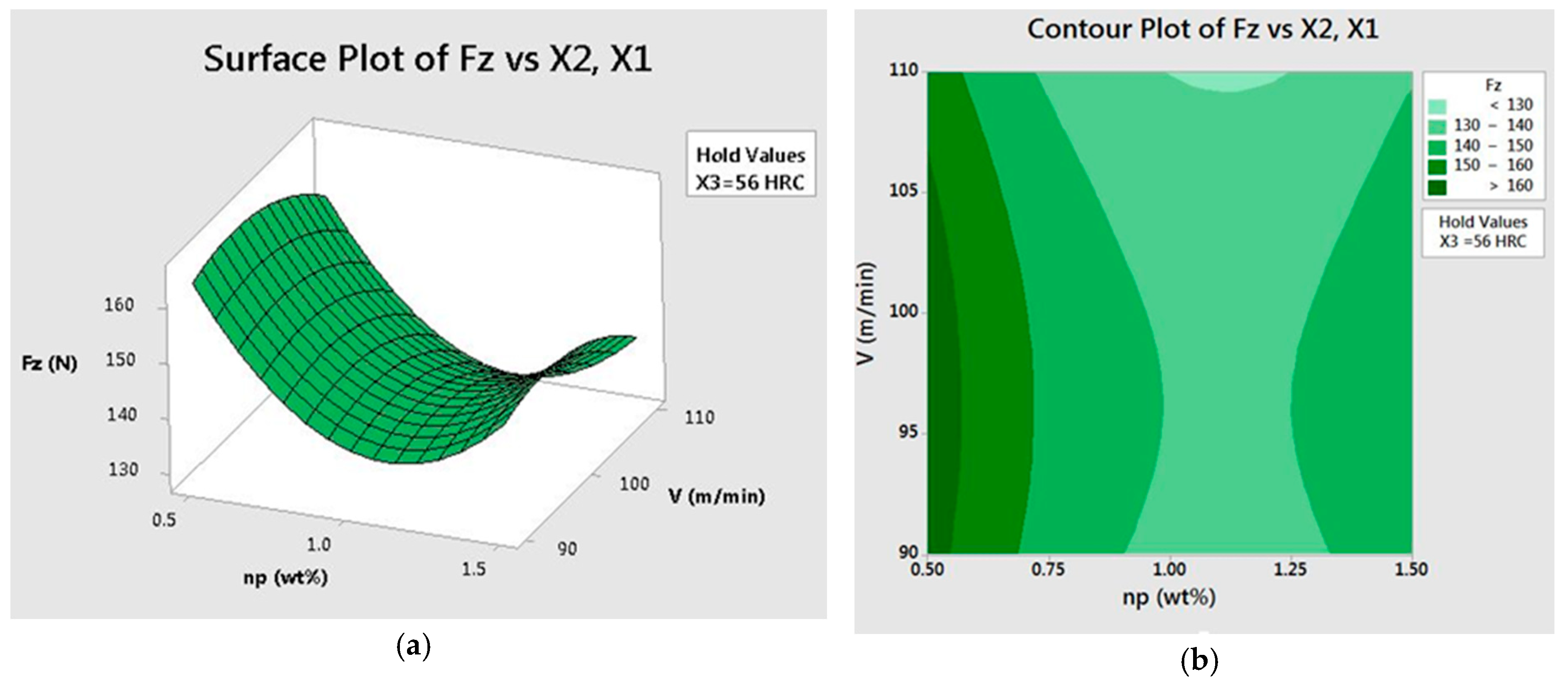
Performance Evaluation Of A Downwind Diffuser On Vertical Axis Wind Turbine Wang International Journal Of Energy Research Wiley Online Library
Chapter 4: Taylor Series 17 same derivative at that point a and also the same second derivative there. We do both at once and define the second degree Taylor Polynomial for f (x) near the point x = a. f (x) ≈ P 2(x) = f (a)+ f (a)(x −a)+ f (a) 2 (x −a)2 Check that P 2(x) has the same first and second derivative that f (x) does at the point x = a. 4.3 Higher Order Taylor Polynomials
27 Tangent Planes to Level Surfaces Suppose S is a surface with equation F(x, y, z) = k, that is, it is a level surface of a function F of three variables, and let P(x 0, y 0, z 0) be a point on S. Let C be any curve that lies on the surface S and passes through the point P.Recall that the curve C is described by a continuous vector function r(t) = 〈x(t), y(t), z(t)〉.
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
If f(x) is the density function for a random variable X, then we can represent y f(x) graphically by a curve as in Fig. 2-2. Since f(x) 0, the curve cannot fall below the x axis. The entire area bounded by the curve and the x axis must be 1 because of Property 2 on page 36. Geometrically the probability that X is between a and b, i.e.,

Toward A Theory Of Mechanochemistry Simple Models From The Very Beginnings Quapp 2018 International Journal Of Quantum Chemistry Wiley Online Library
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (1 rating) Transcribed image text : Approximate f_x(3, 5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below.

Pdf A Maccormack Tvd Finite Difference Method To Simulate The Mass Flow In Mountainous Terrain With Variable Computational Domain
Question: (1 pt) Approximate fx (3,5) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. 18 2 ㄒㄧ--「-- 4 8 6 8 6 18 ㄒㄧ--「- 12 14 2 16 f. (3,5) ...
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Question: (1 point) Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. 10 2 8 6 10 12 14 y2 16 x=2 8 10 f:(3,5) = - 2 3 · This problem has been ...
If the following is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the z = 0 contour at the origin, going up by 1 for each concentric circle, approximate the rate of change of f(x,y) at (1,1) in the direction of

Solved Point A Contour Diagram For A Function F X Y Is Shown Below Estimate The Position And Approximate Value Of The Global Maximum And Global Minimum On The Region Shown Global Maximum At
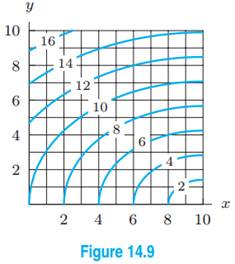
Stewart 14.3.10 [3 pts] A contour map for a function fis given. Use it to estimate f x(2;1) and f y(2;1). Solution: We can estimate f x by observing that as xgoes from 1.5 to 2.5, with y= 1 xed, f seems to go from about 9 to 12. Therefore f x(2;1) is approximately 3. As ygoes from 0.5 to 1.5, with x= 2 xed, fgoes from about 11 to about 9, so f y(2;1) is roughly -2. 2. Stewart 14.3.70 [3 pts ...
Free Linear Approximation calculator - lineary approximate functions at given points step-by-step This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. By using this website, you agree to our Cookie Policy.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: (1 point) Approximate fx (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. Fx (3,5).
Free essays, homework help, flashcards, research papers, book reports, term papers, history, science, politics
Lubricants Free Full Text Improvement In The Hard Milling Of Aisi D2 Steel Under The Mqcl Condition Using Emulsion Dispersed Mos2 Nanosheets Html
This video explains how to use the slope of a secant line to determine the value of a partial derivative using a contour map.Site: http://mathispower4u.com
Question: Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
imum and minimum values of f(x;y) = 2x+ ysubject to x2 + y2 = 5. (a)The contours of fare straight lines with slope 2 (in xyterms), as shown below. (b)Overlaying the constraint, we are allowed to move on a circle of radius p 5. (c)From the graph, the maximum values occurs where the constraint circle just touches the f= 5 contour line, at (x;y ...
Question: Approximate fy(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
Solved Point Approximate F 3 5 Using The Contour Diagram Of F X Y Shown Below I10 10 12 16 10 F 3 5 2
See the answer See the answer done loading. Approximate fx (3,5) using the contour diagram of f ( x, y) shown below. fx (3,5)? Show transcribed image text. Best Answer. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. Transcribed image text: Approximate fx (3,5) using the contour diagram of f (x,y) shown below.

Wind Forced Downwelling Slope Currents A Numerical Study In Journal Of Physical Oceanography Volume 29 Issue 8 1999
fullscreen Expand. Transcribed Image Text. Approximate f (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f (x, y) shown below. 18 12 10 6 X=2 10. check_circle.

Impact Of Back End Of Line Architecture On Chip Package Interaction In Advanced Interconnects Sciencedirect
3 3. Determine the sign of f x and f y at the point using the contour diagram of f in the gure below. (a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S 4. Approximate f x(3;5) using the contour diagram of f(x;y) shown in the gure below.
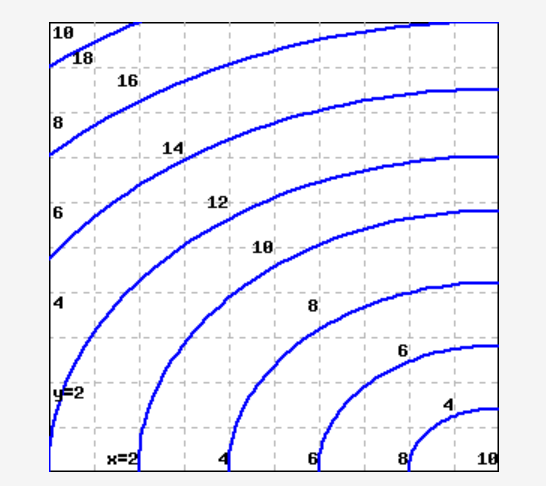
Approximate f x 3 5 using the contour diagram of f x. This preview shows page 4 - 5 out of 5 pages. y0)h. Here, we have f(3,5)≈8, and f(6,5)≈ 6. Thus, we can take fx≈ f(6,5)- f(3,5) 3 = 6- 8 3 = - 0.666667. Of course, we could takeh < 0 and use the contour f= 6 as well, or average the two results.Answer (s) submitted: • -2/3 (correct ...
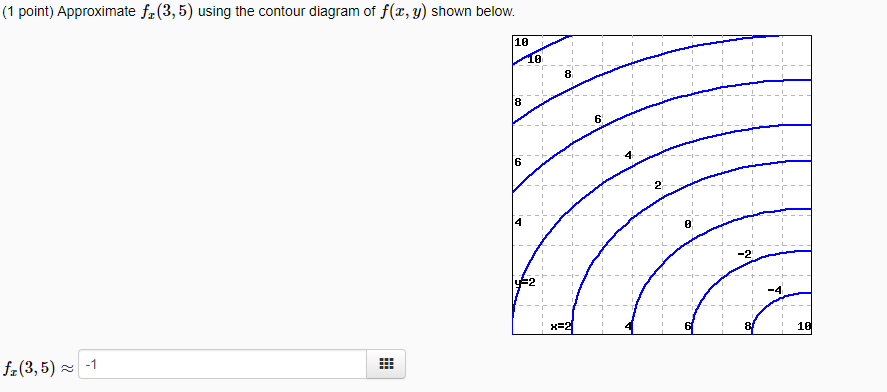
Question: Approximate f_x (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. f_x(3, 5) -1. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
Question: (1 point) Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x, y) shown below. 20 8. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
Approximate fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y) shown below. fx(3,5)? ... What happens next? After payment, your answer will be immediately delivered to your email (so don't forget to check your spam folder in case you don't see anything!)

Ground Displacements Due To The Deformations Of Shallow Tunnels With Arbitrary Cross Sections In Soft Ground
4 Gradients and directional derivatives in the plane Remark 4.1. The partial derivatives f x and f y tell us the rate of change of f parallel to the coordinate axes. In this section, we consider partial derivatives
Solutions to Graphing Using the First and Second Derivatives. SOLUTION 1 : The domain of f is all x -values. Now determine a sign chart for the first derivative, f ' : f ' ( x) = 3 x2 - 6 x. = 3 x ( x - 2) = 0. for x =0 and x =2 . See the adjoining sign chart for the first derivative, f ' . Now determine a sign chart for the second derivative ...
Level curves of G (x, y) are shown in the figure below. Find its approximate x- and y-derivatives at (3, 3). Ans: {10/1.3, 10/1.4} 3. Let the figure below be the contour diagram of f (x,y ). Find an approximate x derivative at (2, 2) by using the centered difference quotient. Ans:1/2 4. Figure 11 shows the graph of the function P(x, 2) of x that is obtained from P(x, y) b y setting y = 2, and ...
Solved Point Approximate F 3 5 Using The Contour Diagram Of F X Y Shown Below I10 10 12 16 10 F 3 5 2
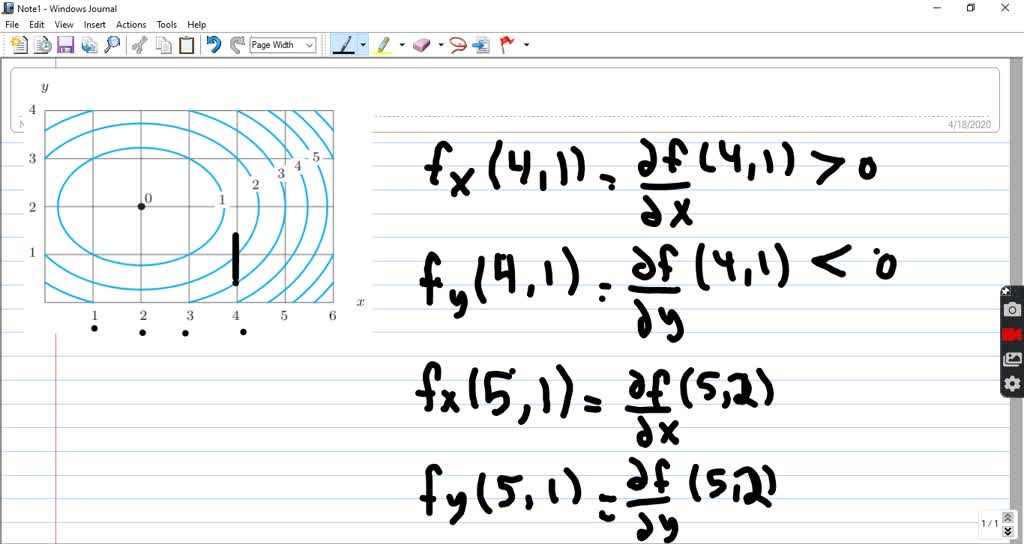
Solved Using The Contour Diagram For F X Y In Figure 8 36 Decide Whether Each Of These Partial Derivatives Is Positive Negative Or Approximately Zero A Quad F X 4 1 B F Y 4 1 C F X 5 2 D Quad




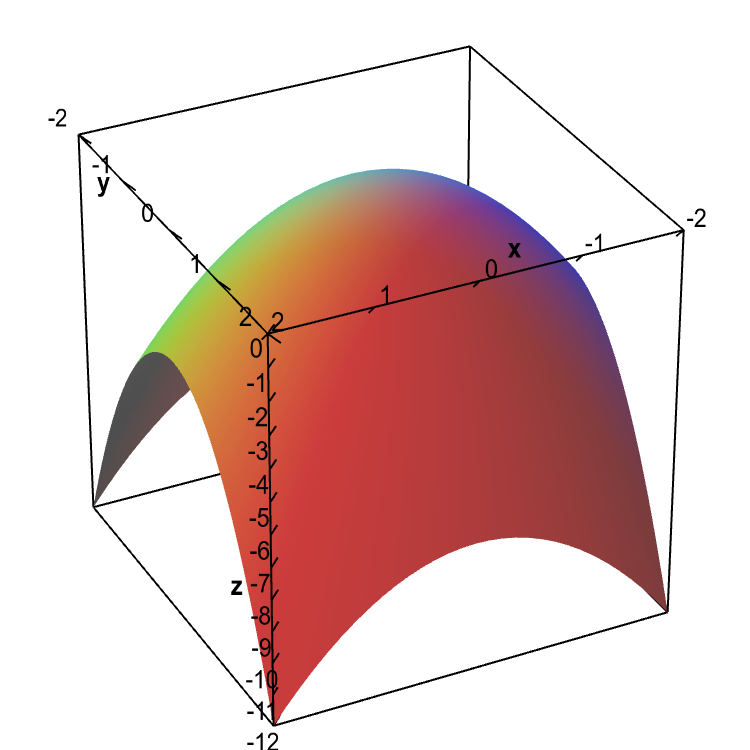






0 Response to "40 approximate fx(3,5)fx(3,5) using the contour diagram of f(x,y)f(x,y) shown below."
Post a Comment