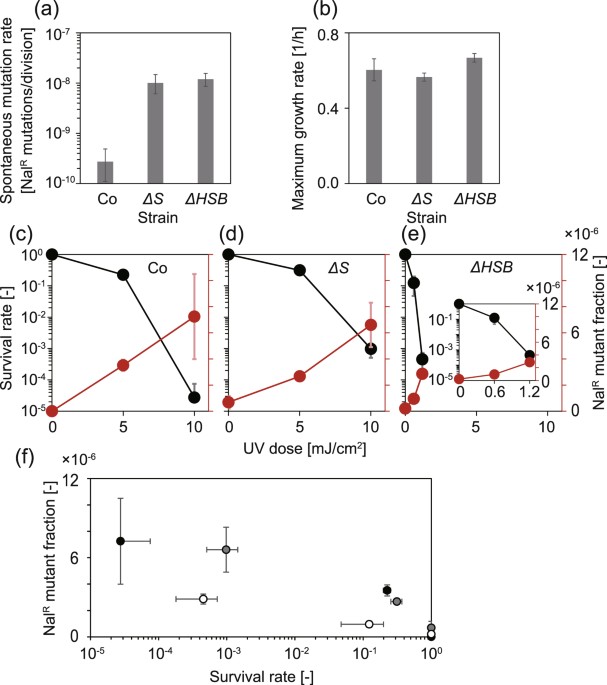
40 draw a ray diagram representing your experiment from part c
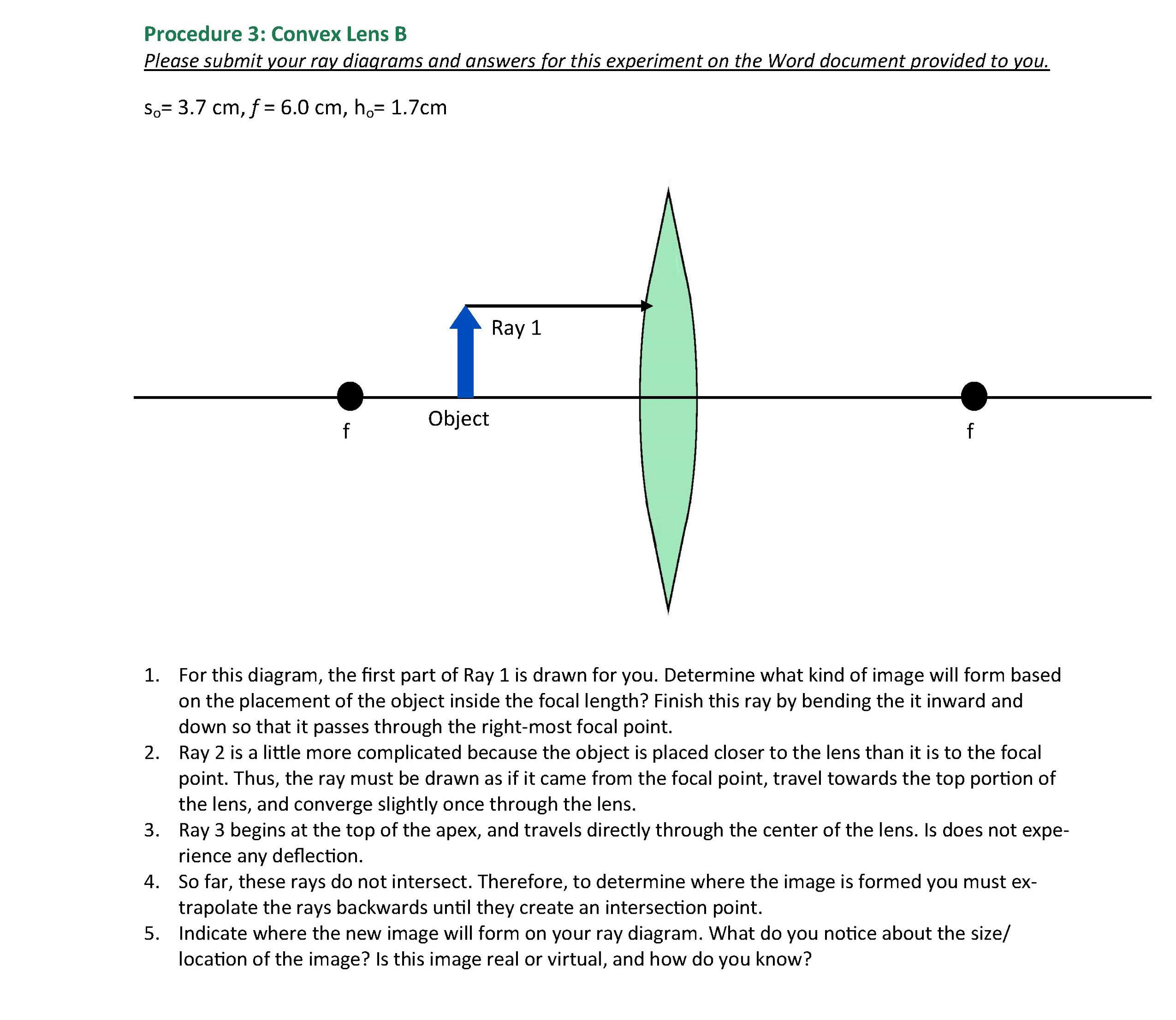
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ (a) Draw ray diagram of refraction of light through a prism and explain the phenomenon of dispersion of light.(b) Write the formula for lens power and define its unit. First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis. So, it passes through focus after refraction. We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. Where both rays meet is point A'. And the image formed is A'B'. This image is formed between F 2 and 2F 2. We can say that.
Question 1: Draw the diagram given below and clearly show the path taken by the emergent ray. Answer: i c = 42 for glass. The ray undergoes refraction as it emerges away from the slab. Question 2: A ray of light moves from a rare medium to a dense medium as shown in the diagram below. Write down the number of the ray which represents the ...

Draw a ray diagram representing your experiment from part c
Lenses Ray Diagram Construction Worksheet Teaching. Long Answer Questions 30. On the diagram, label the point on the mirror where the incident ray from A reflects from the mirror with the letter "x". Draw a scale ray diagram showing the image position and height. Draw a ray diagram for a convex mirror when an object is placed at 2F. Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed : ... (c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image. Mark clearly F and 2F in the diagram. ... A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm ... 5. Redraw Figure 9 for your lab report to practice ray tracing . 6. Is the image upright or inverted? Is the magnification greater or less than one? Describe the image. Also include the following in your lab report as part of Experiment 1: 7. Make a ray diagram for an object placed closer to a diverging (concave) lens than the focal point.
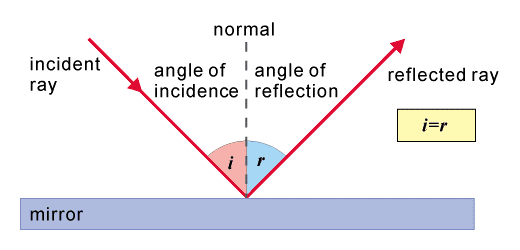
Draw a ray diagram representing your experiment from part c. Ray diagram through the convex lens: Concave Lens Ray Diagram Class 10; CBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual Experiment 7. Convex Lens Experiment Class 10. Aim To find the image distance for varying object distances in case of a convex lens and draw corresponding ray diagrams to show the nature of image formed. Theory. Lens: It is a piece of a ... Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays. (CBSE 2008) Answer: Question 2. Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed: (a) At 2F Using a protractor, draw a normal at C, roughly the middle of AB. Draw a line at 20 o to the normal. Position a plane mirror carefully along AB. Direct a ray of light from a ray box along the 20 o ... The three laws of reflection. Any mirror obeys the three laws of reflection, flat, curved, convex or concave. 1. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal. 2. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray are all in the same plane. 3.
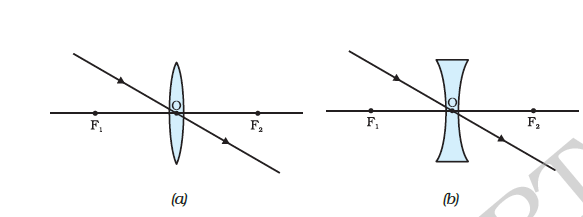
Draw a Venn diagram representing the situation. Find the probability that the customer buys either a novel or a non-fiction book. In the Venn diagram, describe the overlapping area using a complete sentence. Suppose that some customers buy only compact disks. Draw an oval in your Venn diagram representing this event. Ray diagrams help us trace the path of the light for the person to view a point on the image of an object. Ray diagram uses lines with arrows to represent the incident ray and the reflected ray. It also helps us trace the direction in which the light travels. Plane Mirror vs Spherical Mirrors One point is earned for the molecular geometry consistent with the Lewis diagram in part (a). (c) In the SO 2 molecule, both of the bonds between sulfur and oxygen have the same length. Explain this observation, supporting your explanation by drawing in the box below a Lewis electron-dot diagram (or diagrams) for the SO 2 molecule. In each case, draw a diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it. Solution: (i) When the angle of incidence is 0 0 (ii) When the angle of incidence is 45 0. Question: 26. In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
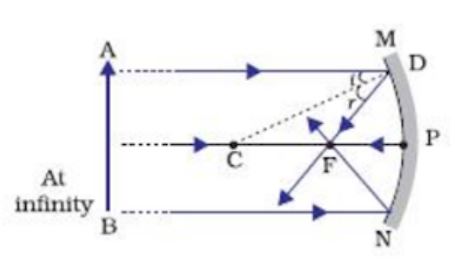
Rule 2 - Ray passing through focus will become parallel to principal axis after reflection. For a concave mirror , we see that ray passing through focus becomes parallel to principal axis after reflection. For a convex mirror, since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis. 5 The diagram shows a cuboid block made from a metal of density 2.5 g / cm 3. 2.0 cm 2.0 cm 10 cm What is the mass of the block? A 8.0 g B 16 g C 50 g D 100 g 6 The diagram shows an object moving at a constant speed in a circular path in the direction shown. A force acts on the object to keep it in the circular path. The method for drawing ray diagrams for concave mirror is described below. The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the center of curvature (C) of a concave mirror. Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two ... A ray of green light enters a liquid from air, as shown in the figure. The angle 1 is 45 o and angle 2 is 30 o. (a) Find the refractive index of liquid. (b) Show in the diagram the path of the ray after it strikes the mirror and re-enters in air.
A.) The sound waves were pushed closer together. Emmy is running a marathon to try to get a Boston time. She runs at a constant velocity of 6mph from 7:00 am to 9:00 am. At 10 a, her velocity was 8mph. She completed her race at 10:30am at a velocity of 10mph. Calculate her acceleration from 10:00am-10:30 am.
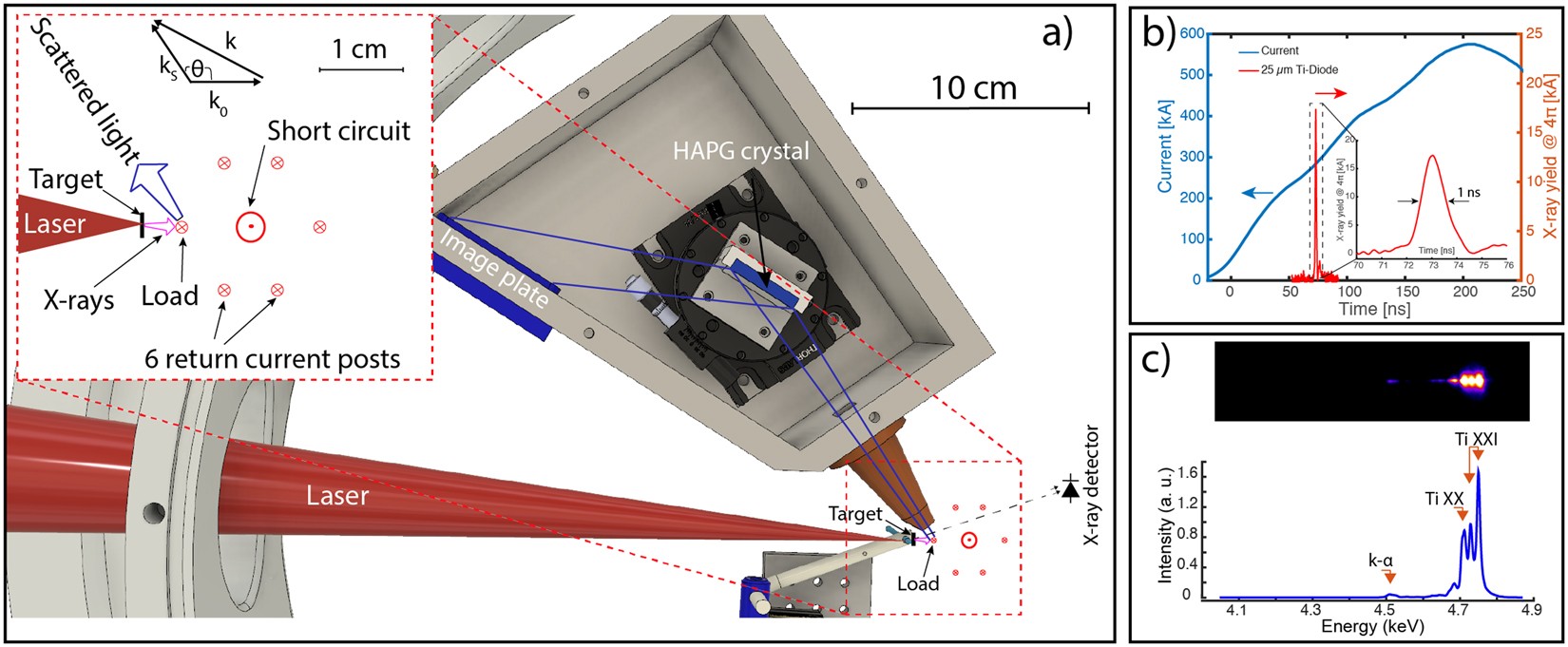
Measurement Of Temperature And Density Using Non Collective X Ray Thomson Scattering In Pulsed Power Produced Warm Dense Plasmas Scientific Reports
The first ray to draw will go from the top of the object towards the centre of curvature of the mirror, although it will not get there (the dashed line is a construction line added to make the diagram clearer, it does not represent the path of a ray). This ray is reflected back along the same path.
(a) Draw a ray diagram to explain the term angle of deviation. (2017 D) (b) Why do the component colours of incident white light split into a spectrum while passing through a glass prism, explain. (c) Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of a rainbow. Answer:
Drawing Ray Diagrams - a Step-by-Step Approach. This section of Lesson 2 details and illustrates the procedure for drawing ray diagrams. Let's begin with the task of drawing a ray diagram to show how Suzie will be able to see the image of the green object arrow in the diagram below. For simplicity sake, we will suppose that Suzie is viewing the ...
3. From this experiment, determine the positions where you can see the pin with your open eye. Draw light rays on the diagram below to support your hypothesis. Remember, the light rays come from the object and go to the eye. 4. Philosophy alert: If you observe the image of the object, and then close your eyes, does the image still exist? Explain.
Draw a ray diagram showing position of the image. Answer: Question 17: Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the determination of the focal length of a convex lens using an auxiliary plane mirror. Answer: Question 18: Draw the ray diagrams of a converging lens, when the object is placed at a distance greater than twice the focal length of the lens ...
A real image is an image that can be projected onto a screen. A virtual image appears to come from behind the lens. To draw a ray diagram: Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel ...
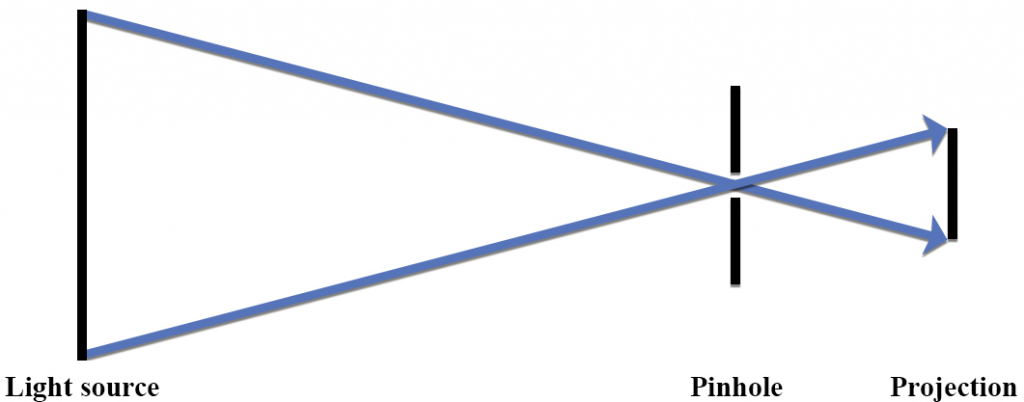
On your original diagram, add the light rays that would make it from the light source in its new position to the screen. How would the position of the light spot on the screen change? 3. Draw a new ray diagram for a similar situation with a new light source, in the shape of a vertical arrow that emits light from all parts.
Draw A Ray Diagram To Show Refraction Of A Ray Of Monochromatic Light Passing Through A Glass Prismdeduce The Expression For The Refractive Index Of G Physics Topperlearning Com Bmxqe3dpp
Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed: ... (c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image. Mark clearly F and 2F in the diagram. ... A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm ...
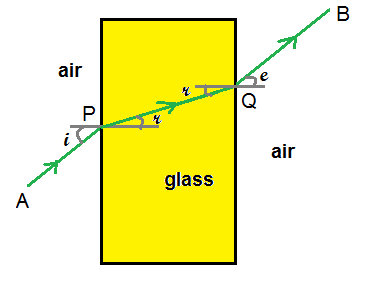
Draw A Ray Diagram To Show The Refraction Of Light Through The Glass Slab And Mark Angle Of Refraction And The Lateral Shift Suffered By The Ray Of Li Science
Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer. Answer 8. If a parallel beam of light is incident on a convex lens then the upper part of the lens bends the incident ray downwards. The lower part bens the ray upwards while the central part passes the ray undeviated. Convex lens
Ray diagrams. To determine where the image is, it is very helpful to draw a ray diagram. The image will be located at the place where the rays intersect. You could just draw random rays from the object to the mirror and follow the reflected rays, but there are three rays in particular that are very easy to draw.
5. Redraw Figure 9 for your lab report to practice ray tracing . 6. Is the image upright or inverted? Is the magnification greater or less than one? Describe the image. Also include the following in your lab report as part of Experiment 1: 7. Make a ray diagram for an object placed closer to a diverging (concave) lens than the focal point.
Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed : ... (c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image. Mark clearly F and 2F in the diagram. ... A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm ...
Lenses Ray Diagram Construction Worksheet Teaching. Long Answer Questions 30. On the diagram, label the point on the mirror where the incident ray from A reflects from the mirror with the letter "x". Draw a scale ray diagram showing the image position and height. Draw a ray diagram for a convex mirror when an object is placed at 2F.
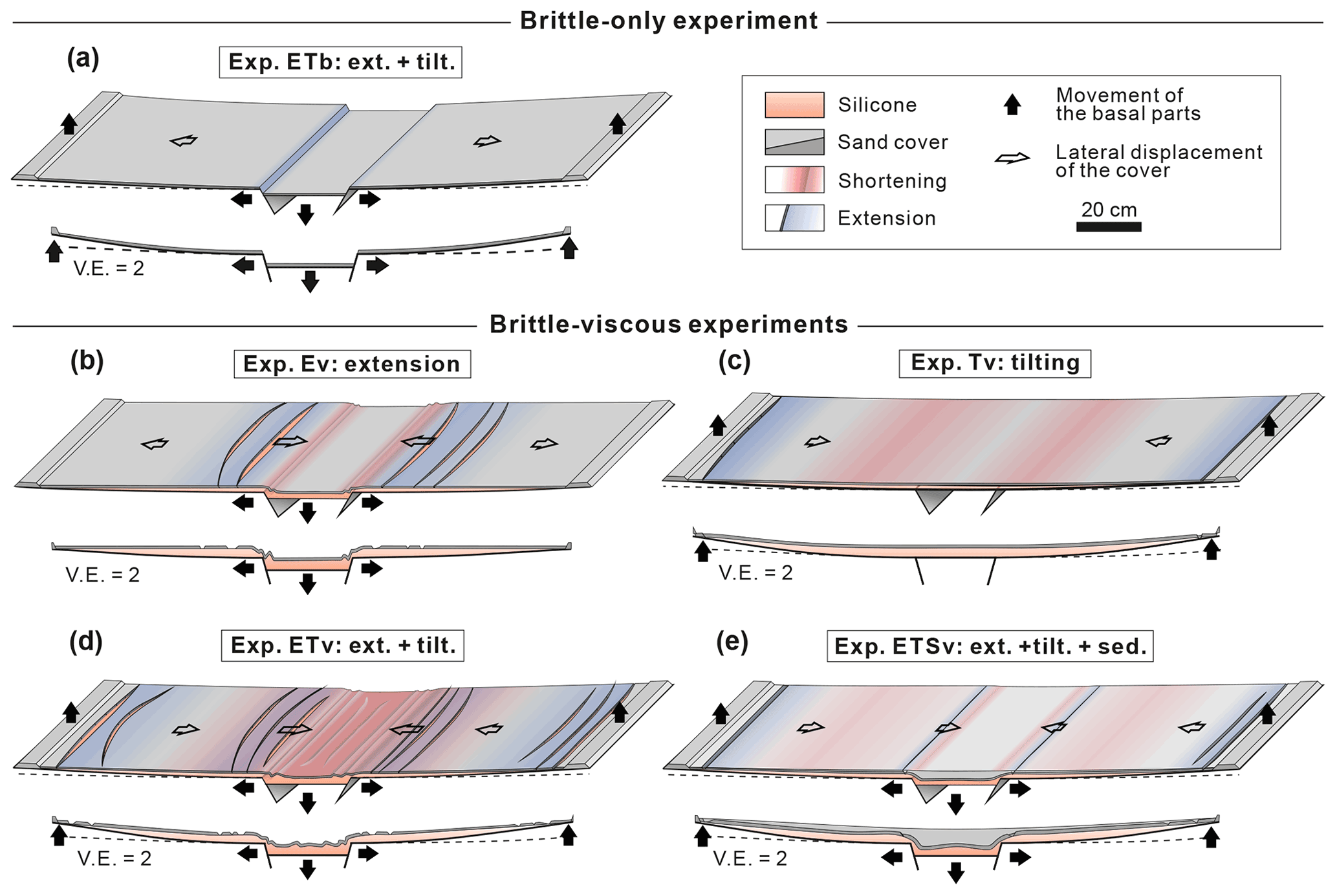
Se Contribution Of Gravity Gliding In Salt Bearing Rift Basins A New Experimental Setup For Simulating Salt Tectonics Under The Influence Of Sub Salt Extension And Tilting
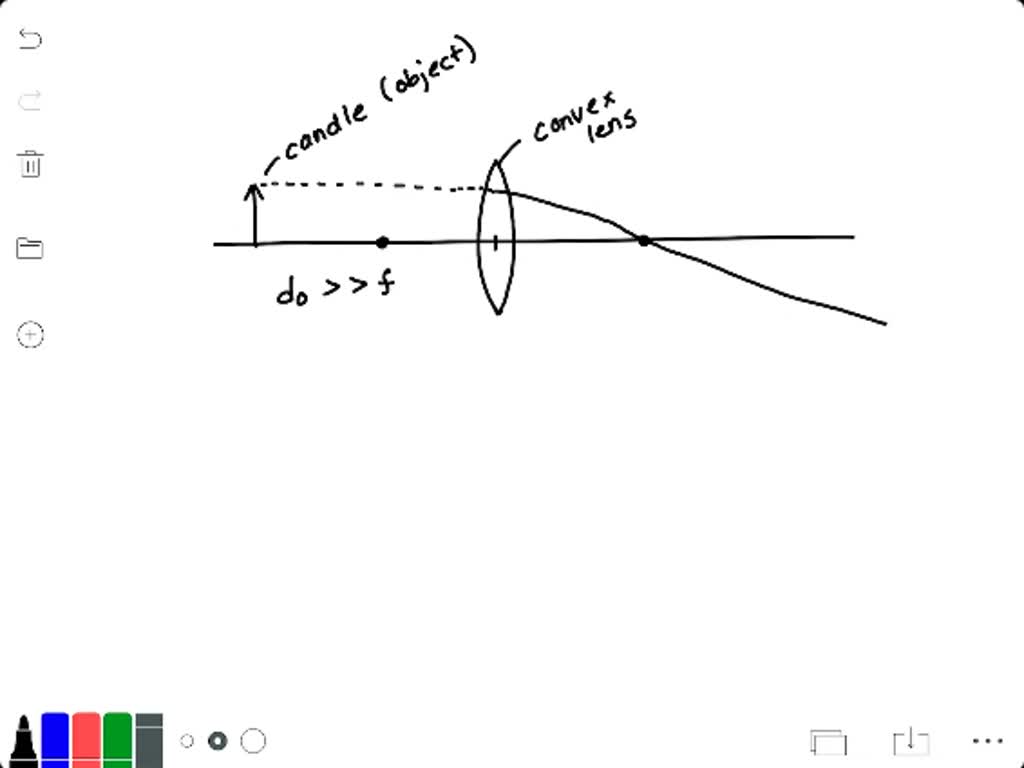
Solved You Have A Convex Lens And A Candle Describe In Detail An Experiment That You Will Perform To Find The Image Of The Candle That This Lens Produces Draw Pictures Of The

Four Students A B C And D Performed An Experiment To Determine The Focal Length Of A Convex Lens By Using A Lighted Candle Kept At A Considerable Distance As The Object

Four Students A B C And D Performed An Experiment To Determine The Focal Length Of A Convex Lens By Using A Lighted Candle Kept At A Considerable Distance As The Object
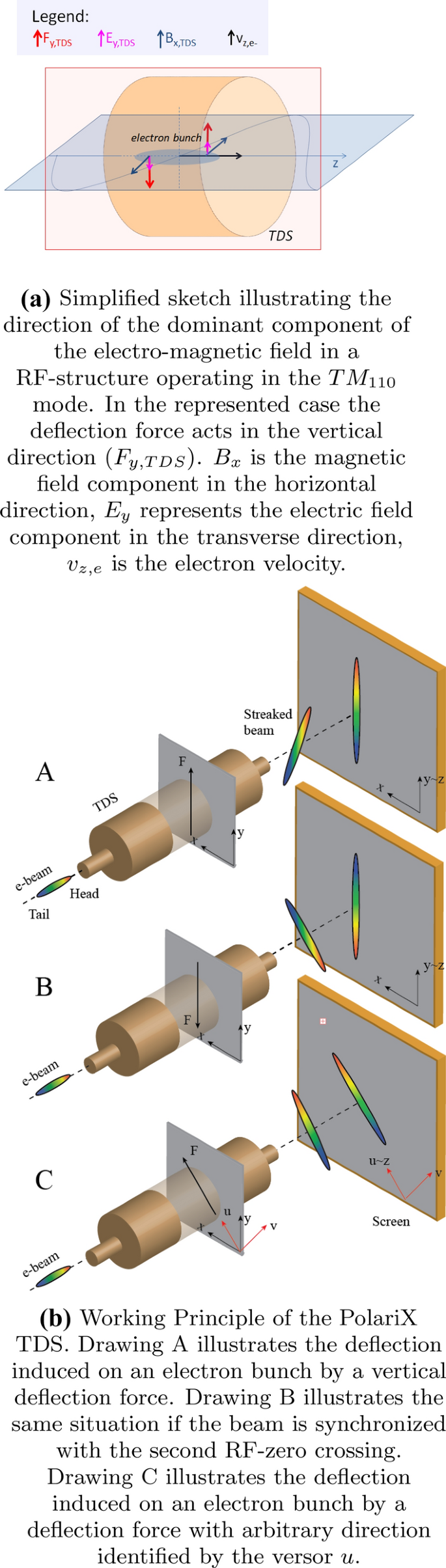
Experimental Demonstration Of Novel Beam Characterization Using A Polarizable X Band Transverse Deflection Structure Scientific Reports

Assessing The Scale Contributing Factors Of Three Carbide Free Bainitic Steels A Complementary Theoretical And Experimental Approach Sciencedirect

Refraction Ray Diagrams Visible Light Spectrum Prism Experiments How To Draw Ray Diagrams Diffraction Total Internal Reflection Water Glass Plastic Explaining A Rainbow Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes










0 Response to "40 draw a ray diagram representing your experiment from part c"
Post a Comment