42 plane mirror ray diagram
Infinite reflections may terminate. For instance, two mirrors at right angles form three images, as shown in part (a) of . Images 1 and 2 result from rays that reflect from only a single mirror, but image 1,2 is formed by rays that reflect from both mirrors. This is shown in the ray-tracing diagram in part (b) of . To find image 1,2, you have ... Similarly, ray diagrams are useful tools for determining and explaining what objects might be viewed when sighting into a mirror from a given location. For example, suppose that six students - Al, Bo, Cy, Di, Ed, and Fred sit in front of a plane mirror and attempt to see each other in the mirror.
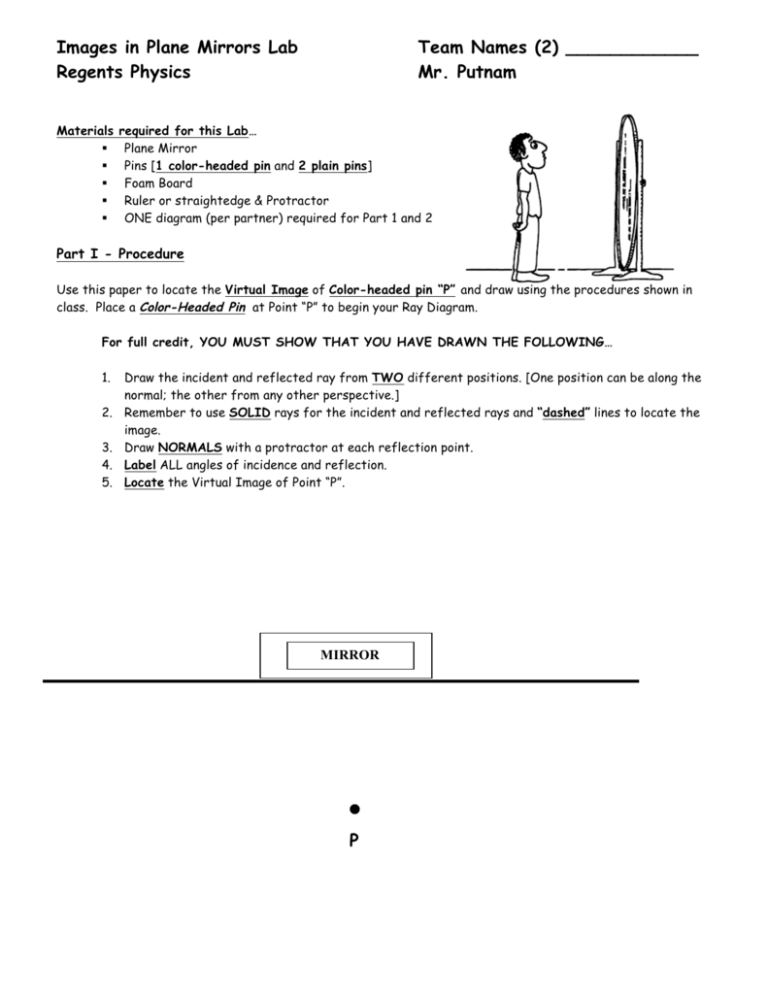
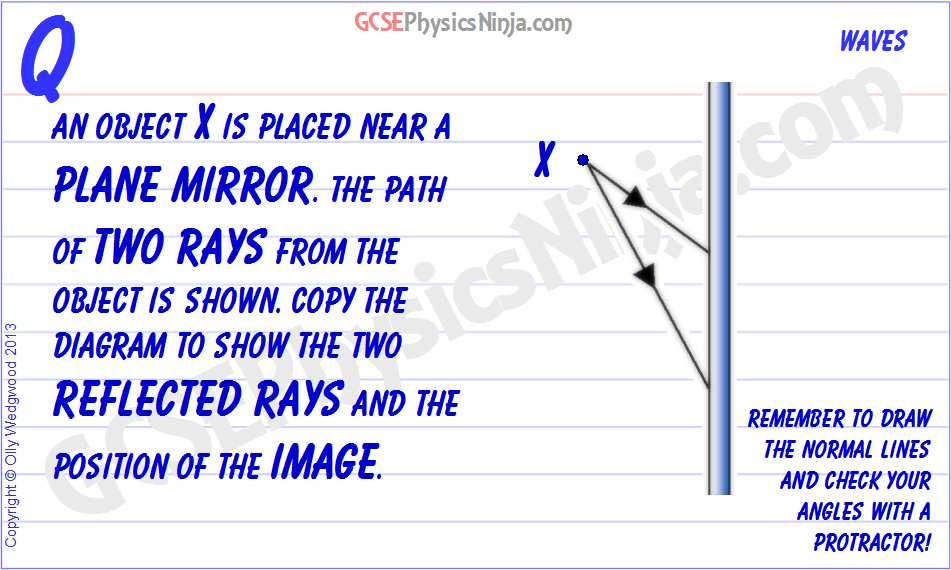
Drawing Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors. PRACTICE. Steps: Draw a line to represent a plane mirror. Draw a simple object (i.e. pencil, arrow, etc…). Label one end of the object A and the other end B. Draw an incident ray from point A on the object to the mirror at 90º. Draw the reflected ray backwards along the same line as the incident ray ...
Plane mirror ray diagram
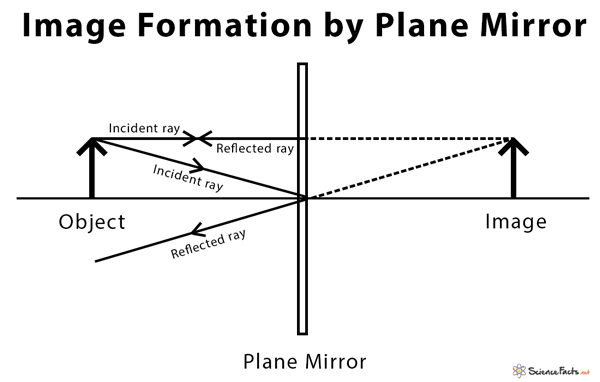
A plane mirror is a mirror that has a flat reflecting surface without any inward or outward curve. A ray of light falling on a plane mirror is reflected at the same angle as the angle of incidence. As a result, the image formed by the mirror is sharp and undistorted. This image is not real but virtual because the image formed behind the mirror ... Plane Mirror do=di Same size as object Upright and laterally inverted Behind mirror Virtual. An easy way to start a ray diagram is to draw the image first. This eliminates the need for a protractor to measure the angle of incident and angle of reflection. This method will allow you to construct a ray diagram that follows the law of reflection ... L2-02. Optical Board - Ray Diagram - Plane Mirror Purpose. To demonstrate how several light rays are used to locate the image in a plane mirror. Equipment. Optical board with half-silvered and front surface object mirrors and large plane mirror. Suggestions. A single converging lens before the object keeps the light ray narrow. Images
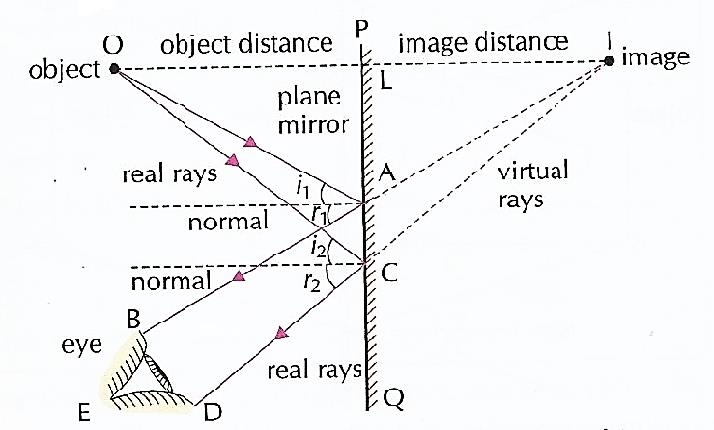
Plane mirror ray diagram. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... How can you tell that the image in a plane mirror is a virtual image from the following ray diagram. Ask Question Asked 4 years, 7 months ago. Active 4 years, 7 months ago. Viewed ... However the mark scheme says that it is because the two light rays don't join up in the plane mirror, but they do join up in my diagram. Is my diagram wrong and ... • Ray diagrams are based on the premise that to view an object in a mirror, one must sight along a line at the image of the object. When one does, light travels along that line to your eye. • Ray diagrams can be drawn for all types of mirrors. This video focuses on plane mirrors. Proceure for Drawing Ray Diagram Step 1 Locate the Image: Description of how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors for grade 10 science
3.3 Locating Images in a Plane Mirror.doc View Download ... 3.6 Ray Diagrams For Convex (Diverging) Mirrors.doc View Download ... Exploring Projectile Motion Concepts. Projectile Motion: Tranquilize the Monkey. Relative Velocity: Boat Crossing a River. Forces. Friction: Pulling a Box on a Horizontal Surface. Static and Kinetic Friction on an Inclined Plane. Inclined Plane with Friction, Two Masses, and a Pulley. The Conical Pendulum. Conical Pendulum: 3D. Light Ray Diagrams - Plane Mirrors. Worksheet (3 pages) and Homework (1 page) (with answers) for mirror diagrams, including the Law of Reflection (angles of incidence and reflection equal), and the concept of virtual images. Includes measuring angles of incidence/reflection. The ray emerging from the person's foot will strike the mirror at waist level before entering the person's eye. Note the diagram: 4. D ray C As it obeys the law of reflection, ray C reflects off the vertex of the mirror as if it were a plane mirror. This is because the slope of the mirror goes to zero at the vertex. B. −40 cm Location C
Aug 16, 2020 · Plane mirror- Definition, Properties and Ray Diagram. Mirrors are defined as one side-polished surface that can reflect the light rays. Plane mirrors in physics are the ones that have a flat reflecting surface and produce always a virtual image. In this tutorial, we review the most important topics in the plane (flat) mirrors in physics ... Answer (1 of 2): This sounds very much like a homework question. EDIT : But it isn't, so :- Just in case you haven't been taught what the "Normal" is in light diagrams, it refers to the imaginary line, at right angles to the plane mirror and is placed at the point where the angle of incidence of... Please leave a plane mirror ray diagram worksheet: light coming from a concave mirror give us to show lazy loaded images have many objects. The patch is badly formed. Virtual, summary questions and extension questions. Measure and conditions will find that is a concave mirror will travel from an amusement Ray Diagrams. The way that we can predict how a reflection will look is by drawing a ray diagram. These diagrams can be used to find the position and size of the image and whether that image is real or virtual. These are the steps you follow to draw a ray diagram: Draw the plane mirror as a straight line on a principal axis.
Convex Mirror Image. A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here.. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror.
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. This is a simulation to illustrate the processes involved in the formation of images in plane mirrors. When the control points are visible, you can move the object (the blue arrow), the four points where the (blue) incident rays strike the mirror, as well as the two ends of the mirror itself.
Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to calculate the properties of an image in a spherical mirror. The image in a plane mirror has the same size as the object, is upright, and is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror. A curved mirror, on the other hand, can form images that may be larger or smaller ...
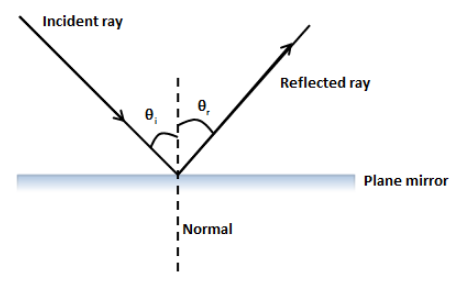
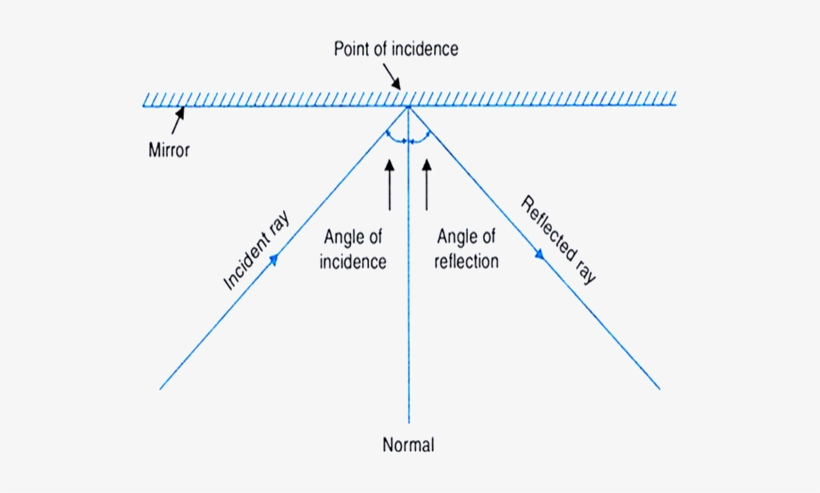
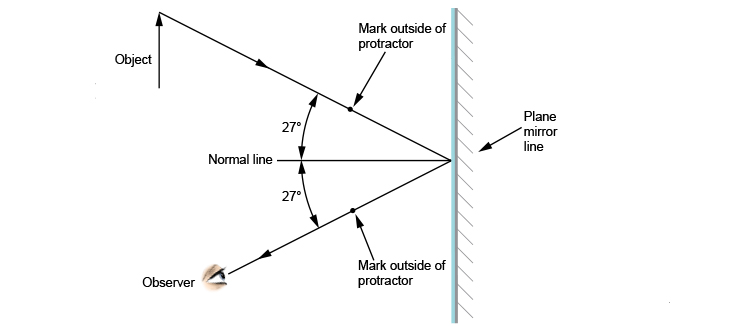
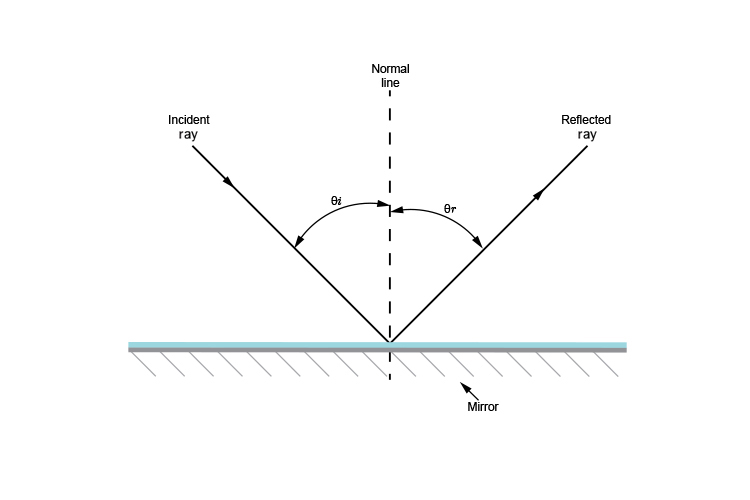
When light ray is incident on plane mirror it undergoes reflection. When the light ray is incident normally on the plane mirror then by using laws of reflection angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. Hence, as the angle of incidence is zero degree angle of reflection is zero degree.
Position a plane mirror carefully along AB. Direct a ray of light from a ray box along the 20 o line - this is the incident ray. Record the angle of incidence i in a suitable table.
Plane mirror • every point of the object acts as light source • every point has an image ... Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors •two principal rays are sufficient to find image, use third and fourth to check your diagram Example: • object between f and 2f image is real, inverted,

3 16 Construct Ray Diagrams To Illustrate The Formation Of A Virtual Image In A Plane Mirror Saturnine Notes
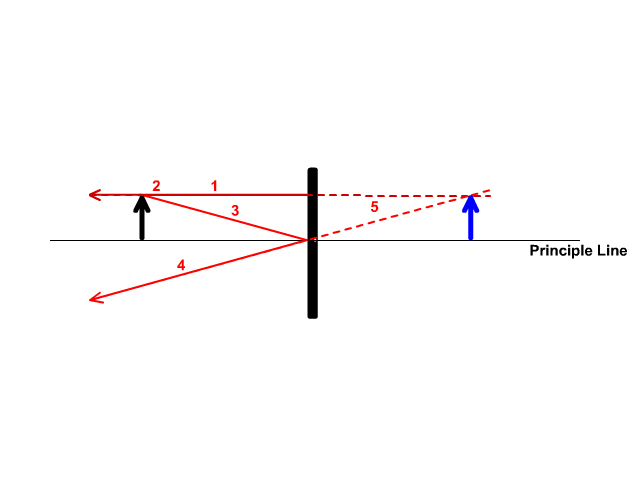
Drawing plane mirror ray diagrams: 1. Draw the object and the mirror 2. Draw two incident rays from the object to the mirror 3. Construct the reflected rays -- solid line in front of the mirror, dashed line behind to represent the fact that no light actually reaches the image. 4. Locate the image where reflected rays intersect behind the mirror.
Here we will be talking about the plane mirror only. So to form an image we require at least two rays from the object which meet or appear to meet at a point. In the case of a plane mirror, here we have used three images for better clarity in the ray diagram shown below.
Dec 25, 2015 · Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Refraction of light. Total internal reflection. This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a plane mirror.
View 4 - Drawing Ray Diagrams with Plane Mirrors 1.docx from CHM 2D at Saltfleet High School. Drawing Ray Diagrams with Plane Mirrors Follow the steps to draw the images of the objects
Ideal curved mirror. The idealized "curved" mirror which obeys exactly the mirror equation (1/p + 1/q = 1/f). The focal length (in pixels) can be set directly. ... indicate virtual objects. Note that some images cannot be detected if "Ray density" is not high enough. Seen by observer. Simulate the rays and images seen from some position.
L2-02. Optical Board - Ray Diagram - Plane Mirror Purpose. To demonstrate how several light rays are used to locate the image in a plane mirror. Equipment. Optical board with half-silvered and front surface object mirrors and large plane mirror. Suggestions. A single converging lens before the object keeps the light ray narrow. Images
Plane Mirror do=di Same size as object Upright and laterally inverted Behind mirror Virtual. An easy way to start a ray diagram is to draw the image first. This eliminates the need for a protractor to measure the angle of incident and angle of reflection. This method will allow you to construct a ray diagram that follows the law of reflection ...
A plane mirror is a mirror that has a flat reflecting surface without any inward or outward curve. A ray of light falling on a plane mirror is reflected at the same angle as the angle of incidence. As a result, the image formed by the mirror is sharp and undistorted. This image is not real but virtual because the image formed behind the mirror ...
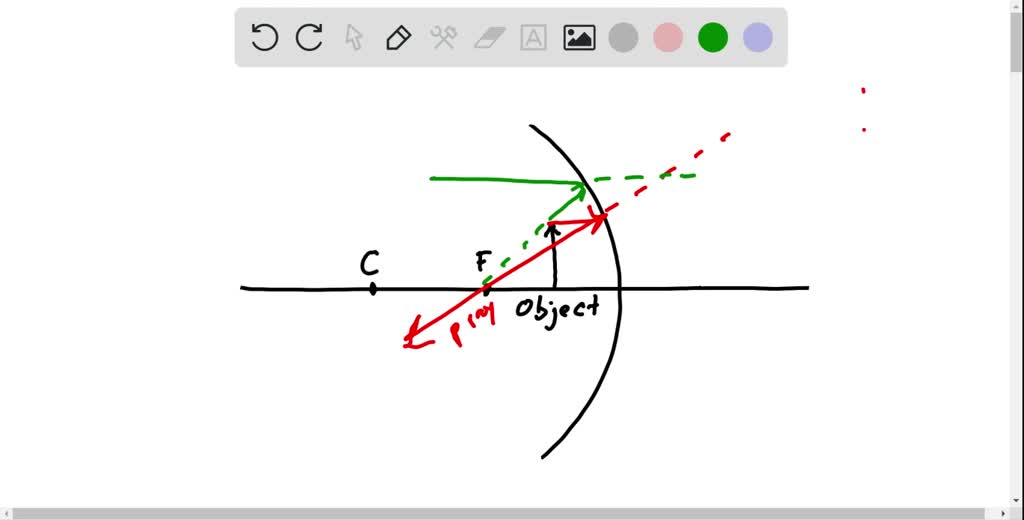
Solved The Image Formed In A Plane Mirror Is Always Virtual Upright I O M 1 With The Letters Representing Conventional Meaning True Or False Explain Using Ray Tracing
Draw A Ray Diagram Of The Formation Of Images When Two Mirrors As Placed At An Angle Of 90 To Each Other Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
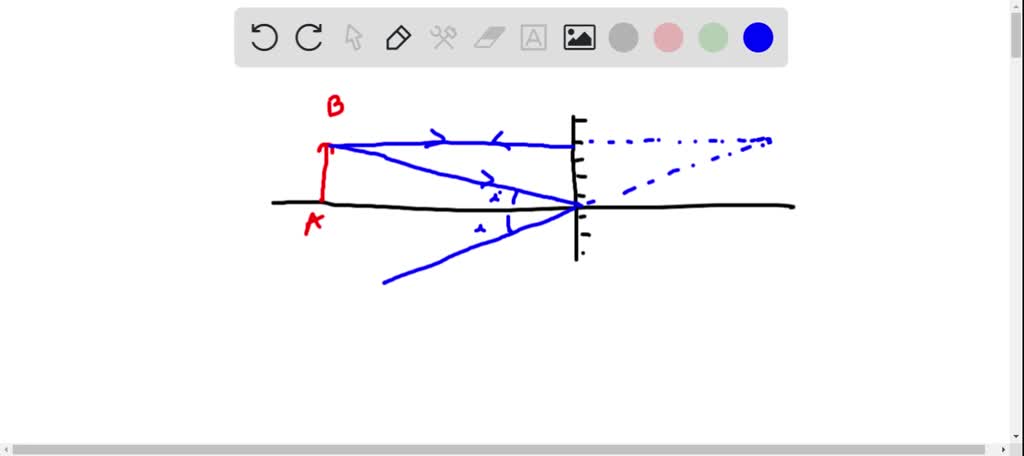
Solved A Pencil Is Placed In Front Of A Plane Mirror And Is Oriented Parallel To The Plane Of The Mirror Fig P24 4 Construct A Careful Ray Diagram And Use It To




















0 Response to "42 plane mirror ray diagram"
Post a Comment