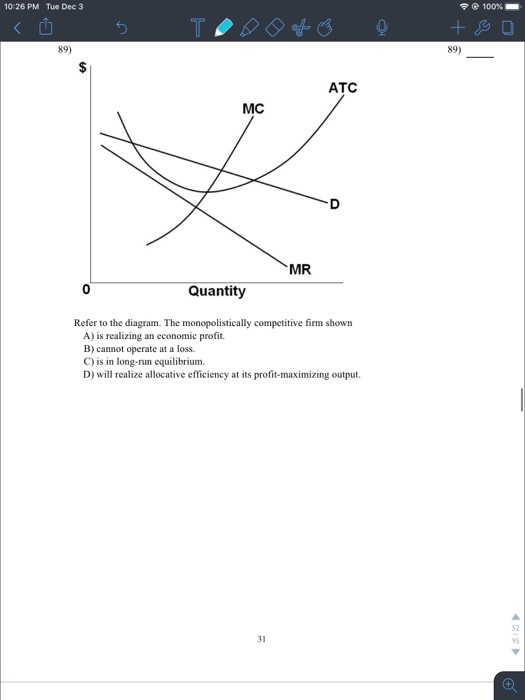
42 refer to the diagram. the monopolistically competitive firm shown
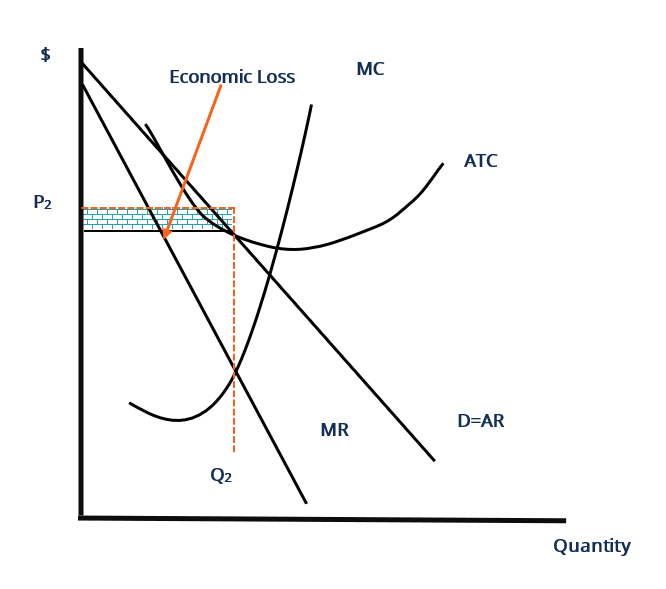
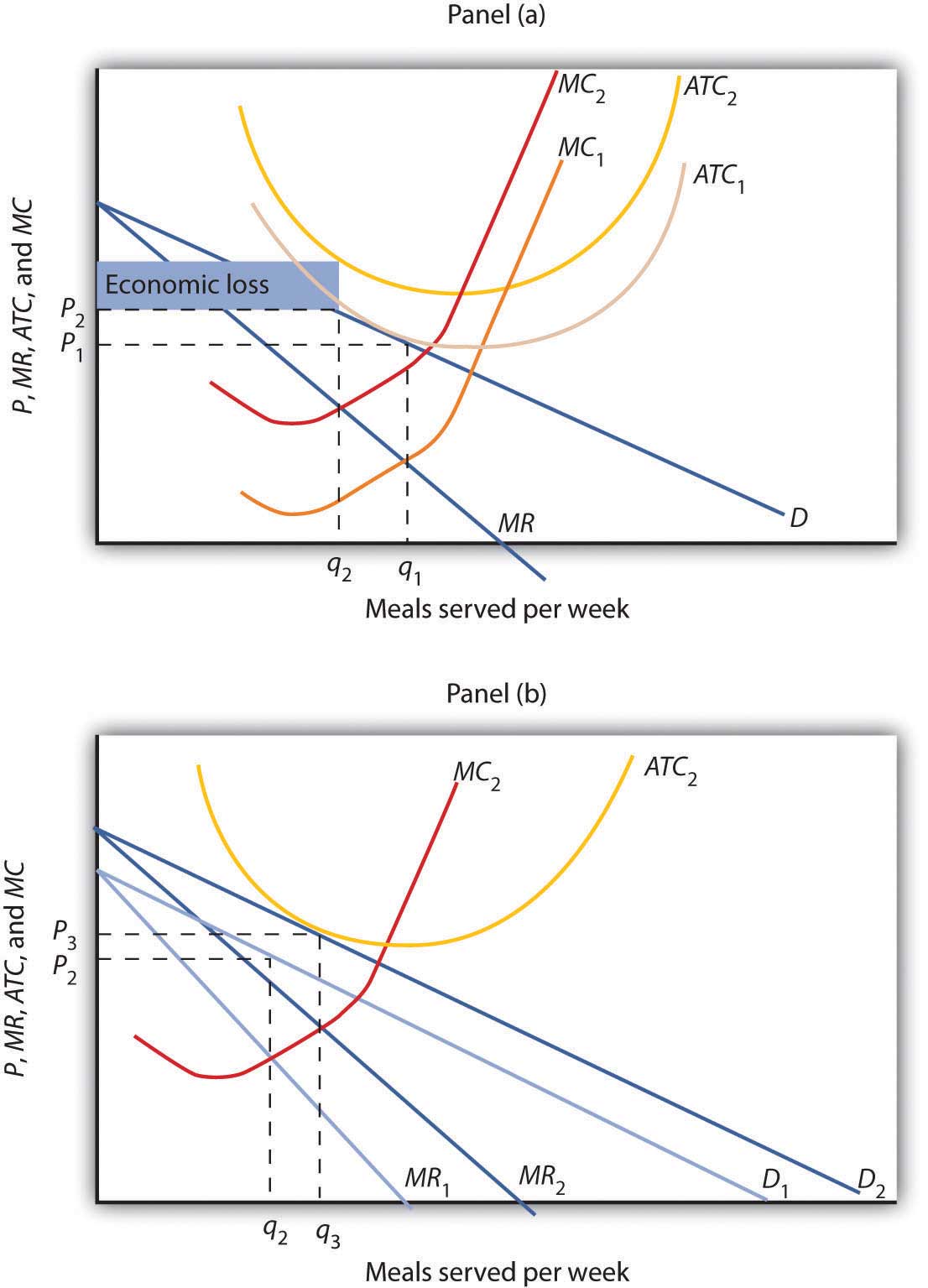
2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. 7refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm long run equilibrium output will be. Long run equilibrium is shown by. This firm is operating. Long run equilibrium price will be. If more firms would enter the industry and product differentiation would weaken.
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium. 3refer to the diagram above. Long run equilibrium output will be. Follow a high price policy. This firm will realize an economic. In short run equilibrium the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price.

Refer to the diagram. the monopolistically competitive firm shown
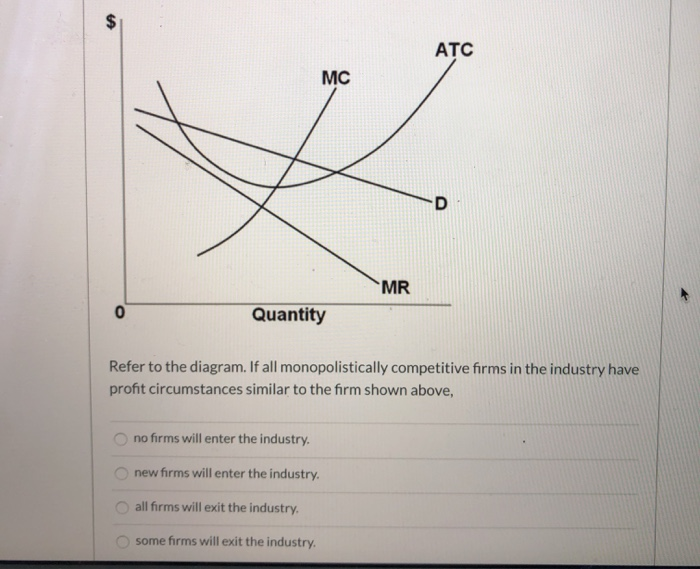
Long run equilibrium output will be. In short run equilibrium the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium. Hence it is quite easy for new firms to enter the market in the longrun. 2refer to the diagram. Start studying econ final. Award: 1.00 point Refer to the diagram. If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit circumstances similar to the firm shown above, new firms will enter the industry. some firms will exit the industry. all firms will exit the industry. no firms will enter the industry. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Short-run equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by: diagram c only. MC ...
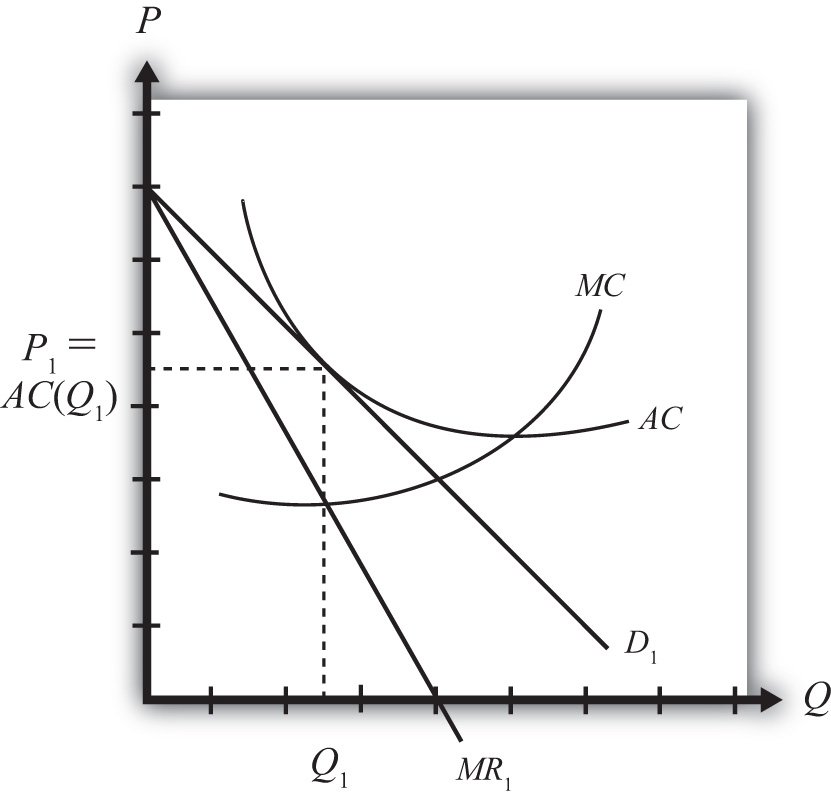
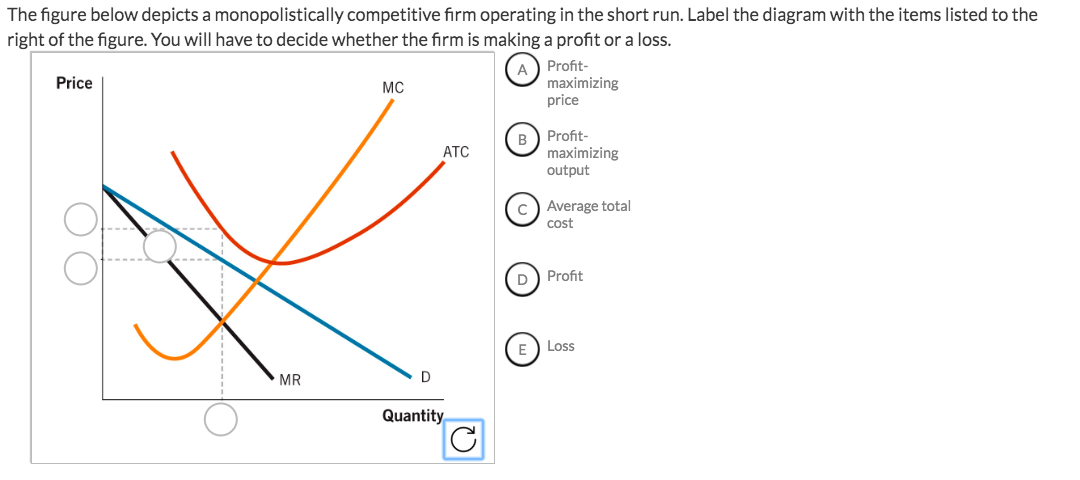
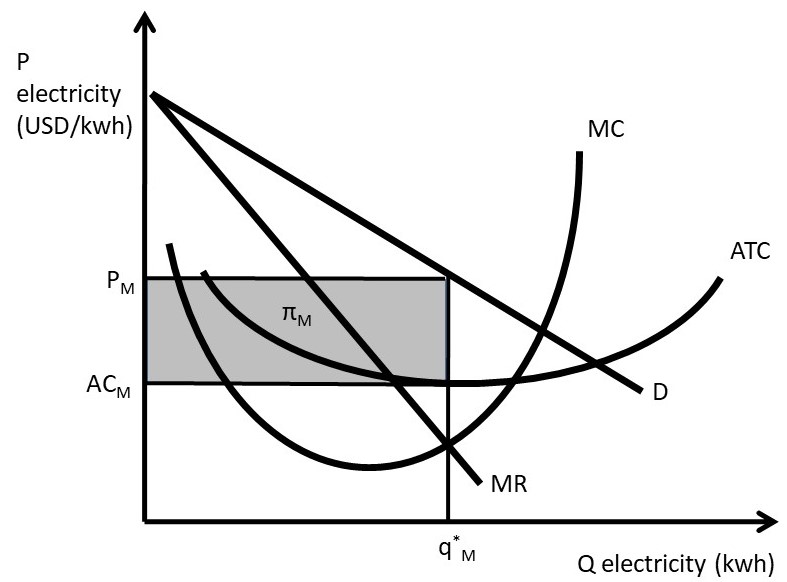
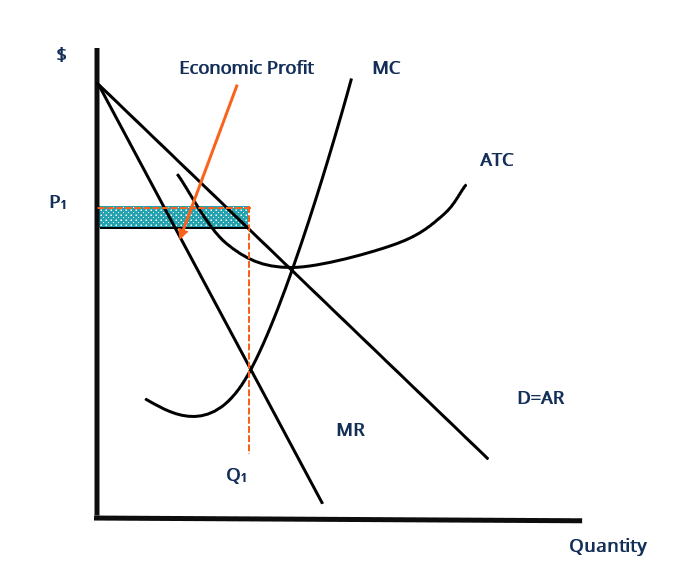
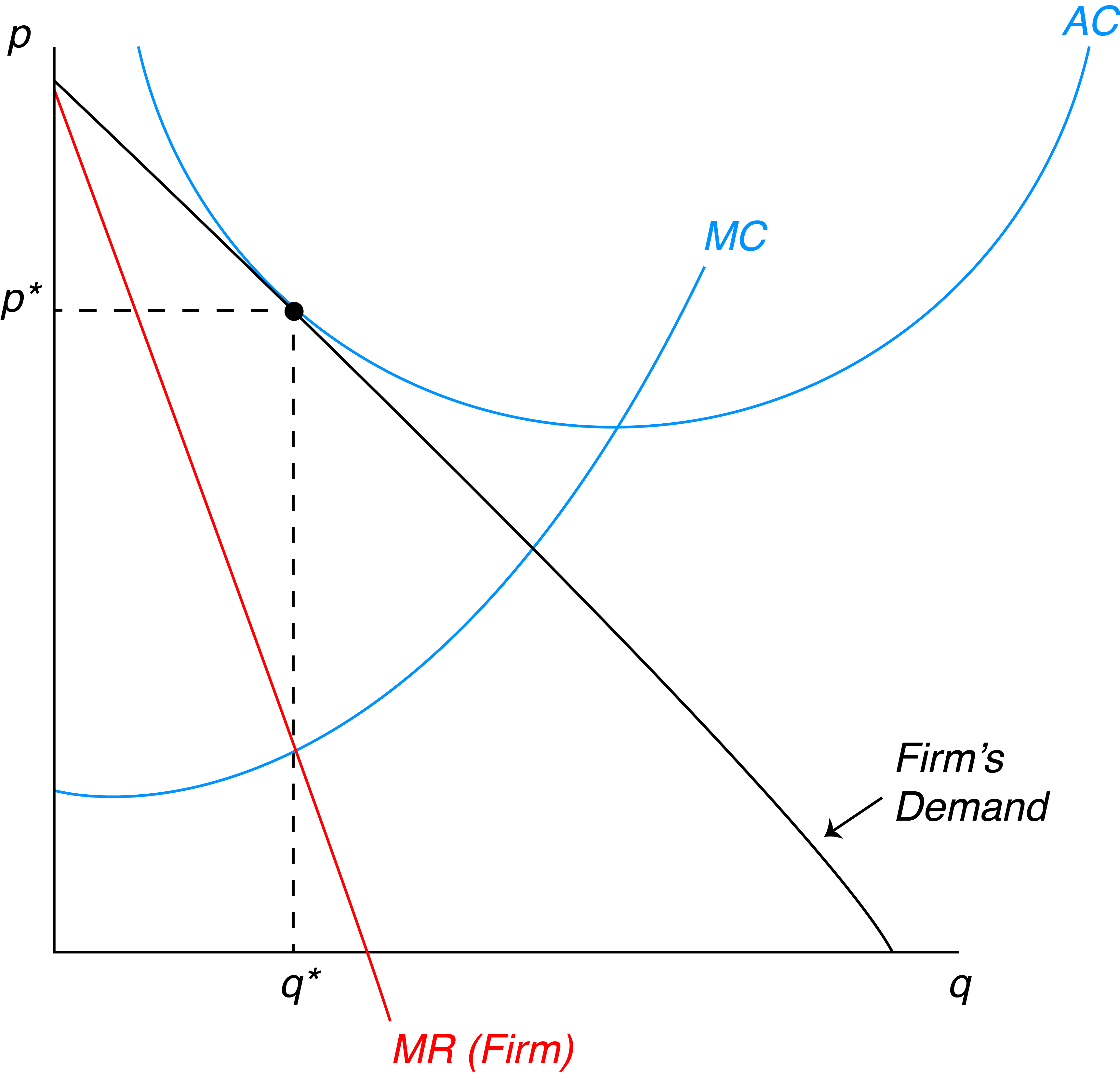
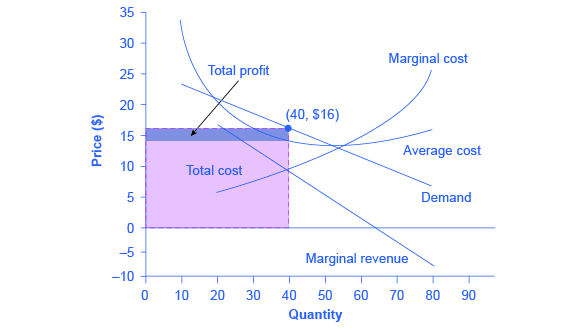
Refer to the diagram. the monopolistically competitive firm shown. The monopolistically competitive firm shown. is realizing an economic profit. In the long run, the price charged by the monopolistically competitive firm attempting to maximize profits ... Refer to the diagram for a non collusive oligopolist. Suppose that the firm is initially in equilibrium at point E, where the equilibrium price and quantity ... A monopolistically competitive firm is not efficient because it does not produce at the minimum of its average cost curve or produce where P = MC. Thus, a monopolistically competitive firm will tend to produce a lower quantity at a higher cost and charge a higher price than a perfectly competitive firm. The monopolistically competitive firm shown a) Will realize. Refer to the above graph of representative firm in monopolistic competition. Draw a diagram of a monopolistically competitive firm showing the firm earning profits in the short run. Which diagram below is correct? OB. Oc. OD. Q MC SRATC Q MC SRATC Q MC SRATC SRATC MC MR Output D MR Output MR Output D MR Output D
Refer to the above diagram. In the short run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price. above ATC. Refer to the above diagram. The monopolistically competitive firm shown. is realizing an economic profit. Refer to the above diagram. If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit ... Refer to the above diagram. If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit circumstances similar to the firm shown above: a. new firms will enter the industry. b. some firms will exit the industry. c. all firms will exit the industry. d. no firms will enter the industry. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. This firm is experiencing Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. This firm is experiencing The economic inefficiencies of monopolistic competition may be offset by the fact that consumers have increased product variety. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. Refer to the above diagram. This firm is experiencing. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium. Betas profits are shown in the northeast corner and alphas profits in the southwest corner of each cell.
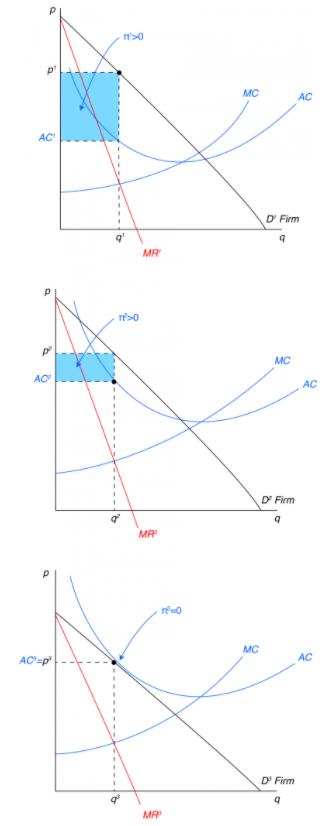
The monopolistically competitive firm shown: a. will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output. b. cannot operate at a loss. Chapter 13 (Monopolistic Competition) Homework. - constant. - increasing. - decreasing. - at their minimum point. Refer to the diagram. The monopolistically competitive firm shown. - will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output. - cannot operate at a loss. 6. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by: 1. diagram a only. 2. diagram b only. 3. diagram c only. 4. both diagrams b and c. 7. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium price will be: 1. above A. 2. EF. 3. A. 4. B. 8. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium. Are shown in the northeast corner and alphas profits in the southwest corner of each cell. Long run equilibrium price will be. In the long run purely competitive firms and monopolistically competitive firms earn zero economic profits. B profit of 480.
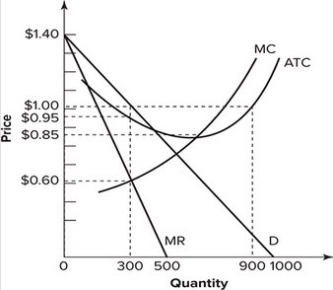
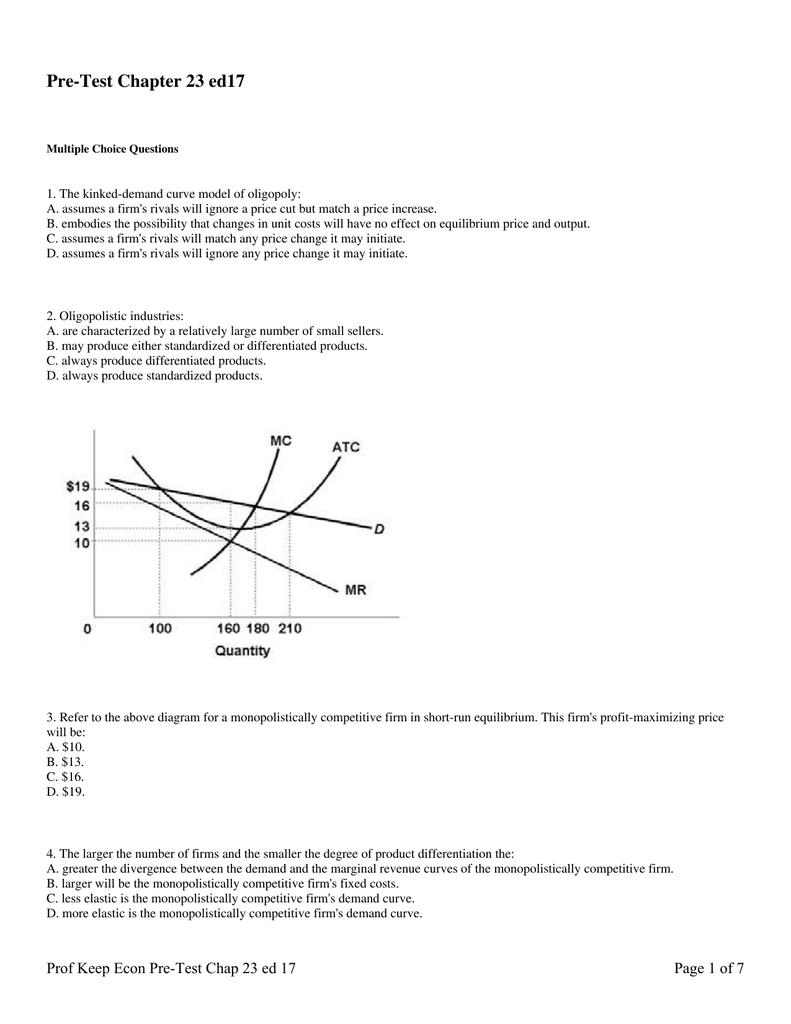
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be. $16. Answer the question on the basis of the following demand and cost data for a specific firm. ... The monopolistically competitive firm shown.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. ... The monopolistically competitive firm shown in the figure
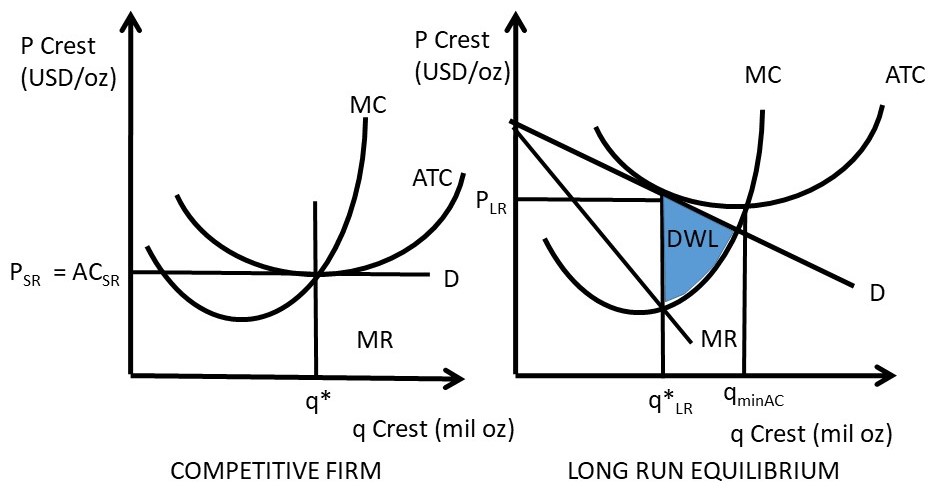
8 4 Monopolistic Competition Principles Of Microeconomics D units at price j. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer the firm is. Refer to the above data. 13 03 explain why monopolistic competition delivers neither productive nor allocative efficiency. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer.
Refer to the diagram. ... Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price takers." ... The monopolistically competitive firm shown:
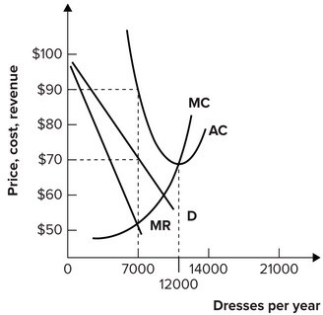
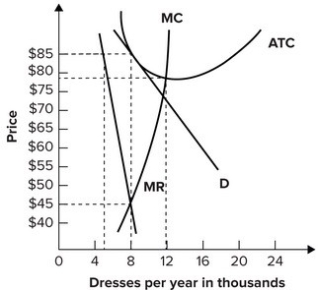
Figure 13 - 4 shows short - run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches. 8) Refer to Figure 13 -4. If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Q a units, what is the price charged? 8) A) P 0 B) P 1 C) P 2 D) P 3
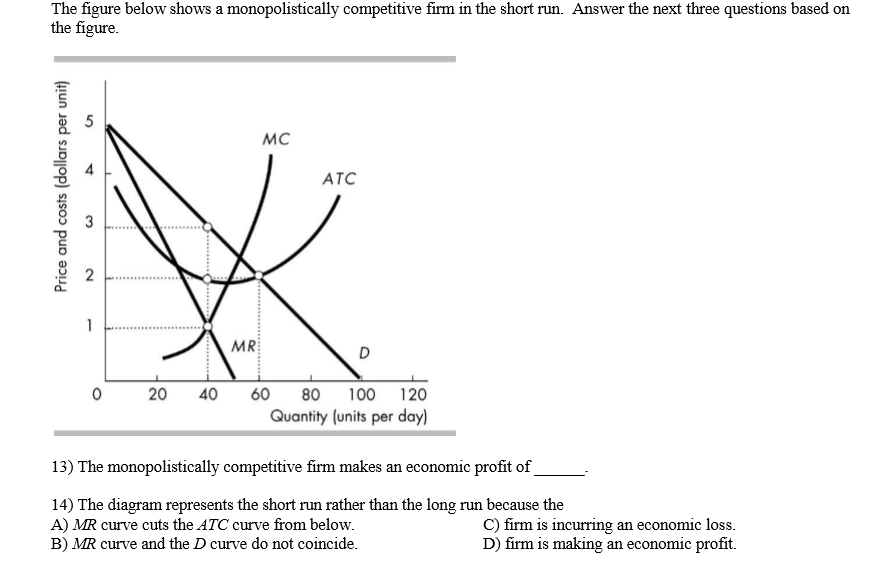
A monopolistically competitive firm's marginal revenue curve: is downsloping and lies below the demand curve. Monopolistically competitive firms: may realize either profits or losses in the short run but realize normal profits in the long run. Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms.
B profit of 480. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. A monopolistically competitive firm is producing at an output level in the short run where average total cost is 350 price is 300 marginal revenue is 150 and marginal cost is 150. When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long run equilibrium.
PLAY. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: Nice work! You just studied 20 terms! Now up your study game with Learn mode.
Refer to the diagram. The monopolistically competitive firm shownA. will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output.
Question: MR Quantity Refer to the diagram. The monopolistically competitive firm shown Multiple Choice is in long-run equilibrium. is realizing an economic profit. Multiple Choice Ο is in long-run equilibrium. Ο is realizing an economic profit. Ο will realize allocativ will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output.
The Monopolistically Competitive Firm In the Diagram is. econ chapter 11 quiz flashcards start studying econ chapter 11 quiz learn vocabulary the monopolistically petitive firm illustrated in the diagram exhibits diagrams flashcards micro econ flashcards start studying micro econ if the number of firms in a monopolistically petitive refer to the diagram for a monopolistically petitive
Consequently the remaining firms will return to normal profitability. Long run equilibrium output will be. 1refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. 3 hard learning objective. Firms to leave the industry market supply to rise and product price to fall.
82. Refer to the diagrams which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by: A.diagram a only. B. diagram b only. C. diagram c only. D. both diagrams b and c. Difficulty: Medium Learning Objective: 12-02 Explain why monopolistic competitors earn only a normal profit in the long run.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: <loss of $320. <profit of $480. <profit of $280. <profit of $600. profit of $480. In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price: <below ATC. <above ATC. <below MC.
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. ... profit of $480. D. profit of $600. E. profit of $360. 7. R-2 F25037. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Short-run equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by: ... diagram b only. C. diagram c only ...
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm long run equilibrium output will be. In the short run chamberlins model of monopolistic competition comes closer to monopoly. 7refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. 4both diagrams b and c.
16. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic. profit of $600. profit of $480. loss of $320. profit of $280. profit of $480. Long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where economic profits are zero results from.

Figure 16 3 This Figure Depicts A Situation In A Monopolistically Competitive Market Be 9 Refer To Figure 16 3 W Homeworklib
Refer to the above diagram. If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit circumstances similar to the firm shown above:.
The profitmaximizing output for this firm will be:160.Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic:profit of $480. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry.
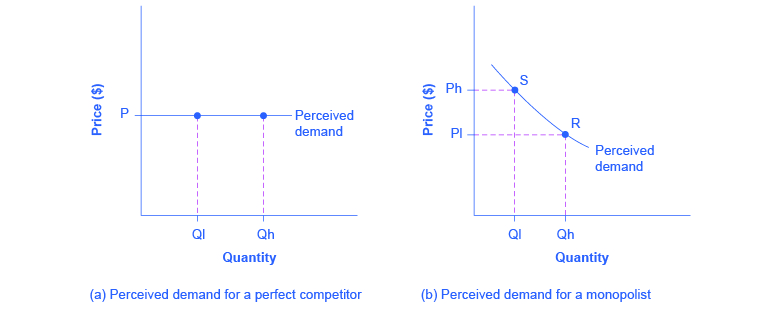
A. greater the divergence between the demand and the marginal revenue curves of the monopolistically competitive firm. B. larger will be the monopolistically competitive firm's fixed costs. C. less elastic is the monopolistically competitive firm's demand curve. D. more elastic is the monopolistically competitive firm's demand curve.
Refer to the diagram below for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: A) loss of $320. B) loss of $280. C) profit of $480. D) profit of $600. E) profit of $360.
Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Short-run equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by: diagram c only. MC ...
Award: 1.00 point Refer to the diagram. If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit circumstances similar to the firm shown above, new firms will enter the industry. some firms will exit the industry. all firms will exit the industry. no firms will enter the industry.

Refer To The Figure Above For A Monopolistically Competitive Firm At The Profit Maximizing Output And Price This Firm Is A Earning An Economic Profit B Earning An Economic Loss C Breaking Even
Long run equilibrium output will be. In short run equilibrium the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium. Hence it is quite easy for new firms to enter the market in the longrun. 2refer to the diagram. Start studying econ final.

Refer To The Graph Above At The Profit Maximizing Level Of Short Run Output This Monopolistically Competitive Firm Will Be Making A Profit Of A 275 B 350 C 500 D 525 Study Com
Refer To The Diagram For A Monopolistically Competitive Firm Long Run Equilibrium Output Will Be Wiring Site Resource










0 Response to "42 refer to the diagram. the monopolistically competitive firm shown"
Post a Comment