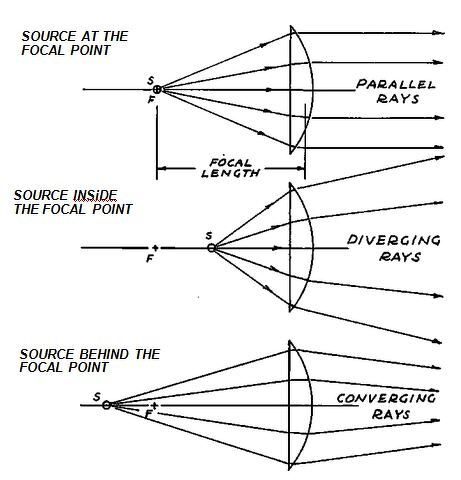
0 ray diagram for convex lenses
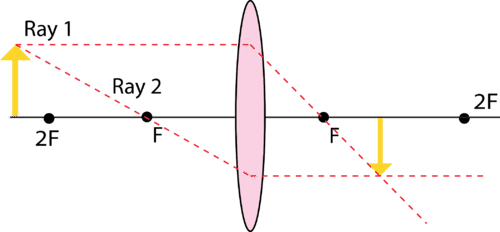
Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Ray 2 heads towards F' before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. image is always virtual, upright and reduced O F I F' Ray diagram for diverging lens Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscienc...
Convex concave ray diagrams. 1. J.M. Gabrielse Ray Diagrams. 2. J.M. Gabrielse Spherical Mirrors (concave & convex) 3. J.M. Gabrielse Concave & Convex (just a part of a sphere) C: the centre of curvature (centre point of the sphere) F: the focus (focus) of the mirror (halfway between C and the mirror) • C • F Principal Axis Curved Surface. 4.
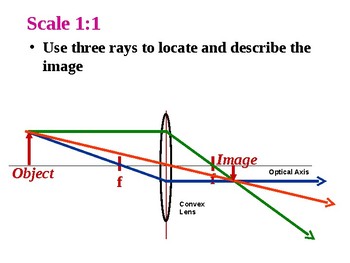
Ray diagram for convex lenses
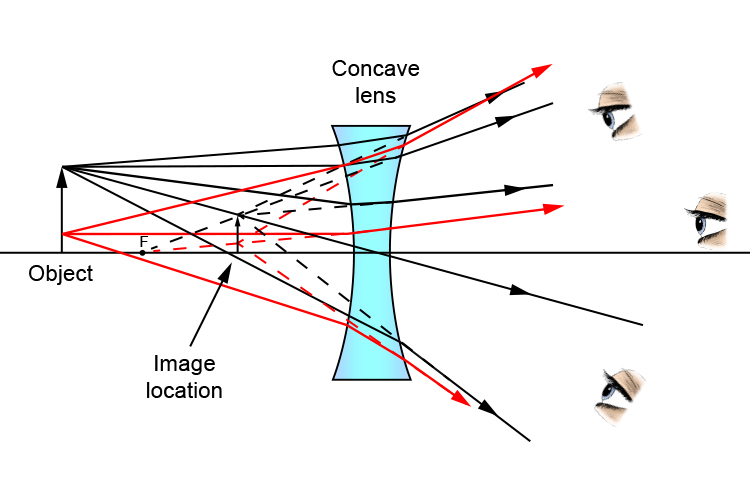
Method for drawing ray diagrams - Concave lens. A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses". The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Example 3: Identifying the Path of a Light Ray That Passes through a Convex Lens. Each of the following diagrams shows a ray entering a thin convex lens. The point marked P is the focal point of the lens. Before the ray enters the lens, it is parallel to the optical axis and it passes through the center of the lens.
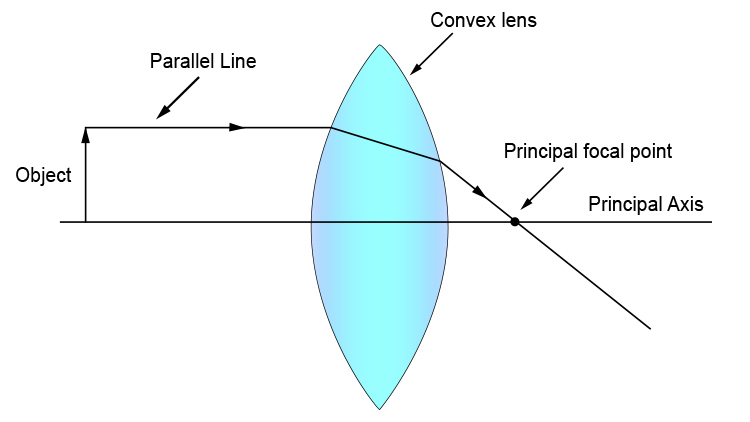
Ray diagram for convex lenses. Ray diagrams for convex lenses are based on the principle that convex lenses converge light rays passing through them. The following points are to be kept in mind while drawing ray diagrams for convex lens:-A ray of light passing through the optical center of a convex lens passes through the lens undeviated. A ray of light parallel to the principal axis, on passing through the lens, gets ... Ray tracing a convex lens: object inside focus The image appears larger (and farther away) than the object. This is a magnifying glass. (Remember: a magnifying glass is a convex lens.) Aside: near-sighted people need concave/diverging lenses; can a marooned myopic start a fire with his eye-glasses? Ray tracing diagram for convex lens. "A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element. A compound lens is an array of simple lenses (elements) with a common axis; the use of multiple elements allows more optical aberrations to be corrected than ... Ray Diagram for a Convex Lens. Once again, a ray diagram can help us understand what a lens does. Send rays out from the object, refract them through the lens, and see where they go. The image is where the rays intersect. Rays that are easy to draw include: The parallel ray goes from the tip of the object horizontally to the lens. It refracts ...
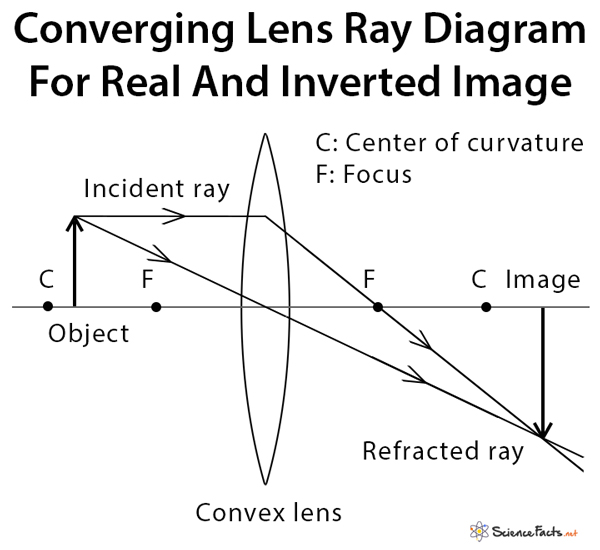
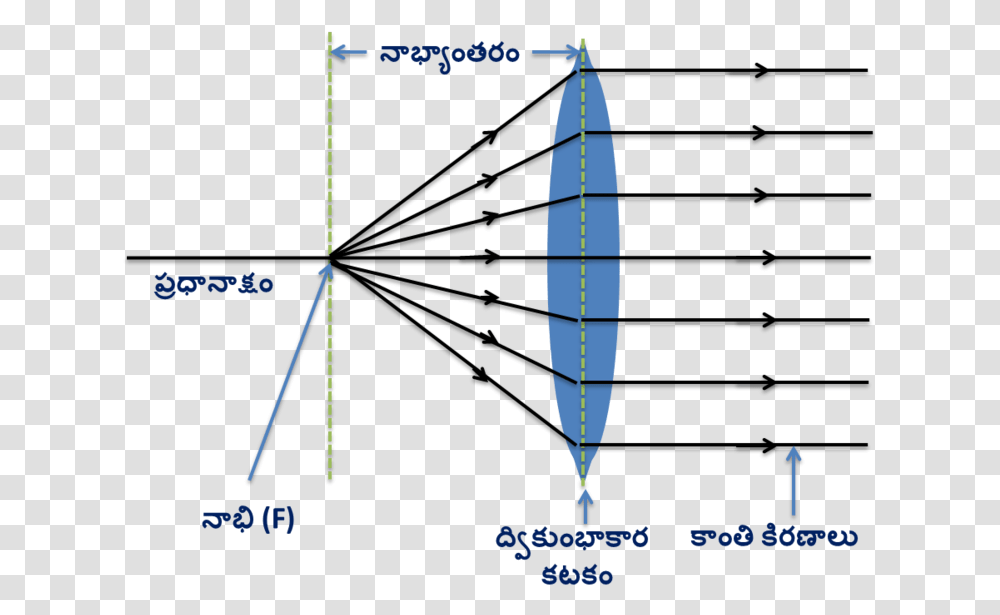
The example "Ray tracing diagram for convex lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions. The convex lens ray diagram shown in the image has been shaped so that all light rays that enter it parallel to its axis cross one another at a single point on the opposite side of the lens. Such a lens is called a converging lens for the converging effect it has on light rays. The point at which the rays cross is defined to be the focal point F of the lens. My question feels weird, but it came up in my mind .When we draw ray diagram for a object (say AB) which is perpendicular to principal axis at A, then after reflection(/refraction) by spherical mirror(/lens) the point where rays originating from B intersect to other ray from B for image formation,let's name it B'. Then by convention or something i might not have knowledge of the image is A'B' where A' is perpendicular of B' on principal Axis. So my question is how does this convention t... I have been trying to read ray diagrams for a little while. Any tips or techniques in reading them?
Ray Diagram For Convex Lens. Here are a number of highest rated Ray Diagram For Convex Lens pictures upon internet. We identified it from obedient source. Its submitted by organization in the best field. We say yes this kind of Ray Diagram For Convex Lens graphic could possibly be the most trending subject behind we allocation it in google gain ... Don't yell at him, he's tring to do right by us. He even gave away some free sunglasses. A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ... Good evening everyone. So, the title's pretty much it, I'm writing up a report on telescopes and microscopes and I need to include a ray diagram, so I was wondering if there was a better way of doing it rather than Paint. Thanks in advance!
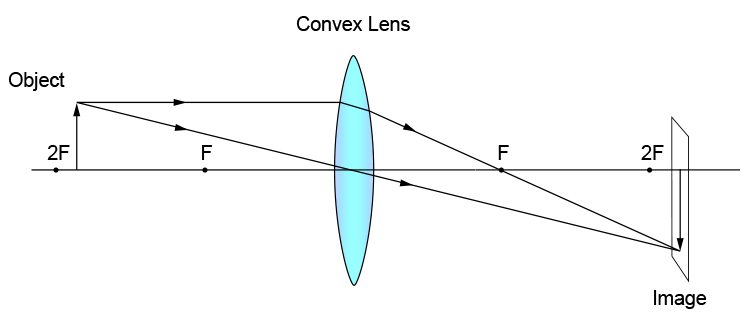
A convex lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a convex lens. To draw a ray diagram and find the location of the image that would be created on a screen you only need to draw two ray lines.
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray.
http://www.physicshelp.caFree simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website
A worksheet to construct ray diagrams to show where images are formed by a converging convex lens and a diverging concave lens. Draw a ray diagram and use the information from the ray diagram to fill in the box. Aimed at aqa gcse physics. 10 draw a ray diagram for a 3 0 cm tall object placed 10 0 cm from a converging lens having a focal length ...
If you proliferate your Graviton lenses and then remove the "old" non-proliferated lenses from your active ray receivers, eventually you'll get a permanent pop-up about an out of bounds index, only recourse is to quit the game and load a save prior to the error occurring. It may not happen the first few times but it does happen 100% of the time after about a dozen lens removals. I can replicate this at-will.
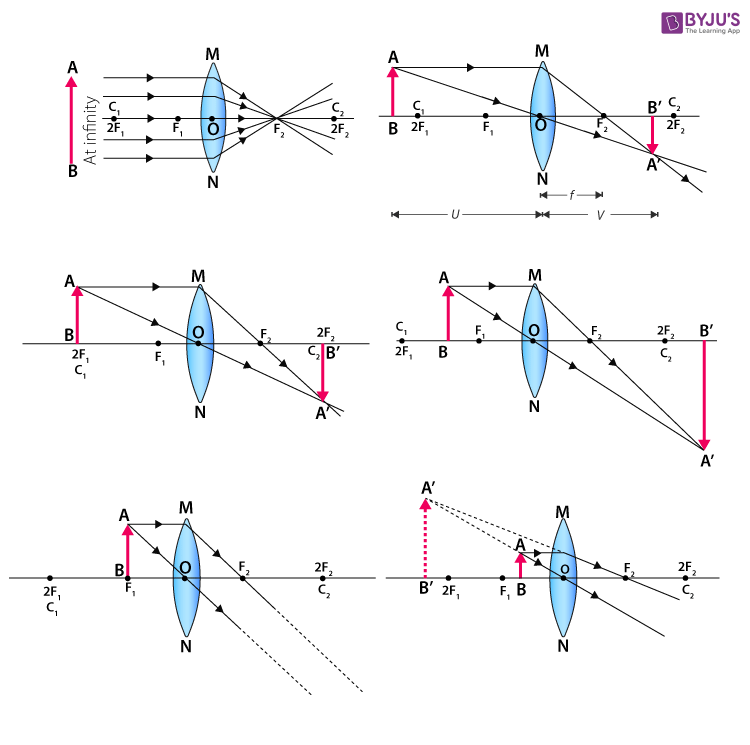
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
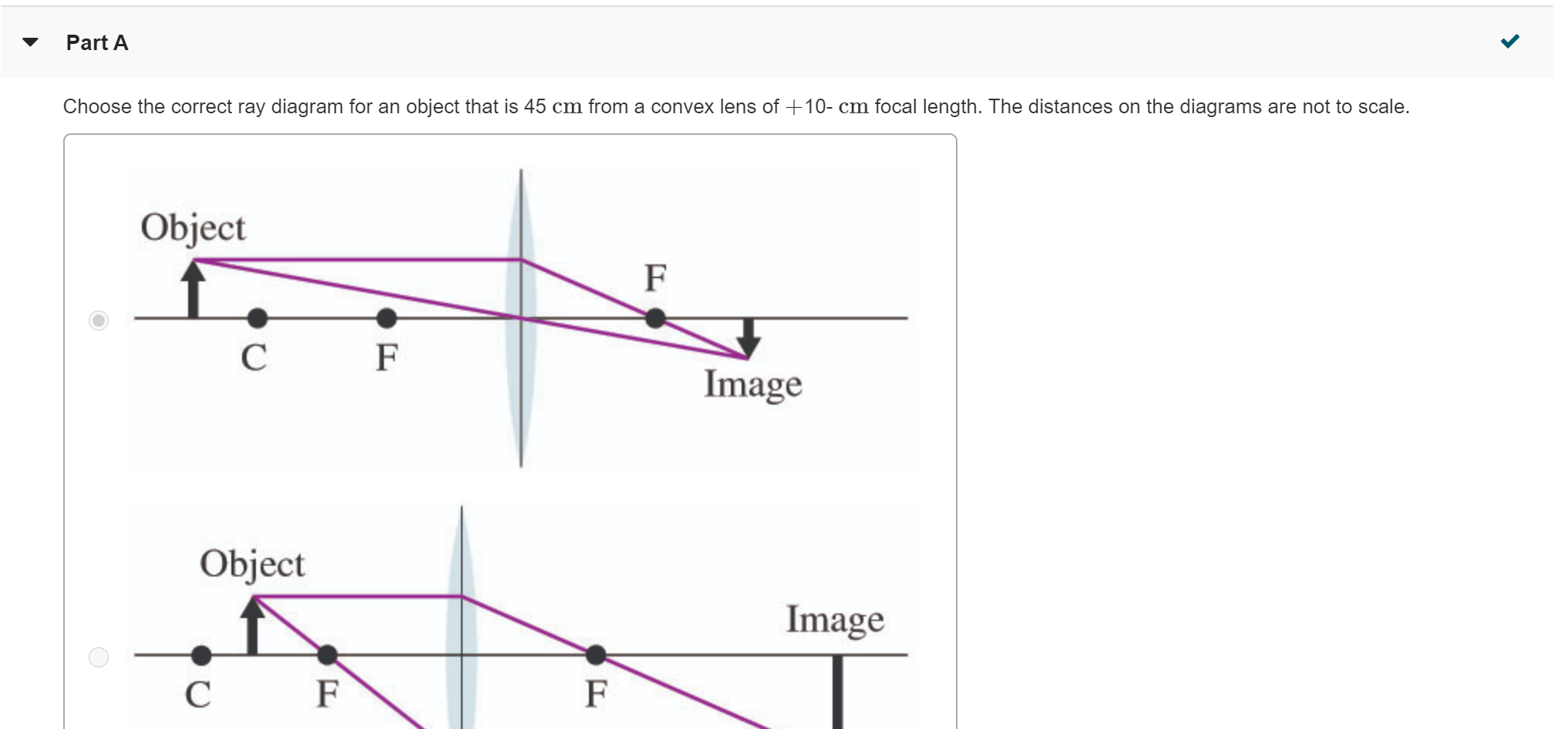
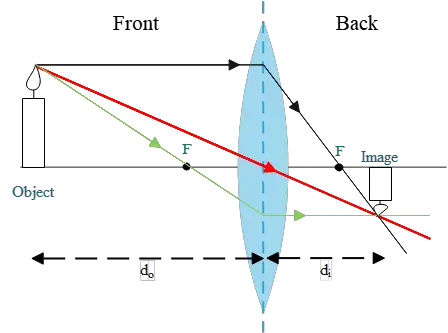
A pencil is placed 25 cm away from a convex lens which has a focal length of 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram for the image of the pencil. Step 1: Identify the focal length of the convex lens (f) and ...
The naming feels so counterintuitive; it’s hard to distinguish and recognize each of these. How do you guys set them straight in you head?
Are they liable? Can I get money back? I'm very pissed off and after taking them back to get repaired they're still loose. Thanks!
For one question on my science homework, it asks to draw a ray diagram that shows how contacts help us see. My question is how would I create a ray diagram where the image lines up perfectly at the retina. I'm so confused.
Rule 2 - Ray passing through focus will become parallel to principal axis. For a convex lens, we see that ray passing through focus on left becomes parallel to principal axis after refraction. For a concave lens , since focus is on the right side, it appears that ray passes through focus, and then it becomes parallel to principal axis.
Here is a (link)[http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/geoopt/raydiag.html] to what I'm talking about. In any physics textbook, they draw 3 or more rays to find where the object will appear as the light passes through the lens. BUT, I haven't been able to find a mathematical proof for why 3 or more rays should intersect at the same point. The focal point is not an answer, but certainly a clue. Anybody have an idea or reference?
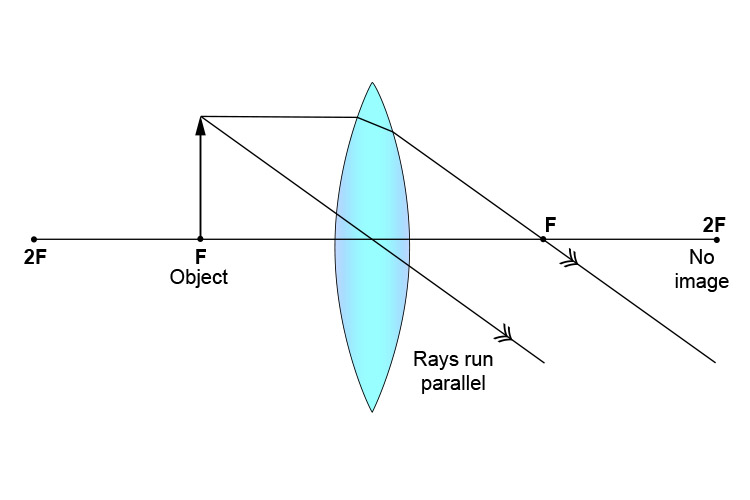
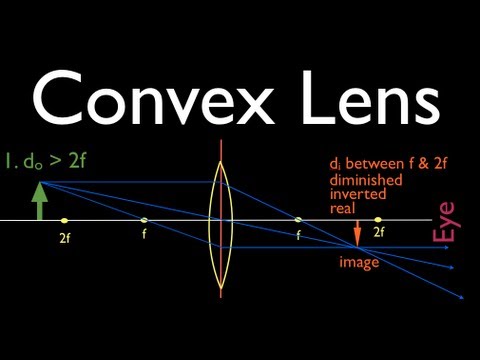
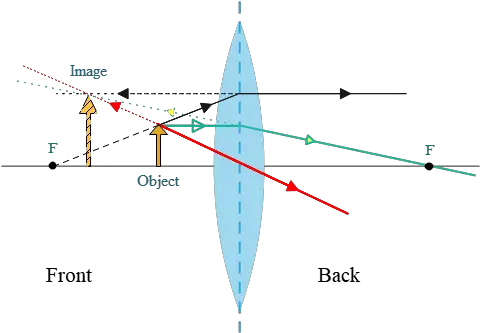
Ray diagram for an object placed between 2F and F from a convex lens In a film or data projector, this image is formed on a screen. Film must be loaded into the projector upside down so the ...
Here in this post, you will get Ray Diagrams for Images formed by convex & concave lenses as a Quick Reference. Image formation by lenses is an interesting topic of the Light chapter. Here along with the ray diagram, you will get the related details like Object position, image position, and nature of the image.
A camera or human eye Cameras and eyes contain convex lenses. Ray diagrams for double convex lenses were drawn. Where both reflected rays meet is point A. A lens is a transparent object that causes the light that passes through it to refract. A ray diagram is a tool used to determine the location size orientation and type of image formed by a lens.
Mine are all scratched up but don’t want to buy a whole new pair.
I finally understand ray diagrams, but I have another problem. When plotting the ray diagram of a convex lens refraction with the object sitting between F' and O (lens), the description says the refracted image should be at 2F' and beyond. Mine sits at F', and I do not know why it changed, or how it happened. Hopefully someone can answer. Thank you in advance
Arial Calibri Default Design Lenses What phenomenon is evident in lenses? Basic Types of Lenses Convex Lens Concave Lens Type of Image Convex Lens Ray Diagram for Convex Lens Rules for Ray Diagrams for Convex Lens PowerPoint Presentation Summary for Convex Lens Sign Convention Magnification Lens Equation Concave Lens Summary for Concave Lens ...
I googled it and everything says direct so I should be fine with my windows open. I am putting it the furthest away from the window as I can obviously.
Convex Lens - Ray diagram. Last updated at Nov. 18, 2021 by . For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positions Hence, we take different cases Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity In this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)
Q2: How many foci does a convex lens have? Q3: Each of the following diagrams shows a ray entering a thin convex lens. The point marked P is the focal point of the lens. Before the ray enters the lens, it is parallel to the optical axis and it passes through the center of the lens. Which diagram correctly shows the path of the ray after it has ...
Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.
The convex lens ray diagrams give people an idea about the position of the image and the object. The students can also have ideas about the nature of the lens. They can also know how the light rays experience a change in path due to a convex lens's presence there.
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:
Example 3: Identifying the Path of a Light Ray That Passes through a Convex Lens. Each of the following diagrams shows a ray entering a thin convex lens. The point marked P is the focal point of the lens. Before the ray enters the lens, it is parallel to the optical axis and it passes through the center of the lens.
The method of drawing ray diagrams for double convex lens is described below. The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens.
Method for drawing ray diagrams - Concave lens. A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses".














---teachoo.png)



0 Response to "0 ray diagram for convex lenses"
Post a Comment