39 free body diagram statics
https://goo.gl/ICIenR for more FREE video tutorials covering Engineering Mechanics (Statics & Dynamics)This video represents a comprehensive example of solvi... Statics and Dynamics. In Statics, one requirement is learning to solve freebody diagram problems. In this task, the student is presented a concrete situation like that in Figure EX1, showing one or more objects along with the forces acting on the system. The first job is to
The free body diagram. Statics:The Next Generation (2nd Ed.) Mehta, Danielson, & Berg Lecture Notes for Sections 5.1,5.2. Draw a FBD of the bent rod supported by a smooth surface at B and by a collar at A, which is fixed to the rod and is free to slide over the fixed inclined rod.
Free body diagram statics
As with all statics problem, a free-body diagram will assist in solving the problem. In this example, all forces acting on the elevator cabin is first analyzed. The 5000 lb weight is divided evenly between the cables due to symmetry. Consequently the force of each cable will be. P = 5000 / 2 = 2,500 lb. A graphical demonstration of a free body subjected to external forces is referred to as a free-body diagram (FBD). In addition to the external forces on a (free) body, there are internal forces within the (free) body. The internal forces are forces between the particles of a body. In solving problems in Mechanics, mainly in Statics, the important step is to draw the free body diagram FBD. The free body diagram is a material point or a particle that represents an object of interest to study. It is located in the origin of a coordinate system. It uses the particle model. 2. Drawing free-body diagram, the steps. Draw a picture of the situation, that is the motion diagram,
Free body diagram statics. Figure 6.1.1 Free body diagram of the i-th link The force fi−1,i and moment −1,i are called the coupling force and moment between the adjacent links i and i-1. For i=1, the coupling force and moment are 0,1 and 0,1. These are interpreted as the reaction force and moment applied to the base link to which the arm mechanism is fixed. 28.02.2015 · An educational video from Actus Potentia. Free Body Diagram, frames, internal forces, equilibrium equations, solution strategy, examples. 19.03.2013 · 18 Free body diagrams, statics Thread starter jonjacson; Start date Mar 18, 2013; Mar 18, 2013 #1 jonjacson. 427 36. Hi to everybody Homework Statement Well I need to identify the forces acting on the bodies using free body diagramas, it´s not necessary to calculate anything, it´s only to learn about free body diagrams. I will write my thoughts about the FBD … MEM202 Engineering Mechanics - Statics MEM 7.2 Plane Trusses Method of Joints 1. Draw a free-body diagram of the entire structure and determine the reactions (if r = 3). 2. Draw free-body diagrams for all members (assume tensile forces in all members) and all joints. 3. Set up the equilibrium equations for each joint and
Statics (MET 2214) Free-Body Diagram (FBD): To apply equilibrium equations we must account for all known and unknown forces acting on the particle. The best way to do this is to draw a free-body diagram of the particle. FBD: A diagram showing the particle under consideration and all the forces and moments acting on this particle. FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (Section 5.2) 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) support reactions, and, c) the weight of the body. Idealized model. Free-body diagram (FBD) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape. 14. What is static equilibrium 15. How to draw good free-body diagrams (FBDs) 16. Why is the tension the same everywhere in a rope 17. How to calculate forces of three ropes pulling in different directions 18. Using symmetry in statics problems 19. How to find the mass pulling on a spring when given the deflection 20. How to find the force ... In this video, we learn how we can draw free body diagrams of frames and machines. We first start with showing the differences of frames, machines and trusse...
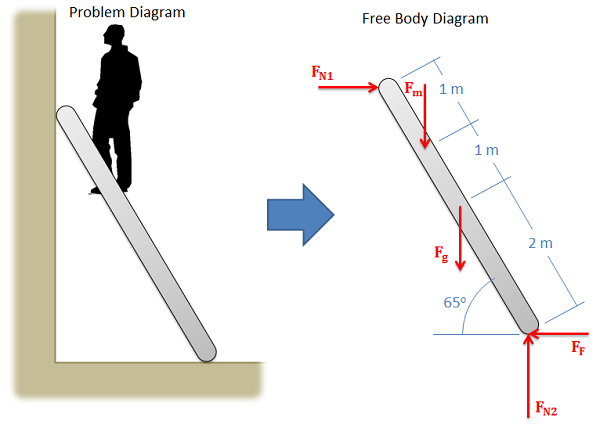
Free Body Diagram Example : A Free-body diagram (FBD) is an essential tool when the forces on an object need to be determined using equilibrium equations. They help focus attention on the object of interest in order to determine the forces acting on it. Creating FBD's is a straightforward process: Identify the object that will be isolated. Make an approximate sketch of the object … FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS (Section 5.2) 1. Draw an outlined shape. Imagine the body to be isolated or cut "free" from its constraints and draw its outlined shape. 2. Show all the external forces and couple moments. These typically include: a) applied loads, b) the weight of the body, and c) support reactions (can be difficult). Forces Statics and FBD's Intro 6th.notebook 2 November 08, 2016 Objectives: •Students will understand what a force is and what forces can do •Students will understand what is meant by static equilibrium •Students will be able to correctly draw Free Body Diagrams A free body diagram is a tool used to solve engineering mechanics problems. As the name suggests, the purpose of the diagram is to "free" the body from all other objects and surfaces around it so that it can be studied in isolation.
An FBD represents the body of interest and the external forces acting on it. ... Often a provisional free body is drawn before everything is known. The purpose of ...
12.08.2016 · that the free-body diagram serves the purpose of focusing accurate attention on the action of the external forces; therefore, the diagram should not be cluttered with excessive information. Force arrows should be clearly distinguished from other arrows to avoid confusion. When these steps are completed a correct free-body diagram will result. Now, the appropriate …
The first thing I tried was a free body diagram cutting through A and C to create one body and C and B to create another. ... Browse other questions tagged statics or ask your own question. The Overflow Blog Stack Gives Back 2021. Safety in numbers: crowdsourcing data on nefarious IP addresses ...
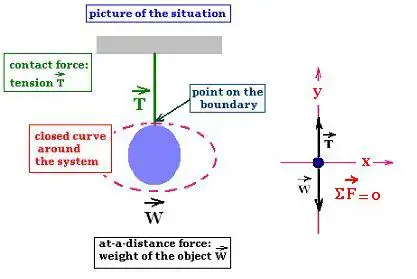
The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be drawn.
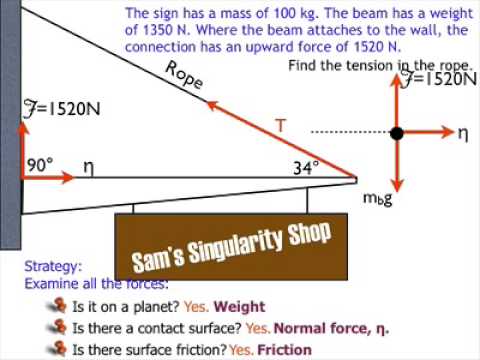
acting on a body which prevents or resists the slipping of a body relative to a second body. Experiments show that frictional forces act tangent (parallel) to the contacting surface in a direction opposing the relative motion or tendency for motion. For the body shown in the figure to be in equilibrium, the following must be true:
Statics: Lecture Notes for Sections 5.1,5.2 1 Chapter 5 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY & FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS Today's Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free-body diagram. READING QUIZ 1. If a support prevents translation of a body, then the support exerts a _____ on the ...
10.01.2020 · The free body diagram is one of the most important ideas in statics. Here's a description along with an easy example.
Engineering Statics uses algebra and trigonometry and is suitable for use with either calculus- or non-calculus-based academic statics courses. Completion of a beginning physics course is helpful for success in statics, but not required as all the key concepts are included in this course. Topics Covered: Forces; Free Body Diagrams
Free body diagrams are the tool that engineers use to identify the forces and moments that influence an object. They will be used extensively in statics, and you will use them again in other engineering courses so your effort to master them now is worthwhile. Although the concept is simple, students often have great difficulty with them. 🔗
What are Free Body Diagrams? One of the most useful aids for solving a statics problem is the free body diagram (FBD). A free body diagram is a graphic, dematerialized, symbolic representation of the body (structure, element or segment of an element) in which all connecting "pieces" have been removed. A FBD is a
In Chapter 5 we saw that each two-dimensional free-body diagram results in up to three linearly independent equations. By disassembling the structure we now have more free-body diagrams available, and can use them to find more unknown values. Here’s a few more details on the number of equations that come from each type of two-dimensional free ...
Free Body Diagrams of Gear Trains Shih-Liang (Sid) Wang ... From the principal of force transmissibility in statics, we know that any point along the ... For a body to be in equilibrium, the external forces and the moments acting on the body both sum to zero. Therefore, Fig. 6 shows the force on a gear, not a FBD. ...
Free-Body Diagram of a Rigid Body:Free-body diagrams play a crucial role in the statics of rigid bodies. A free-bodydiagram is a road map that enables one to identify all the unknown loads(forces and moments) prior to the formulation and solutionof equilibrium equations. In this section, we provide some hints to simplifythis task, and will look at some examples offree-body diagrams.
The free-body diagram is used to identify the unknown forces acting on the object when applying the equilibrium equation (1.1) to the object. The procedure for solving equilibrium problems is therefore as follows: 1. Draw a free-body diagram—you must choose an object to isolate that results in a free-body diagram including
In solving problems in Mechanics, mainly in Statics, the important step is to draw the free body diagram FBD. The free body diagram is a material point or a particle that represents an object of interest to study. It is located in the origin of a coordinate system. It uses the particle model. 2. Drawing free-body diagram, the steps. Draw a picture of the situation, that is the motion diagram,
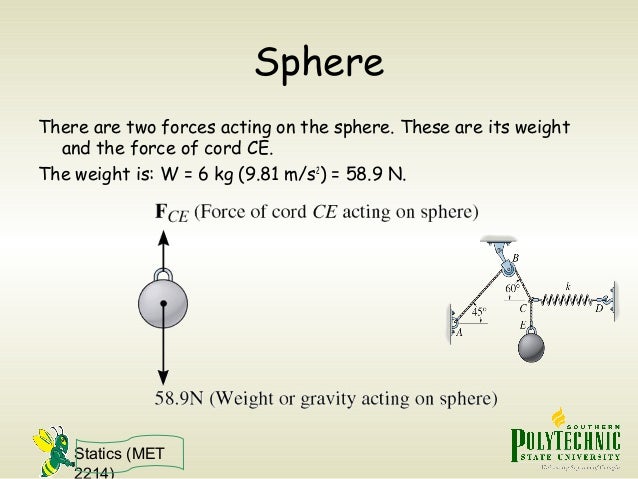
A graphical demonstration of a free body subjected to external forces is referred to as a free-body diagram (FBD). In addition to the external forces on a (free) body, there are internal forces within the (free) body. The internal forces are forces between the particles of a body.
As with all statics problem, a free-body diagram will assist in solving the problem. In this example, all forces acting on the elevator cabin is first analyzed. The 5000 lb weight is divided evenly between the cables due to symmetry. Consequently the force of each cable will be. P = 5000 / 2 = 2,500 lb.



![Statics] Help with the Free Body Diagram : r/EngineeringStudents](https://external-preview.redd.it/4JaMB3eXTnuaBcrpTe9sRLcwm3GemzbX4L6vuXvaRA8.png?auto=webp&s=439b09578f2a573ca72d6370816c5933741f2277)













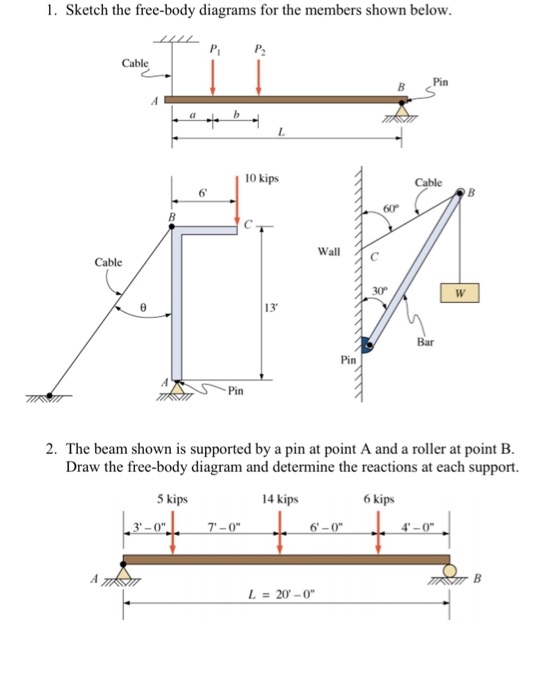
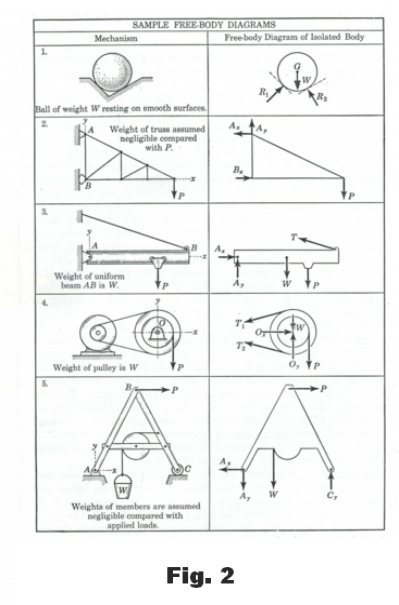
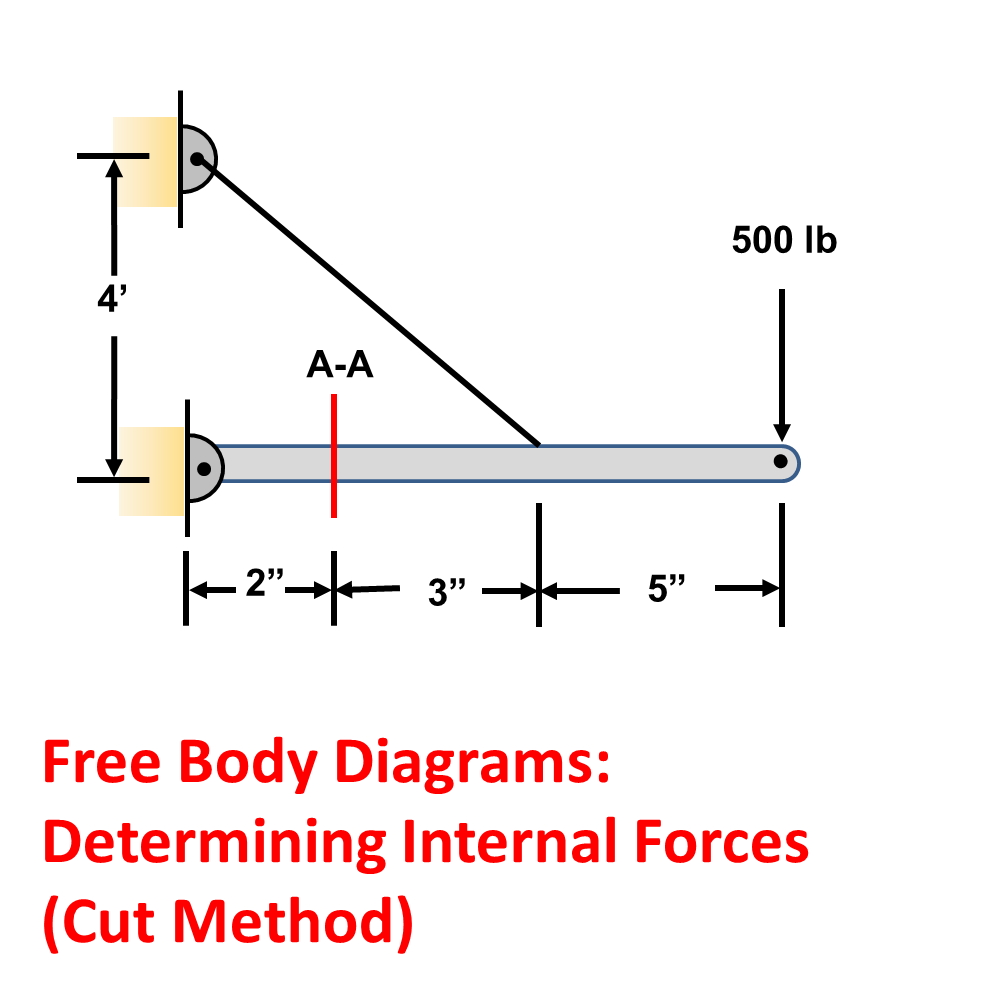
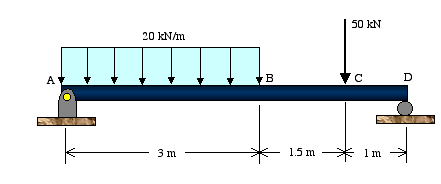


0 Response to "39 free body diagram statics"
Post a Comment