42 electron transport chain diagram
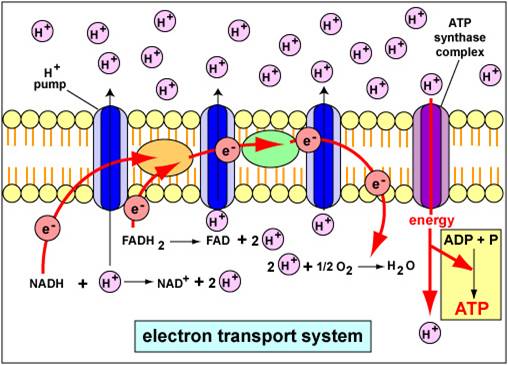
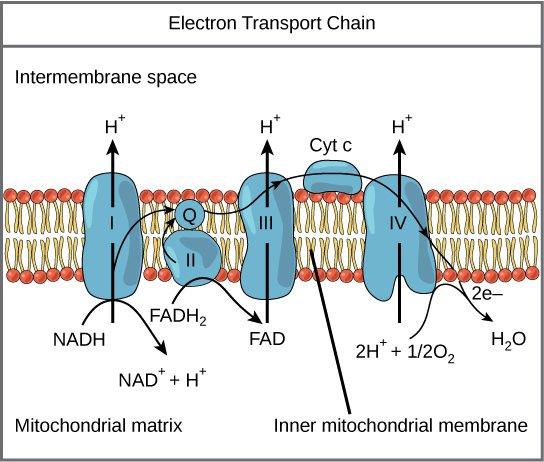
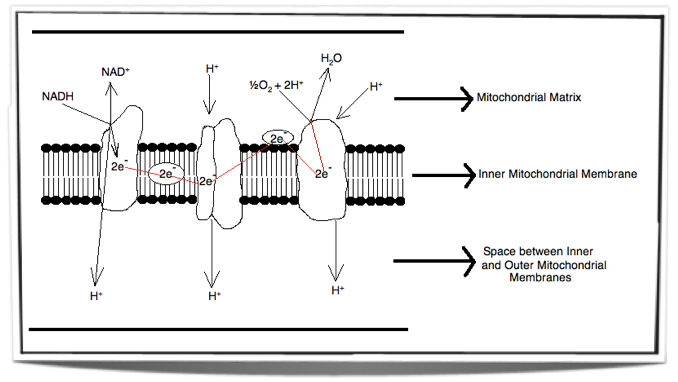
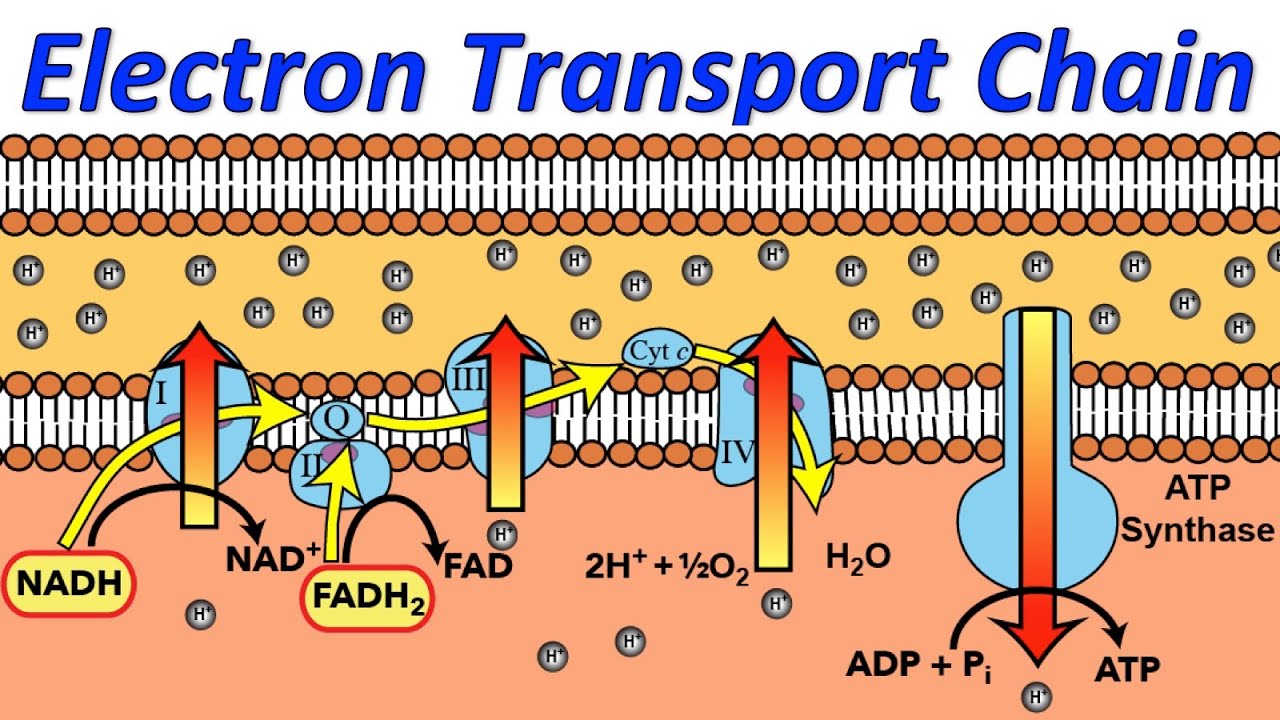
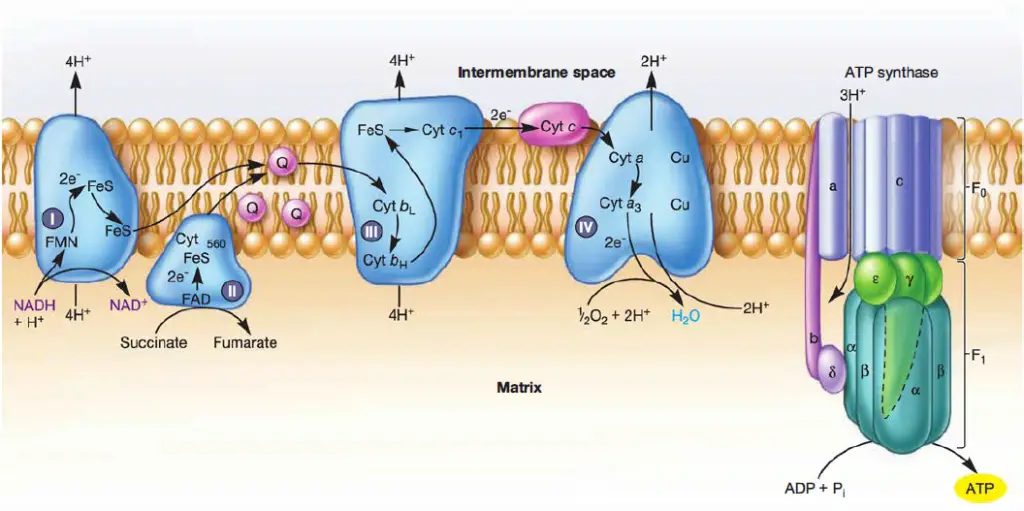
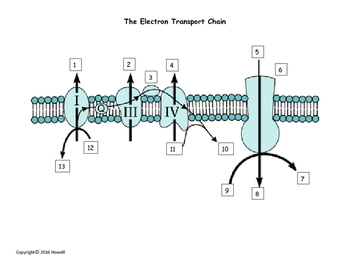
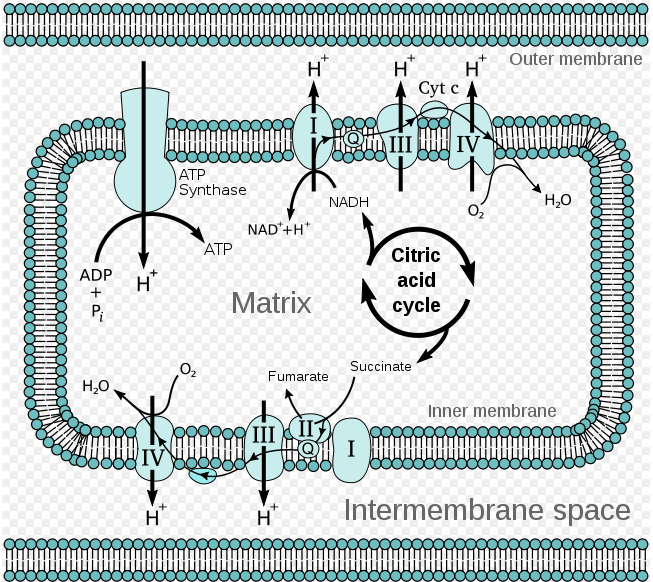
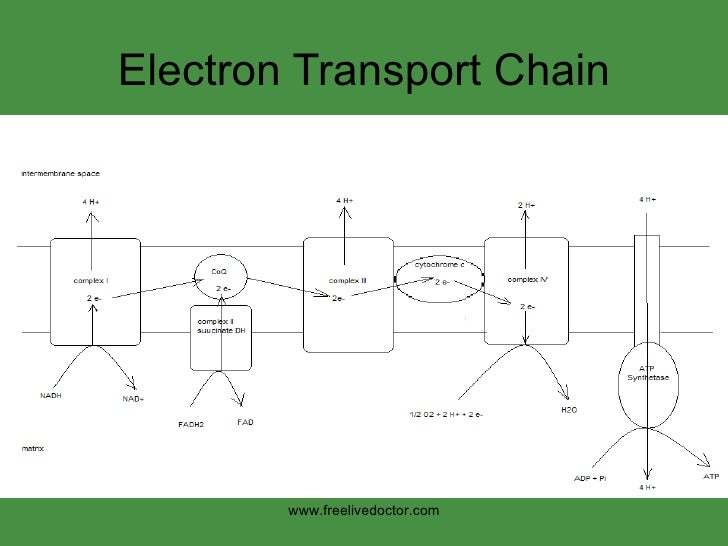
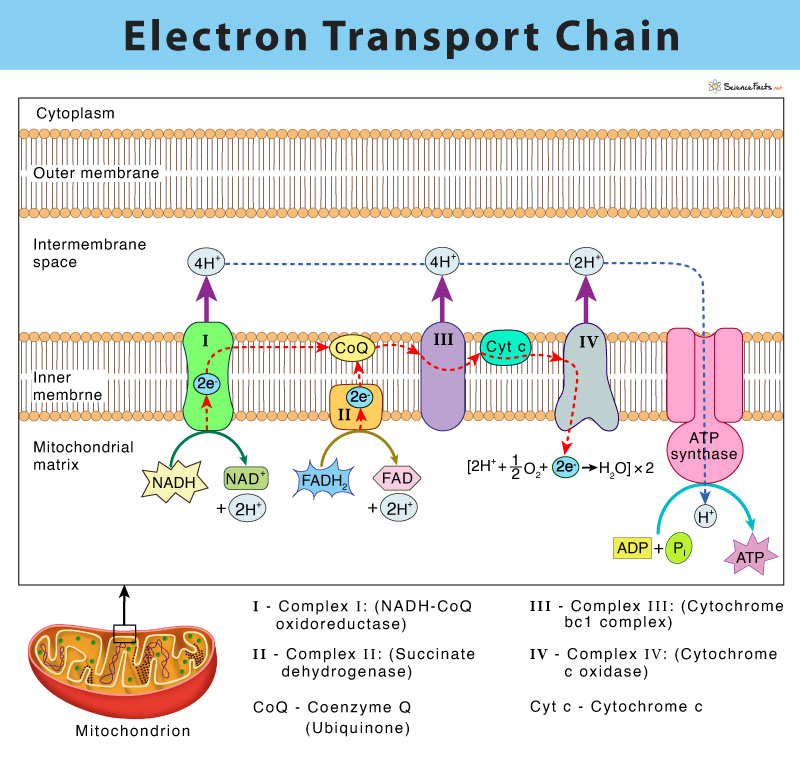
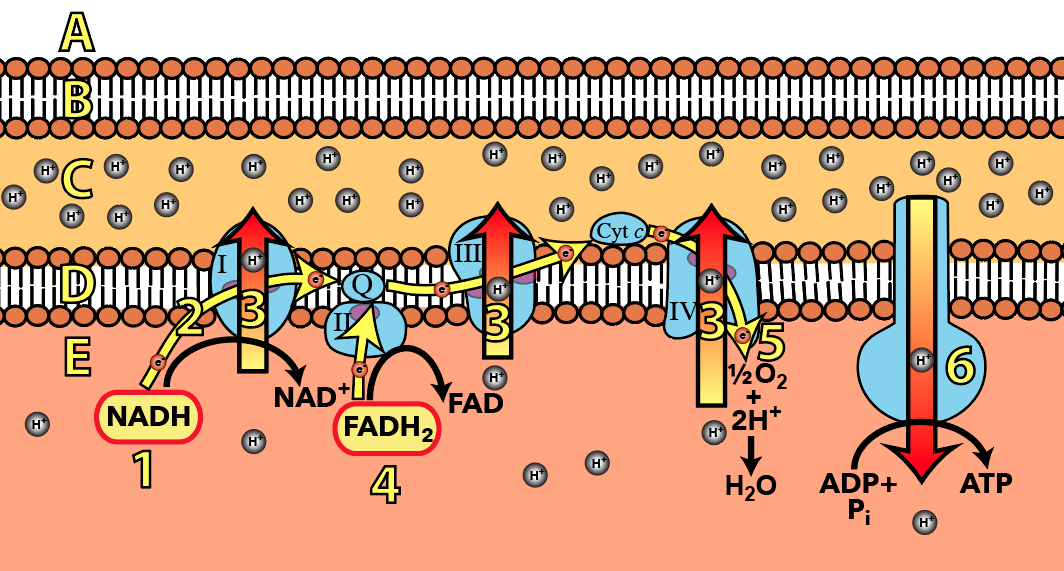
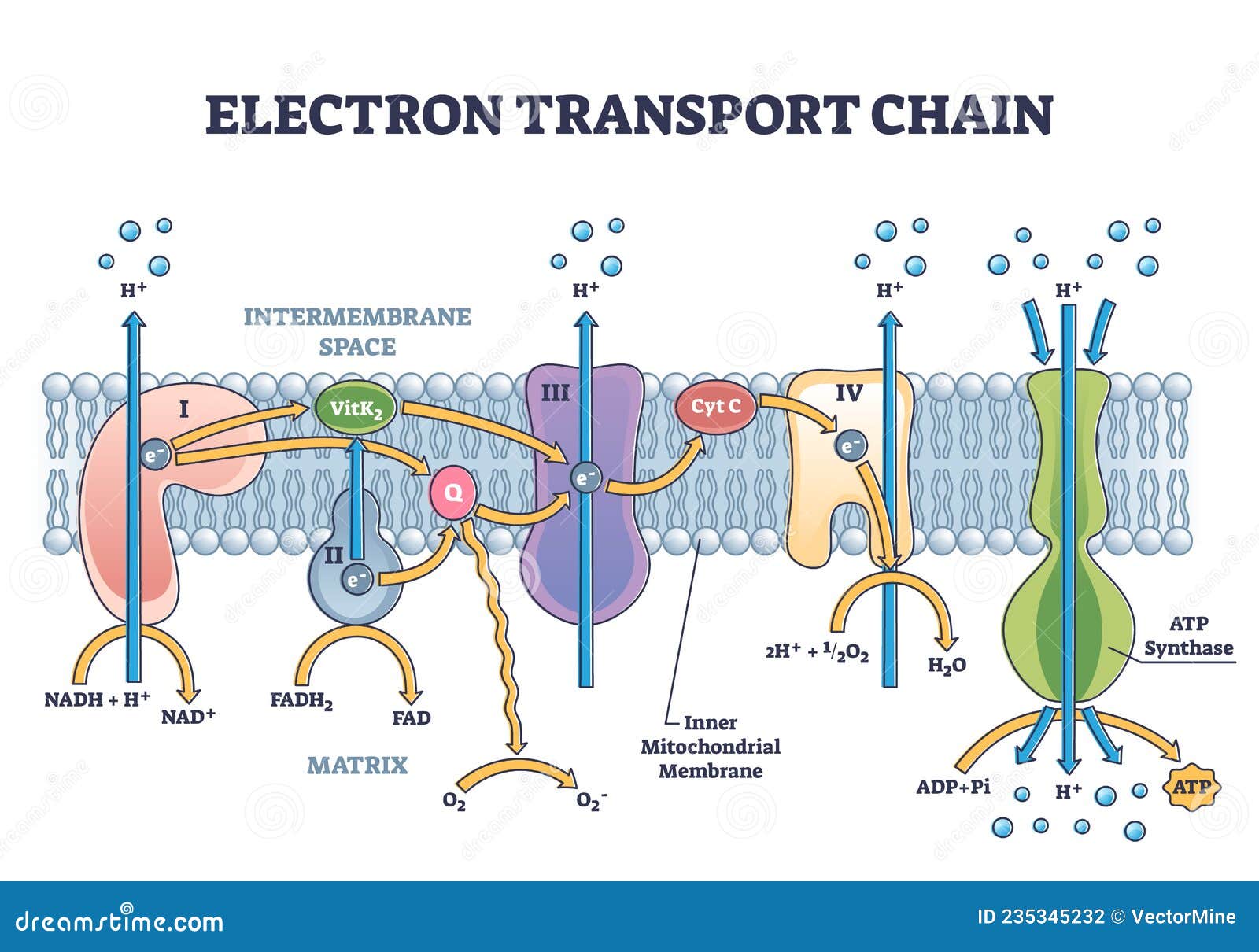
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H + ions) across a membrane.Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are membrane-bound. Electron transport is a sequence of redox reactions that mimic a relay race or bucket brigade in which electrons are easily transported from one part to the end point of the chain where the electrons decrease molecular oxygen and produce water. There are four protein-composed electron transport chain complexes, labelled I through IV in the ...
Effects of end group functionalization and level alignment on electron transport in molecular devices Gunn Kima and Shuchun Wang Center for High Performance Simulation and Department of Physics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina 27695-7518, USA Wenchang Lu, Marco Buongiorno Nardelli, and J. Bernholcb...

Electron transport chain diagram
Oxidative phosphorylation, incorporating two interdependent processes - the flow of electrons through electron transport chain down to the oxygen and chemiosmotic coupling-, is the final stage of cellular respiration.. Highly energetic electrons that are extracted during the decomposition of food molecules by cellular metabolic pathways are stored in electron carriers - NADH and FADH 2. 19 and 20 are the most popular electron transport layer (ETL) materials. However, their complicated fabrication method, with the application of a high annealing temperature (>200 °C) for the crystallization of the metal oxides, is not compatible with roll-to-roll manufacturing processes for high throughput.18,21 To solve this... In this work, we show that Saccharomyces cerevisiae frataxin orthologue Yfh1p interacts physically with succinate dehydrogenase complex subunits Sdh1p and Sdh2p of the yeast mitochondrial electron transport chain and also with electron transfer flavoprotein complex ETFα and ETFβ subunits from the electron transfer...
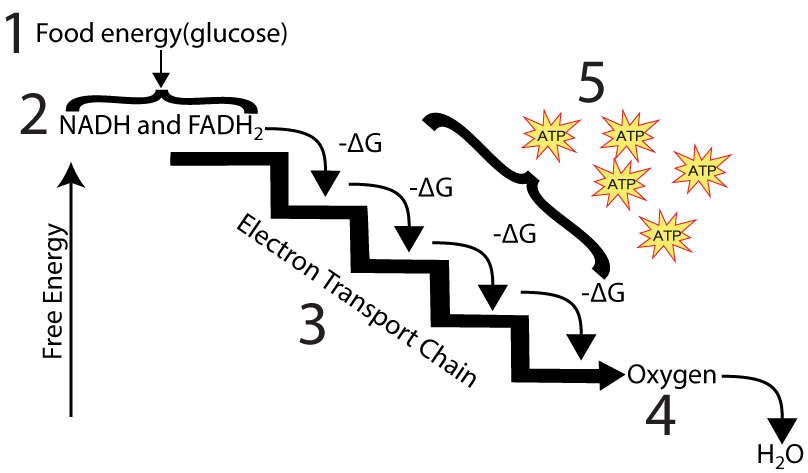
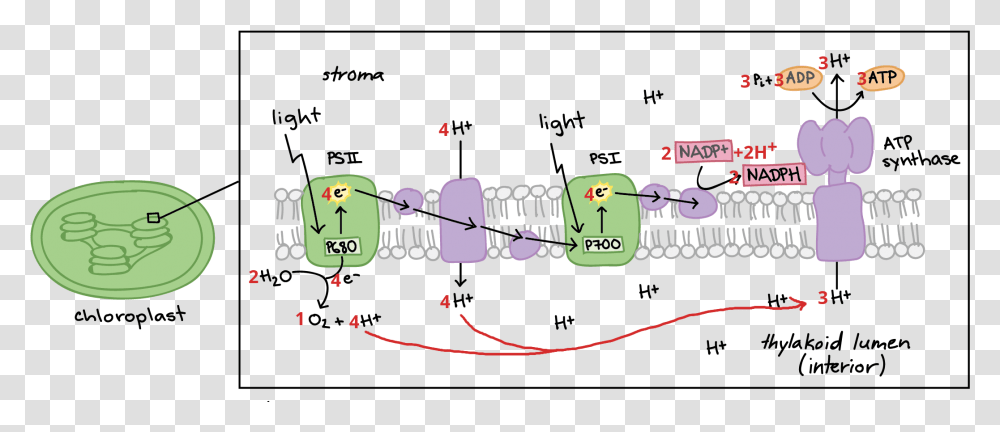
Electron transport chain diagram. Subject Matter of Electron Transport Chain: The primary function in photosynthesis is the raising of an electron to a higher energy level in chlorophyll. Then the electron is transferred to an acceptor. It is, as if, there is a hole in the chlorophyll which invites filling. This hole is plugged by electrons from water. Electron Transport Chain in Mitochondria. A complex could be defined as a structure that comprises a weak protein, molecule or atom that is weakly connected to a protein. The plasma membrane of prokaryotes comprises multi copies of the electron transport chain. Complex 1- NADH-Q oxidoreductase: It comprises enzymes consisting of iron-sulfur and ... 7 Simple steps in diagrams and 1 page of clear, step-by-step text.Traces glucose uptake, Glycolysis, Krebs, Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation all in one clear diagram.Includes a simple diagram of entire process and a more detailed diagram.Also a diagram with numbered blanks for The high-energy carriers NADH and FADH 2 can themselves be oxidized by the electron transport chain. During oxidation, energy is lost by the oxidized molecule while energy is gained by the reduced molecule. The electron transport chain is composed of a series of molecules that alternatively become oxidized and reduced by one another.
As an electron passes along an electron-transport chain embedded in a lipid-bilayer membrane, it can bind and release a proton at each step. In this diagram, electron carrier B picks up a proton (H+ ) from one (more...) Go to:The Redox Potential Is a Measure of Electron Affinities In biochemical reactions, any electrons removed... Show details Electron-Transport Chains and Their... Respiratory Chain The Respiratory Chain Includes Three... Overview of the Electron Transport Chain guys here i shown to draw electron transport chain...if you want to see drawing tutorial of any other biology diagram ..please write me in comment box..i wil... Start studying Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Diagram. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
The electron transport chain is a set of proteins and other organic molecules found in the inner membrane of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells and the plasma membrane of prokaryotic cells. The electron transport chain has two primary functions: it produces a proton gradient—storing energy that can be used to create ATP during chemiosmosis ... Respiration is one of the most vital and basic features of living organisms. In mammals, respiration is accomplished by respiratory chain complexes located on the mitochondrial inner membrane. In the past century, scientists put tremendous efforts in understanding these complexes, but failed to solv … Polymeric and supramolecular arrays for directional energy and electron transport over macroscopic distances. Acc. Chem. Res.25, 569–574 (1992). CAS Article... Side Chain of Small-Molecule n-Type Organic Semiconductors in Stress Stability of Single-Crystal Transistors Shohei Kumagai, Craig P. Yu […] & Toshihiro Okamoto The... Advertisement View all journals Search Login Explore content Journal information Publish with us Subscribe... Electrons from the NADPH and FADHare transferred to O via the electron transport chain generating the energy carrier ATP and oxidized NADP and FAD ( ). As in animal mitochondria, the plant electron transport system is composed of five respiratory complexes, which form supercomplexes ( ). Depending on the substrate, electrons...
All three small molecules exhibit different solubility behavior based on their alkyl chain length in common organic solvents. ,, andshow quite deep LUMO energy levels (around −4.2 eV) which is promising for better air-stable electron transport. Under ambient atmosphere, we found that electron mobilities of solution-processed...
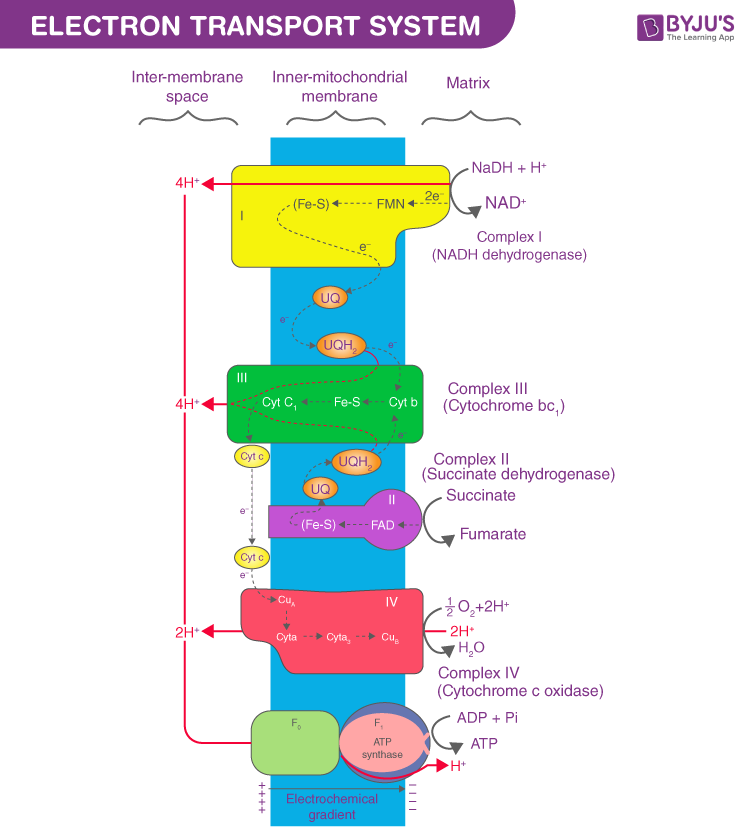
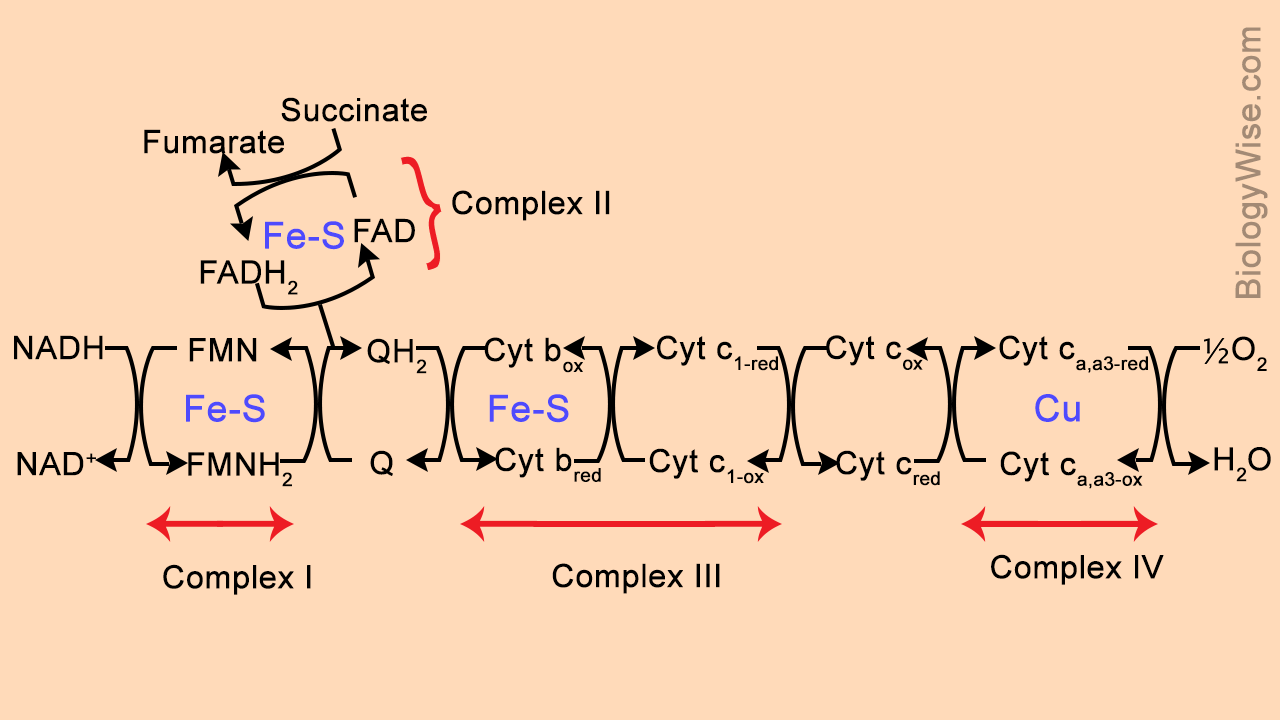
Introduction The proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane maintained by action of electron transport chain Chain consists of 6 proteins associated... This is a complex reaction mechanism and no attempt has been made in the above diagram to explain how the 4 electrons from 4 Cyt C are conveyed to the O2 (it doesn...
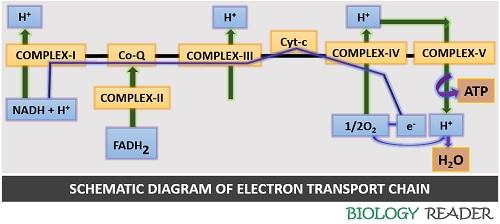
Electron transport system. The metabolic pathway through which the electron passes from one carrier to another, is called the electron transport system (ETS). Electron transport system takes place in inner mitochondrial membrane. Electron transport chain comprises of the following: Complex I: NADH dehydrogenase; Complex II: succinate dehydrogenase
The electron transport chain is also called the Cytochrome oxidase system or as the Respiratory chain. The components of the chain include FMN, Fe-S centers, coenzyme Q, and a series of cytochromes (b, c1, c, and aa3). The energy derived from the transfer of electrons through the electron transport chain is used to pump protons across the ...
Electron Transport Chain Definition. The electron transport chain is a crucial step in oxidative phosphorylation in which electrons are transferred from electron carriers, into the proteins of the electron transport chain which then deposit the electrons onto oxygen atoms and consequently transport protons across the mitochondrial membrane.This excess of protons drives the protein complex ATP ...
Electron Transport Chain Definition. The Electron Transport System also called the Electron Transport Chain, is a chain of reactions that converts redox energy available from oxidation of NADH and FADH 2, into proton-motive force which is used to synthesize ATP through conformational changes in the ATP synthase complex through a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
The effective hydration of the polymer chains was determined by comparison of alpha(N) values of the probe across the phase diagram with "calibration" curves of alpha(N) in pure PEG, pure PPO, and mixtures of the homopolymers, measured as a function of the water content Z(w), where Z(w) is the number of water molecules per...
Containing Electron-Transporting Groups on the Main Chain / Polymeric Nanosphere Formed from Temperature-Responsive Polymer Composed of (N,N-Dimethylamino)Ethyl Methacrylate and Ethyl Acrylamide / The Early Stage of the Morphology Development of Immiscible Polymer Blends during Melt Blending: Compatibilized vs. Uncompatibilized...
Cytoplasmic dynein 2, in contrast, specifically carries out retrograde intraflagellar transport in cilia and flagella (Ishikawa and Marshall, 2011). Cytoplasmic dynein is a large homodimer that consists of a heavy chain (>500 kDa) and several smaller associated subunits, each present in two copies. The dynein heavy chain...
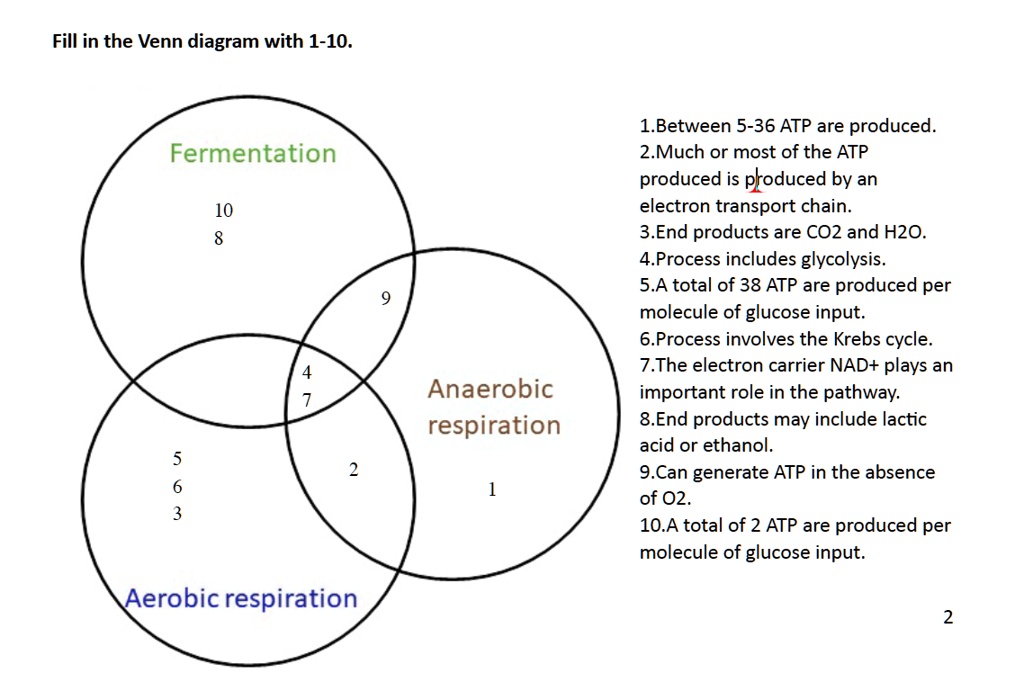
The electron transport chain is the last stage of the respiration pathway. It is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules. In total, 38 ATP molecules are produced from one molecule of ...
Electron Transport Chain (overview) • The NADH and FADH2, formed during glycolysis, β-oxidation and the TCA cycle, give up their electrons to reduce molecular O2 to H2O. • Electron transfer occurs through a series of protein electron carriers, the final acceptor being O2; the pathway is called as the electron transport chain.
This NADH donates its electrons to the electron transport chain in complex 1, resulting. in the net production of 3 ATP. This system is more energy efficient, but slower. What are some agents that block the Electron Transport Chain? 1) Amytal 2) Sodium Azide 3) Rotenone 4) Antimycin A 5) Cyanide Amy SAw Roten Ants, Cya.
Solution for Define Linear Electron Flow. Explain each step of Linear Electron Flow (Electron Transport Chain) in
In the electron transfer chain, electrons move along a series of proteins to generate an expulsion type force to move hydrogen ions, or protons, across the mitochondrial membrane. The electrons begin their reactions in Complex I, continuing onto Complex II, traversed to Complex III and cytochrome c via coenzyme Q, and then finally to Complex IV.
The electron transport chain is the last stage of the respiration pathway and is the stage that produces the most ATP molecules. The electron transport chain is a collection of proteins found on ...
Sep 08, 2021 · The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In the former, the electrons come from breaking down organic molecules, and energy is released. In ...
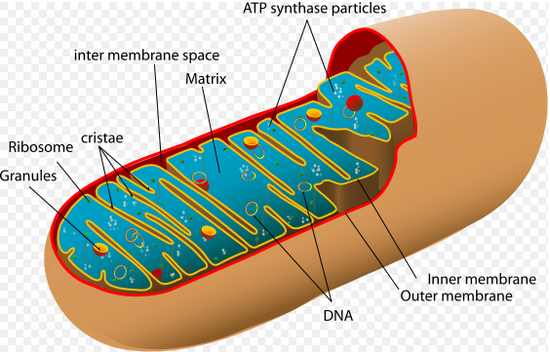
In this review, we will introduce recent advances of the mitochondrial ETC (electron transport complexes) research in three parts: the structure details of respirasome, the relationship between cristae shape and respiratory chain organization, and the highly disputed issues including substrate channeling, electron transfer pathway, and the ...
The electron transport chain is a series of molecules that accept or donate electrons easily. By moving step-by-step through these, electrons are moved in a specific direction across a membrane. The movement of hydrogen ions are coupled with this. This means that when electrons are moved, hydrogen ions move too.
Electron Transport Electron Transport Chain Diagram A major source of cellular energy production, in the form of ATP, is derived from the proton motive force supplied to mitochondrial ATP synthase. The main driver of the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane is the electron transport system.
ADVERTISEMENTS: The electron transport chains of bacteria (prokaryotes) operate in plasma membrane (mitochondria are absent in prokaryotes). Some bacterial electron transport chains resemble the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Paracoccus denitrificans is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic soil bacterium. It is a model prokaryote for studies of respiration. When this bacterium grows ...
The electron transport chain is a series of electron transporters embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that shuttles electrons from NADH and FADH 2 to molecular oxygen. In the process, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, and oxygen is reduced to form water. The electron transport chain (Figure 1 ...
Electron Transport Chain Steps Explained with Diagram. The electron transport chain is an essential metabolic pathway that produces energy by carrying out a series of redox reactions. This BiologyWise article provides a simple explanation of this pathway.
Research Article Modular origins of biological electron transfer chains Hagai Raanan, Douglas H. Pike, Eli... for electron transfer reactions that form the energetic basis of life. These structural modules are, in... Abstract Oxidoreductases catalyze electron transfer reactions that ultimately provide the energy for life. A... oxidoreductase electron transfer metalloprotein... Similar Articles Nanosecond heme-to-heme electron transfer...
Abstract The light reactions in photosynthesis drive both linear and cyclic electron transport around photosystem I (PSI). Linear electron transport generates both ATP and NADPH, whereas PSI cyclic electron transport produces ATP without producing NADPH. PSI cyclic electron transport is thought to be essential for balancing the...
In this work, we show that Saccharomyces cerevisiae frataxin orthologue Yfh1p interacts physically with succinate dehydrogenase complex subunits Sdh1p and Sdh2p of the yeast mitochondrial electron transport chain and also with electron transfer flavoprotein complex ETFα and ETFβ subunits from the electron transfer...
19 and 20 are the most popular electron transport layer (ETL) materials. However, their complicated fabrication method, with the application of a high annealing temperature (>200 °C) for the crystallization of the metal oxides, is not compatible with roll-to-roll manufacturing processes for high throughput.18,21 To solve this...
Oxidative phosphorylation, incorporating two interdependent processes - the flow of electrons through electron transport chain down to the oxygen and chemiosmotic coupling-, is the final stage of cellular respiration.. Highly energetic electrons that are extracted during the decomposition of food molecules by cellular metabolic pathways are stored in electron carriers - NADH and FADH 2.







/electron-transport-chain-58e3be435f9b58ef7ed96112.jpg)









0 Response to "42 electron transport chain diagram"
Post a Comment