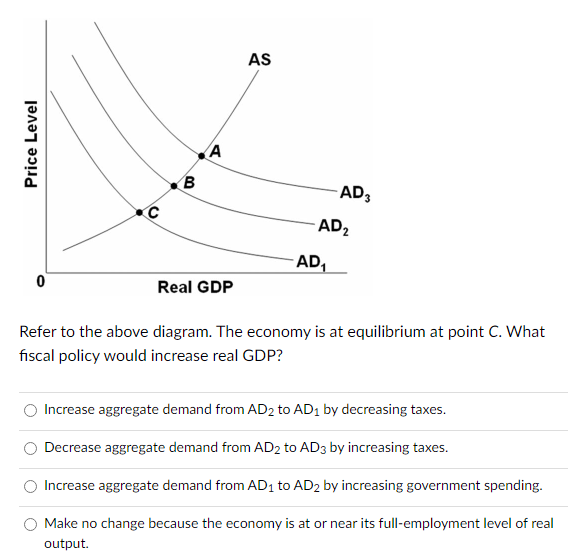
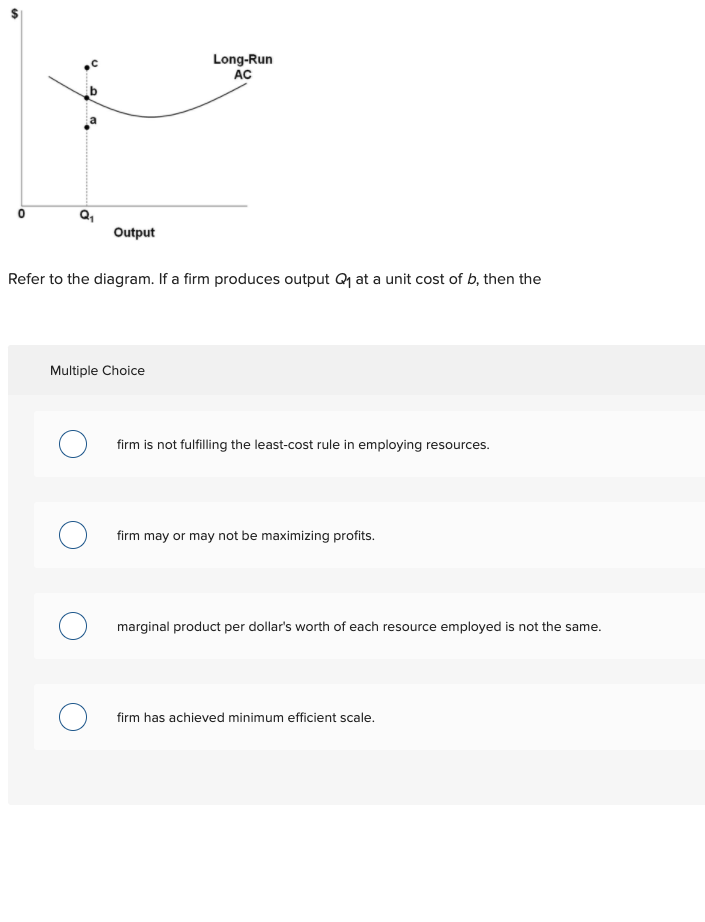
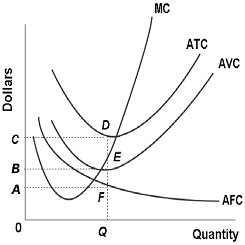
36 refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a
Refer to the diagram. A decrease in the cost of resources would cause a... A) shift from S2 to S1 . ... At output level Q1, in this diagram, A) resources are overallocated to this product and productive efficiency is not realized. ... If average variable cost is $74 and total fixed cost is $100 at 5 units of output, then average total cost at ...
At 5 units of output average fixed cost average variable cost and average total cost are. Realize a 25 economic profit. Given the 75 product price at its optimal output the firm will. Refer to the above diagram for output level q per. At output level q2. Refer to the diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm.
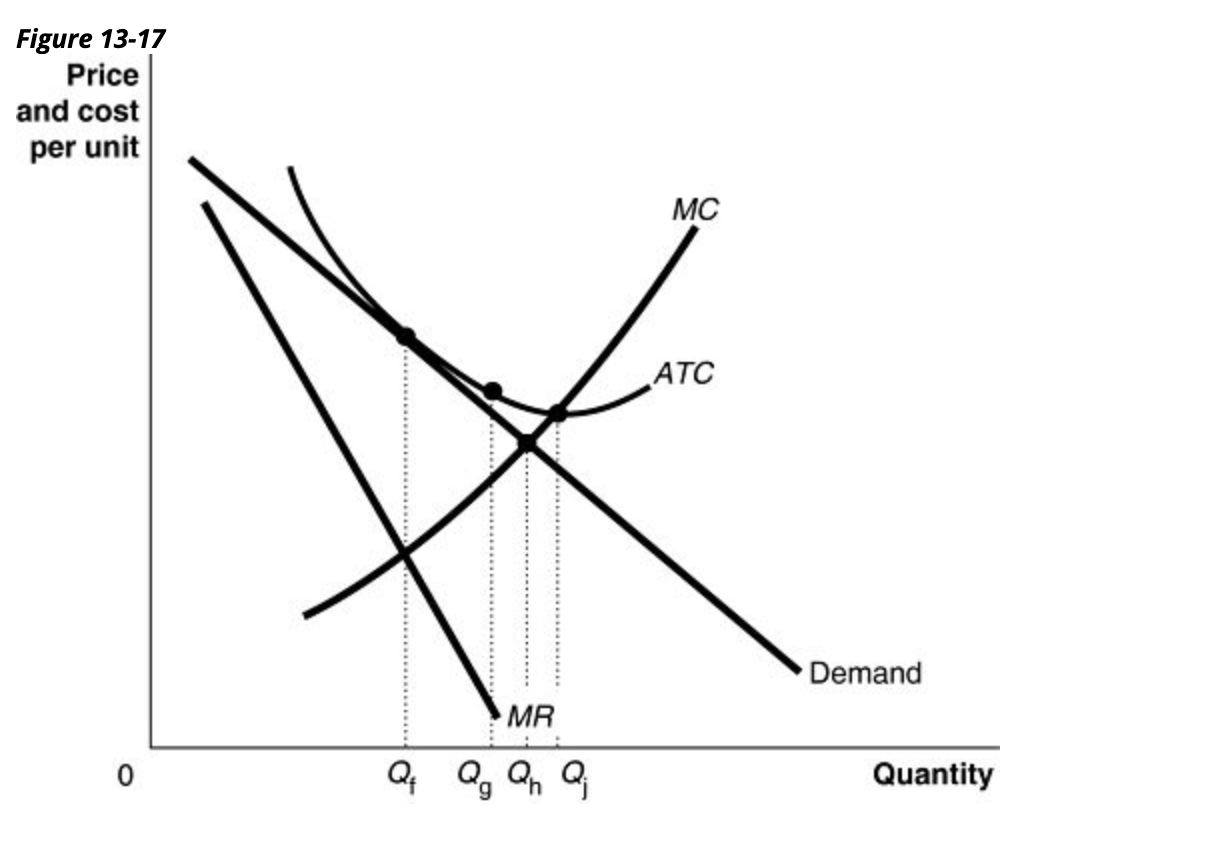
2) Refer to Figure 13 -17. Suppose the firm is currently producing Q f units. What happens if it increases its output to Q g units? 2) A) Its average cost of production will fall and its profit will rise. B) It will move from a zero profit situation to a loss situation. C) It will move from a zero profit situation to a profit situation.
/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)
Refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a
A) q1 B) q2 C) q3 D) q4 Answer: C Diff: 2 Type: A 14) Refer to Figure 9.5. Assume this firm is in a constant-cost industry. For this firm to be in long-run equilibrium, the firm must be producing A) q1 units of output. B) q2 units of output. C) q3 units of output. D) an amount that is indeterminate from this information.
A firm's cost of production is £12 per unit of output. If P is the price of the output good and Q is the number of units produced, which of the following statements is correct? Point (Q, P) = (2,000, 20) is on the isoprofit curve representing the profit level £20,000.
A) Firmʹs short-run supply curve B) Average total cost curve. C) Average variable cost curve D) Average fixed cost curve. Answer: D. 13) Imposition of an output tax on all firms in a competitive industry will result in. A) a downward shift in each firmʹs marginal cost curve. B) a downward shift in each firmʹs average cost curve.
Refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a.
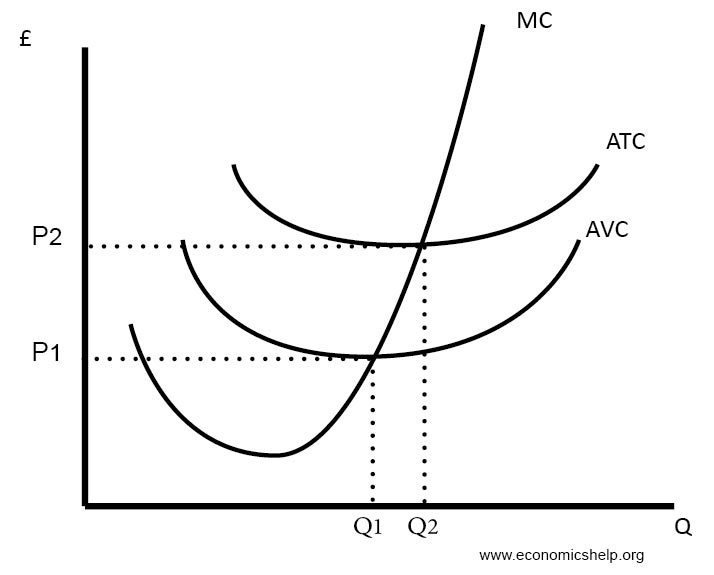
At that level of output, average fixed cost: A) is $2.50. B) is $4. C) is $100. D) cannot be determined from the information provided. Answer: A. Type: G Topic: 4 E: 420 MI: 176 180. Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. Suppose that average variable cost is $8 at 40 units of output.
1. the level of output that coincides with the intersection of the MC and AVC curves. 2. minimization of the AFC in the production of any good. 3. the production of the product-mix most desired by consumers. 4. the production of a good at the lowest average total cost. 5. If the price of product Y is $25 and its marginal cost is $18: 1.
Business Economics Q&A Library The diagram below shows the demand curve and marginal cost and marginal revenue curves for a new heart medication for which the pharmaceutical firm holds a 20-year patent on its production and sales. This protection gives the firm monopoly power for the 20 years of the patent. MC Po \ F P1 I B P2 J A K\ D Qo Output MR FIGURE 10-7 Refer to Figure 10-7.
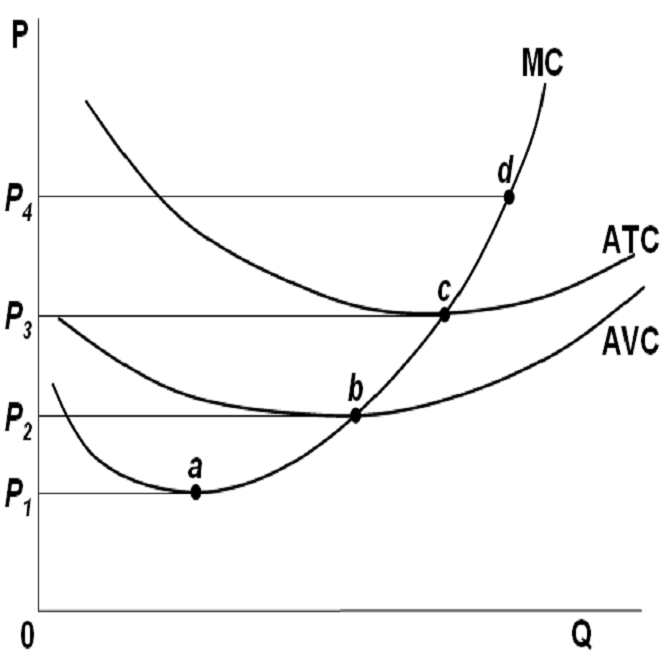
Refer to Figure 11-9 above to solve the following problems. asked Jul 8, 2016 in Economics by Trina. a. Calculate the fixed cost of production. b. Calculate the average total cost of production when the firm produces 20 units of output. c. Calculate the average variable cost of production when the firm produces 20 units of output. d. Calculate ...
FIGURE 10-6 -Refer to Figure 10-6. Assume this pharmaceutical firm charges a single price for its drug. At its profit-maximizing level of output it will produce A) Q0 units and charge the perfectly competitive price. B) Q0 units and charge a price of p0. C) Q1 units and charge a price of p1. D) Q0 units and charge a price of p2.
Economics questions and answers. Long-Run AC 0 Output Refer to the diagram. The production of units of output at an average cost of a Multiple Choice can be achieved if the firm would hire the optimal mix of resources. would entail X-inefficiency is not possible. given present technology and resource prices can be realized if the last dollar ...
2) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P3, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output F or shut down, as it doesnʹt matter which. C) produce output D.
The functional relationship between the cost of production and the output is called the cost function. It is expressed as. C = f(Q x) Where, C = Cost of production. Q x = Units of output x produced In other words, the output-cost relationship for a firm is depicted by the cost function.
____ 66. Assume the following for a certain industry: (l) there is no incentive for firms to enter or exit the industry; (2) for some firms in the industry, short-run average total cost is greater than long-run average total cost at the level of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost; (3) all firms in the industry are currently producing the quantity of output at which marginal ...
The following figure shows the private cost and social cost of producing Good X. Refer to the figure above. Total welfare can be increased by _____. Select one: A. increasing output above Q1 units B. increasing the market price above P2 C. reducing output below Q1 units D. lowering the market price below P1
Output (Q) Total Fixed Cost Average Fixed Cost 10 £2000 £1000 20 Fixed costs (FC) are independent of output and must be paid out even if the production stops. Capital-intensive industries with a high ratio of fixed to variable costs offer scope for economies of scale. AFC = Fixed Costs (FC) / Output (Q). Costs Output (Q) Average Fixed Cost
Which piece of information would NOT be helpful in calculating the marginal cost of the 75th unit of output? A) The total cost of 75 units. B) The total cost of 74 units ... Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q1 . A) marginal cost is falling. B) average total cost is falling. ... A growing firm's average cost of production will decline over ...
14) In a diagram showing the average total cost and average variable cost curves, the minimum point of the average total cost is 14) A) at a larger level of output than the minimum point of the average variable cost. B) at the same level of output as the minimum point of the average variable cost.
Refer to the diagram. At output level Q: Multiple Choice ... Marginal cost measures the cost per unit of output associated with any level of production. ... divided by its marginal product. D. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and has average variable costs of $150. The firm's ...
141. Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q1 at an average total cost of ATC1, then the firm is: A) producing the potentially profit-maximizing output, but is failing to minimize production costs. B) incurring X-inefficiency, but is realizing all existing economies of scale.
Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q 1 at an average total cost of ATC 1 , then the firm is: A.
Knowledge of the cost-output relation helps the manager in cost control, profit prediction, pricing, promotion etc. The relation between cost and its determinants is technically described as the cost function. C= f (S, O, P, T ….) Where; C= Cost (Unit or total cost) S= Size of plant/scale of production. O= Output level.
the total cost of producing 200 or 300 units is no greater than the cost of producing 100 units. Tags: Question 14 . ... The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's economic profit ... Refer to the diagram. At output level Q2,
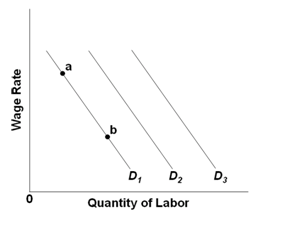
Refer to the diagram. The production of Q1 units of output at an average cost of a. is not possible, given present technology and resource prices. ... Refer to the diagram. The MRC curve lies above the labor supply curve because ... In the short run, a tool manufacturer has a fixed amount of capital. Labor is a variable input. The cost and ...
Refer to the above diagram. Maximum at point a. Average product total product units of variable factor input. If labor is the only variable input the average product of labor is at a. If a labor force in excess of q3 is employed. Refer to the above diagram. Production And Cost The Shape Of A Firm S Cost Curves In Long Run And Short Run
Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of B are: A) unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B) unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. C) obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. D) obtainableandimplyleast-costproductionofthisoutput.
Refer to the diagram, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 and D2 the new curves. ... commission imposes upon a nondiscriminating natural monopoly a price that is equal to marginal cost and below average total cost at the resulting output, then: ... Refer to the diagram. The production of Q1 units of output ...
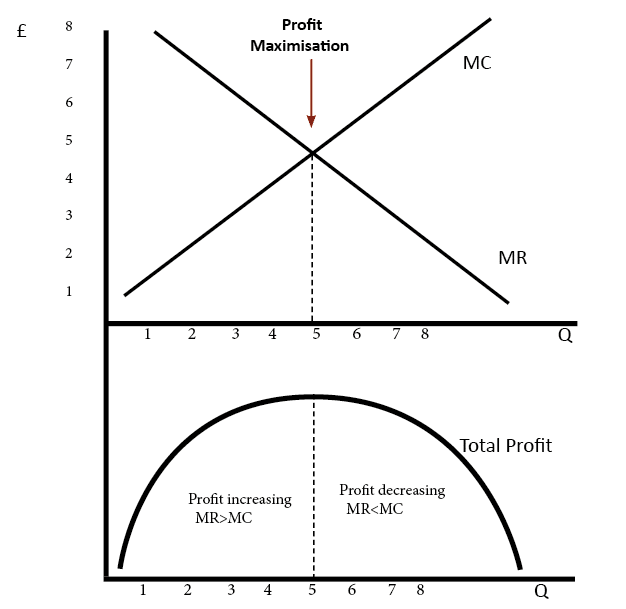
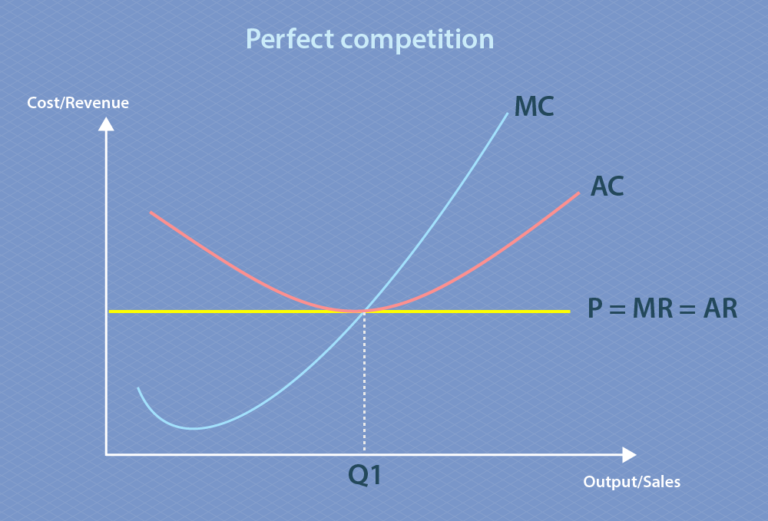
Again, the perfectly competitive firm will choose the level of output where Price = MR = MC, but in this case, the quantity produced will be 75. At this price and output level, where the marginal cost curve is crossing the average cost curve, the price the firm receives is exactly equal to its average cost of production.




















0 Response to "36 refer to the diagram. the production of q1 units of output at an average cost of a"
Post a Comment