37 gold foil experiment diagram
In 1905, Ernest Rutherford did an experiment to test the plum pudding model. His two students, Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, directed a beam of alpha particles at a very thin gold leaf suspended ... With the help of a diagram, explain the observations conclusion made by him he made from his experiment (4 marks) Question: 14. In 1911, Ernest Rutherford tested Thomson's hypothesis by devising his "gold foil experiment i. With the help of a diagram discuss Ernest Rutherford's model. 11.5 marks) it. With the help of a diagram, explain the ...
Illustration about Ernest Rutherford experiment to discover the structure of the atom by firing alpha particles at a gold foil target. Fully labelled diagram. Illustration of particles, rutherford, nuclear - 106716549

Gold foil experiment diagram
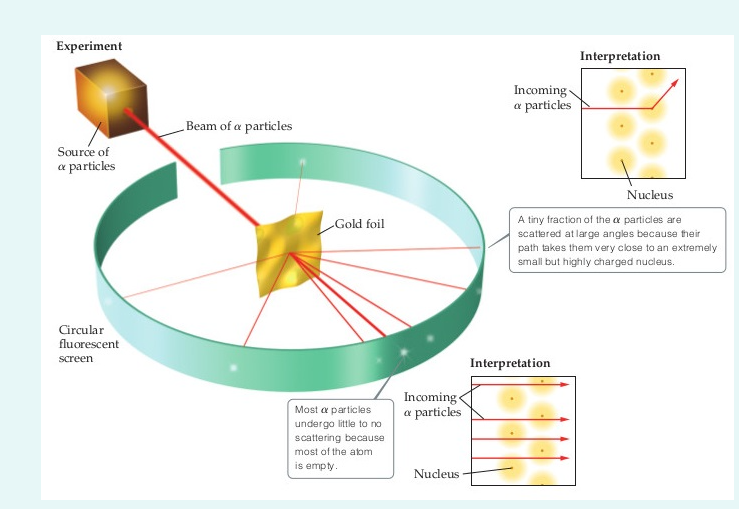
Rutherford in 1911, carried out an experiment called 'Gold foil experiment' and could conclude the nature of an atom and the position of the protons present in the atom decisively. He also proposed the position and behaviour of electrons. They bombarded fragile sheets of gold foil with fast-moving alpha particles. Nov 16, 2018 — Diagram of Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment. gold-foil-.tiff, 100.29 KB; (Last Modified on November 16, 2018) ... The gold-foil experiment showed that the atom consists of a small, massive, positively charged nucleus with the negatively charged electrons being at a great distance from the centre. Niels Bohr built upon Rutherford's model to make his own. In Bohr's model the orbits of the electrons were explained by quantum mechanics.
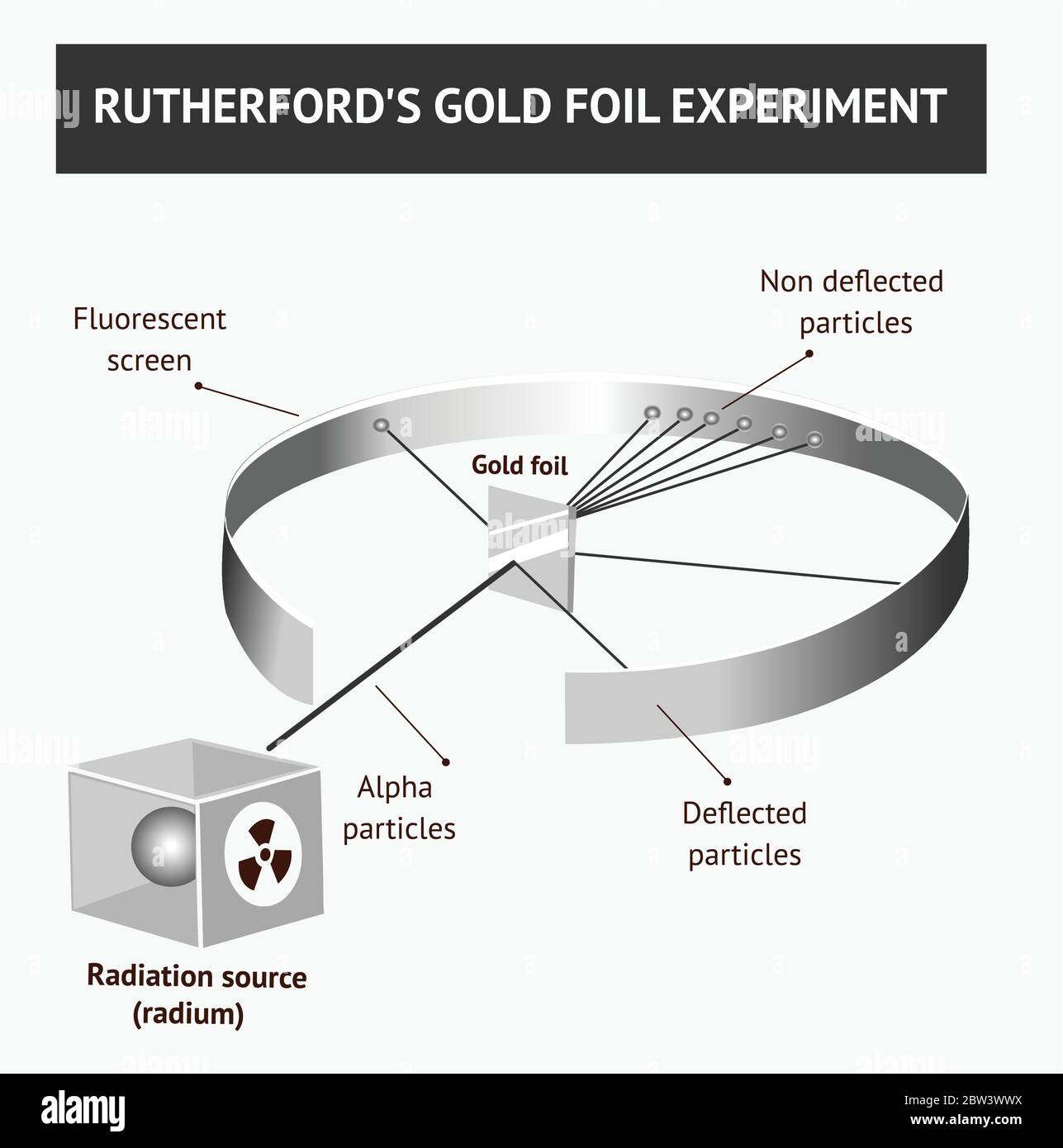
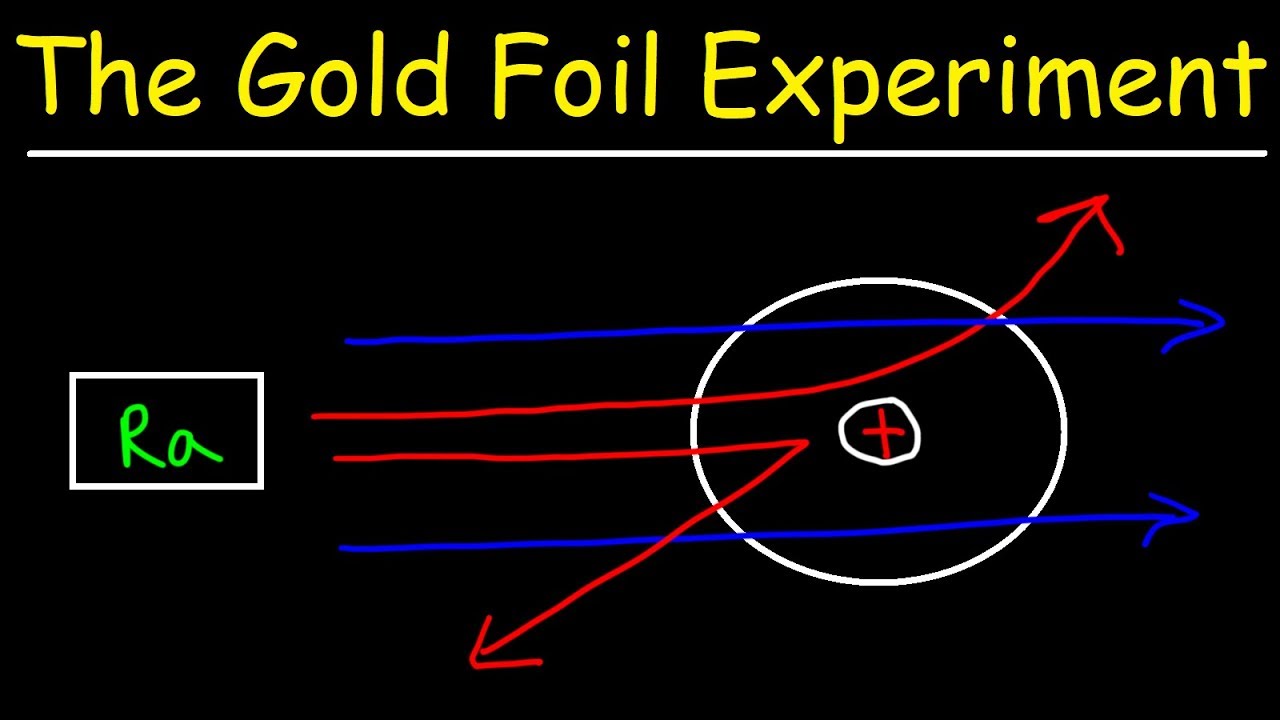
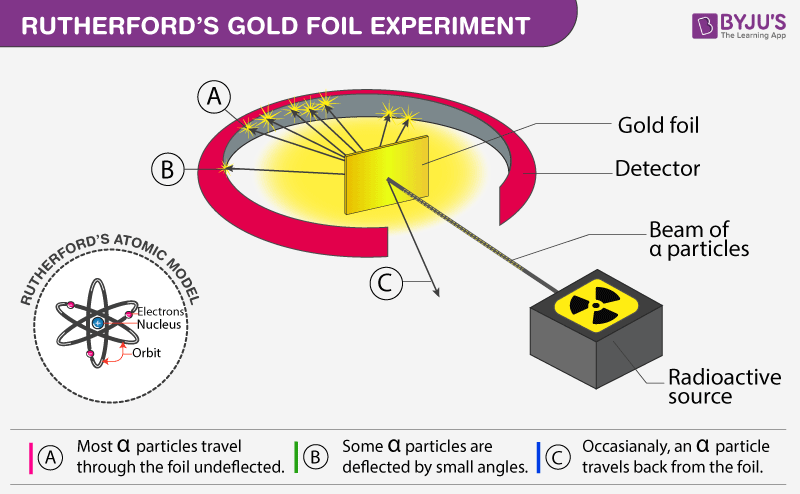
Gold foil experiment diagram. The energy energy level diagram for the atoms is shown on the right. The gas is irradiated with electromagnetic radiation with the energy range from 4 eV to 9 eV. Which set of photon energies might be found in the emission spectrum. (A) 1 eV, 2 eV, and 6 eV (B) 2 eV, 3 eV, and 4 eV (C) 1 eV, 3 eV, and 5 eV (D) 7 eV, 8 eV, and 9 eV 41. The gold foil experiment was a pathbreaking work conducted by scientists Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden under the supervision of Nobel laureate physicist Ernest Rutherford that led to the discovery of the proper structure of an atom. Known as the Geiger-Marsden experiment, it was performed at the Physical Laboratories of the University of ... The diagram shows what happened in the Rutherford and Marsden scattering experiment. Complete this sentence: The particle shown in red will come straight back from the foil because it is _____ by the charge in the gold nucleus. Rutherford designed an experiment for this. In this experiment, fast moving alpha (α)-particles were made to fall on a thin gold foil. He selected a gold foil because he wanted as thin a layer as possible. This gold foil was about 1000 atoms thick. α-particles are doubly-charged helium ions.
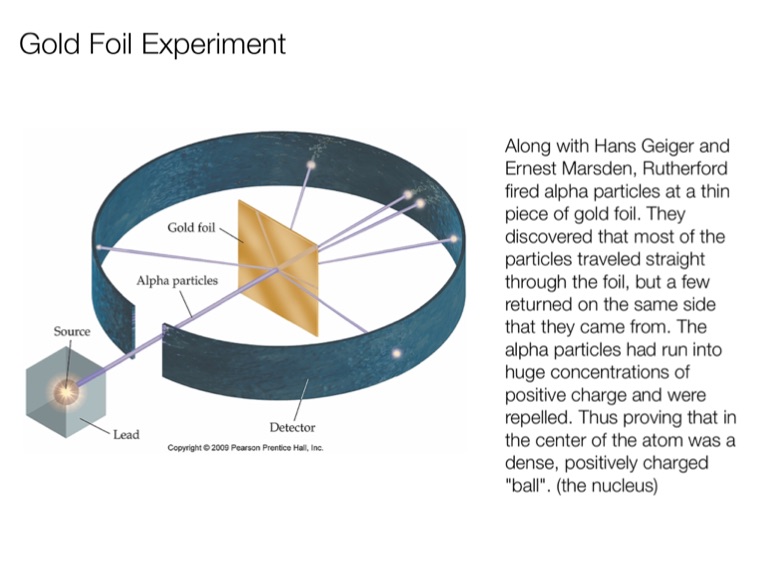
Rutherford passed beams of alpha particles through a thin gold foil and noted how the alpha particles scattered from the foil.. Observations of Rutherford's alpha ray scattering experiment:. 1. Most of the α-particles passed straight through the gold foil without any deviation.. 2. Some of the α-particles were deflected by the foil by some angles. It was so difficult for me to understand the rutherford gold foil experiment. but u made it so easy to understand this concept.thank u sooo much. Reply. Raghav says. February 26, 2019 at 7:28 am. Thanks for this explanation. Reply. Rani says. March 2, 2019 at 7:07 pm. Thank u so much. Reply. Thomson's cathode ray experiment and Rutherford's gold foil experiment If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. After Thompson's atomic theory, Ernest Rutherford, Thompson's student, conducted the experiment which countered his teacher's atomic theory. In 1911, he performed the experiment using the alpha particles. He shoot the alpha particle through the gold foil. This experiment resulted that most of the alpha particles passed through the gold foil.
Geiger and Rutherford fired α particles at a piece of gold foil and detected where those particles went, as shown in this schematic diagram of their experiment. Most of the particles passed straight through the foil, but a few were deflected slightly and a very small number were significantly deflected. Find gold foil experiment stock images in HD and millions of other ... Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment infographic diagram showing deflected and undeflected ... Title: how to draw rutherford scattering experiment| how to draw diagram of rutherford gold foil experiment | rutherford alpha particle scattering experiment... Ernest Rutherford's gold foil experiment helped scientists understand the charge of an atom. Follow along with Rutherford's experiment in this lab and understand the surprising results and ...
Physicist Ernest Rutherford established the nuclear theory of the atom with his gold-foil experiment. When he shot a beam of alpha particles at a sheet of ...
Jan 31, 2013 — The Gold Foil Experiment. In 1911, Rutherford and coworkers Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden initiated a series of groundbreaking experiments that ...
The Rutherford gold foil experiment or alpha particles scattering experiment remains a famous experiment in the history of science. Between 1908 and 1913, a series of experiments were performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden under the guidance of Ernest Rutherford. From left to right: Ernest Rutherford, Hans Geiger, and Ernest Marsden.
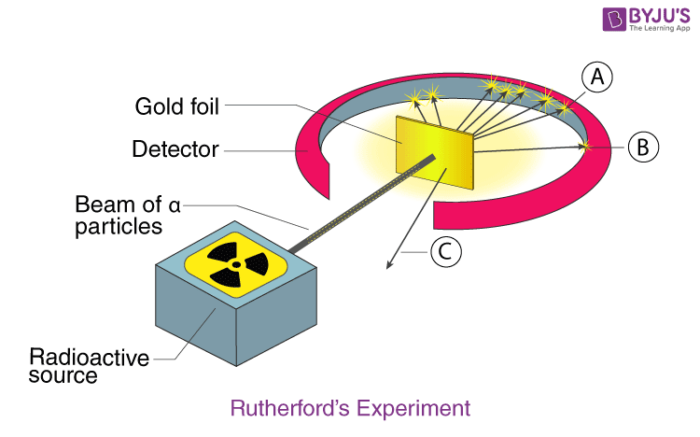
Chemistry Lab #2 Rutherford's Backscattering Experiment Mrs. Rankin Read the following: A key experiment in understanding the nature of atomic structure was completed by Ernest Rutherford in 1911. He set up an experiment that directed a beam of alpha particles (helium nuclei) through a gold foil and then onto a detector screen.
Fig. 2 - Ernest Rutherford. Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment (Geiger-Marsden Experiment). Rutherford teamed up with his assistant, Hans Geiger and Ernst Marsden who was an undergraduate student working in Rutherford's lab; conducted "Gold Foil Experiment" also known as the Geiger-Marsden experiment.His idea was to probe the structure of Atom by firing α-particles or helium ions, at ...
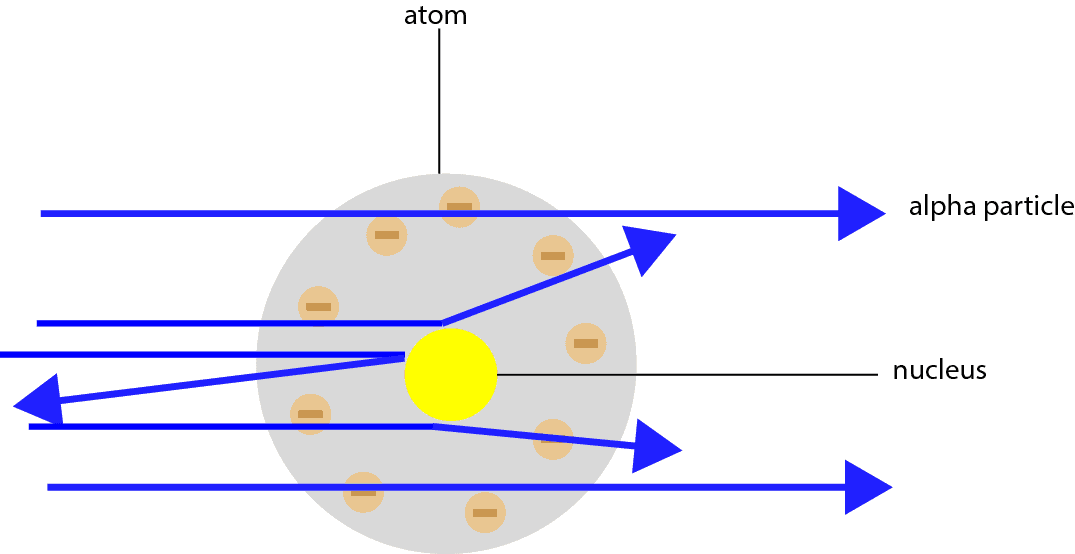
The Geiger-Marsden experiments (also called the Rutherford gold foil experiment) were a landmark series of experiments by which scientists learned that every atom has a nucleus where all of its positive charge and most of its mass is concentrated. They deduced this after measuring how an alpha particle beam is scattered when it strikes a thin metal foil.
Rutherford's gold foil experiment. This is the currently selected item. Bohr's model of hydrogen. Next lesson. Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom. Video transcript - [Voiceover] This is a quote by a physicist as a comment on one of his experimental results. He said, about his experiment, he said, "It was as if you fired a 15-inch shell "at a ...
Illustration of Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment infographic diagram showing deflected and undeflected alpha particles when a beam hit gold foil from ...
gold+foil+experiment Flashcards. Browse 500 sets of gold+foil+experiment flashcards. Study sets Diagrams Classes Users. 6 Terms. Joanna_Kim53. Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment. Rutherford's atomic model. Nucleus. The size of nucleus.
Rutherford's diffraction experiment tests diffraction via a thin foil made of gold metal. Opposite the gold foil is a screen that emits a flash of light when struck by a particle. The passing of many of the particles through suggested the condensed nucleus version of the atom model.
Rutherford Atomic Model Experiment. In Rutherford's experiment, he bombarded high energy streams of α-particles on a thin gold foil of 100 nm thickness. The streams of α-particles were directed from a radioactive source. He conducted the experiment to study the deflection produced in the trajectory of α-particles after interaction with the ...
The gold foil experiment results in the Rutherford model, where the atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons. The Ernest Rutherford model of the ...
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment proved the existance of a small massive center to atoms, which would later be known as the nucleus of an atom. Ernest Rutherford, Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden carried out their Gold Foil Experiment to observe the effect of alpha particles on matter.
Which diagram depicts the plum pudding model of an atom? Diagram B. Which diagram depicts Rutherford's actual results from his gold foil experiment? How did the actual results differ from his expected results? Diagram B. The alpha particles were deflected at large angles.
AN34 Experiment 15 Rutherford Scattering of Alphas from Thin Gold Foil and Other Optional Metal Foils 1 ORTEC ® Equipment Required Purpose In this experiment the scattering of alpha particles by a gold foil will be measured, and the results will be interpreted as experimental cross sections, which will be compared with theoretical equations.
The gold-foil experiment showed that the atom consists of a small, massive, positively charged nucleus with the negatively charged electrons being at a great distance from the centre. Niels Bohr built upon Rutherford's model to make his own. In Bohr's model the orbits of the electrons were explained by quantum mechanics.
Nov 16, 2018 — Diagram of Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment. gold-foil-.tiff, 100.29 KB; (Last Modified on November 16, 2018) ...
Rutherford in 1911, carried out an experiment called 'Gold foil experiment' and could conclude the nature of an atom and the position of the protons present in the atom decisively. He also proposed the position and behaviour of electrons. They bombarded fragile sheets of gold foil with fast-moving alpha particles.























0 Response to "37 gold foil experiment diagram"
Post a Comment